39.0 基础练习
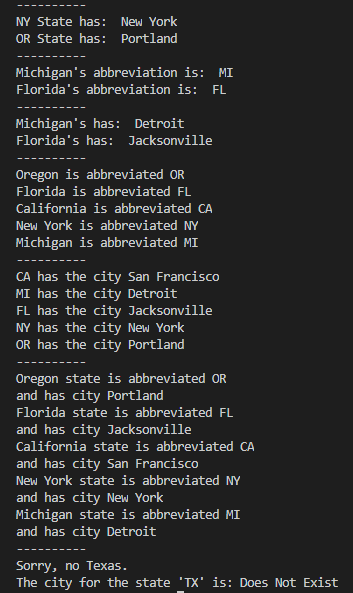
1 # create a mapping of state to abbreviation 2 3 states = { 4 'Oregon': 'OR', 5 'Florida': 'FL', 6 'California': 'CA', 7 'New York': 'NY', 8 'Michigan': 'MI' 9 } 10 11 # create a basic set of states and some cities in them 12 13 cities = { 14 'CA': 'San Francisco', 15 'MI': 'Detroit', 16 'FL': 'Jacksonville' 17 } 18 19 # add some more cities 20 cities['NY'] = 'New York' 21 cities['OR'] = 'Portland' 22 23 # print out some cities 24 print('-' * 10) 25 print("NY State has: ", cities['NY']) 26 print("OR State has: ", cities['OR']) 27 28 # print some states 29 print('-' * 10) 30 print("Michigan's abbreviation is: ", states['Michigan']) 31 print("Florida's abbreviation is: ", states['Florida']) 32 33 # do it by using the state then cities dict 34 print('-' * 10) 35 print("Michigan's has: ", cities[states['Michigan']]) 36 print("Florida's has: ", cities[states['Florida']]) 37 38 # print every state abbreviation 39 print('-' * 10) 40 for state, abbrev in list(states.items()): 41 # print(list(states.items())) 42 print(f"{state} is abbreviated {abbrev}") 43 44 # print every city in state 45 print('-' * 10) 46 for abbrev, city in list(cities.items()): 47 # print(list(cities.items())) 48 print(f"{abbrev} has the city {city}") 49 50 # now do both at the same time 51 print('-' * 10) 52 for state, abbrev in list(states.items()): 53 print(f"{state} state is abbreviated {abbrev}") 54 print(f"and has city {cities[abbrev]}") 55 56 print('-' * 10) 57 # safely get a abbreviation by state that might not be there 58 state = states.get('Texas') 59 60 if not state: 61 print("Sorry, no Texas.") 62 63 # get a city with a default value 64 city = cities.get('TX', 'Does Not Exist') 65 print(f"The city for the state 'TX' is: {city}")
输出结果
39.1 字典的帮助文档
用help()命令调出dict释义
39.2 字典不能做的事情
和列表相比,可以看到字典本身就没有任何和顺序有关的操作,比如从前端加如元素、排序等
39.3 对字典使用 for 循环
总之,先按照要求做做看把。
d = {'1': 'a', '2': 'b', '3': 'c', '4':'d'}
# 使用 for 循环遍历字典
for k in d:
print("当前的键是 %r, 它的值是:%r" % (k, d.get(k)))
for k, v in d.items():
print(k, v)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
字典在 for 循环中只能遍历出键,而不会遍历出对应的值。
遍历 d.items() 时则会获取到键值对组成的元祖,因此需要两个变量分别获取键和值。