1、基本语法
select * from table [start with condition1] connect by [prior] id=parentid
一般用来查找存在父子关系的数据,也就是树形结构的数据;其返还的数据也能够明确的区分出每一层的数据。
start with condition1 是用来限制第一层的数据,或者叫根节点数据;以这部分数据为基础来查找第二层数据,然后以第二层数据查找第三层数据以此类推。
connect by [prior] id=parentid 这部分是用来指明oracle在查找数据时以怎样的一种关系去查找;比如说查找第二层的数据时用第一层数据的id去跟表里面记录的parentid字段进行匹配,如果这个条件成立那么查找出来的数据就是第二层数据,同理查找第三层第四层…等等都是按这样去匹配。
prior还有一种用法:
select * from table [start with condition1] connect by id= [prior] parentid
这种用法就表示从下往上查找数据,可以理解为从叶子节点往上查找父级几点,用第一层数据的parentid去跟表记录里面的id进行匹配,匹配成功那么查找出来的就是第二层数据;上面的那种就是从父级节点往下查找叶子节点。
其他特性
- level关键字,代表树形结构中的层级编号;第一层是数字1,第二层数字2,依次递增。
- CONNECT_BY_ROOT方法,能够获取第一层集结点结果集中的任意字段的值;例CONNECT_BY_ROOT(字段名)。
2、下面来贴两个例子
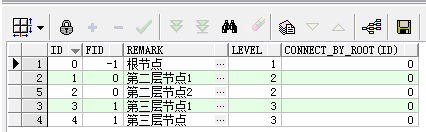
2.1 从根节点查找叶子节点
select t.*, level, CONNECT_BY_ROOT(id) from tab_test t start with t.id = 0 connect by prior t.id = t.fid;
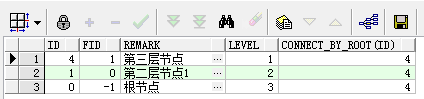
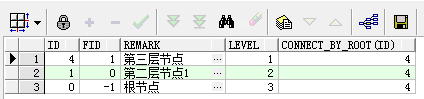
2.2 从叶子节点查找上层节点
-第一种,修改prior关键字位置 select t.*, level, CONNECT_BY_ROOT(id) from tab_test t start with t.id = 4 connect by t.id = prior t.fid; --第二种,prior关键字不动 调换后面的id=fid逻辑关系的顺序 select t.*, level, CONNECT_BY_ROOT(id) from tab_test t start with t.id = 4 connect by prior t.fid = t.id;
3、写几个平常用到的其他一些用法
3.1 生成数字序列结果集
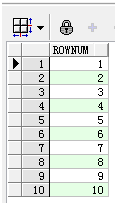
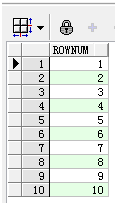
- 使用rownum实现1到10的序列。
select rownum from dual connect by rownum<=10;
结果集如下:
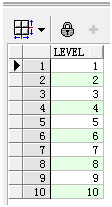
使用level实现1到10的序列。
select level from dual connect by level<=10;
结果集如下:
3.2 查询当前时间往前的12周的开始时间、结束时间、第多少周
select sysdate - (to_number(to_char(sysdate - 1, 'd')) - 1) - (rownum - 1) * 7 as startDate, sysdate + (7 - to_number(to_char(sysdate - 1, 'd'))) - (rownum - 1) * 7 as endDate, to_number(to_char(sysdate, 'iw')) - rownum + 1 as weekIndex from dual connect by level<= 12;--将level改成rownum可以实现同样的效果
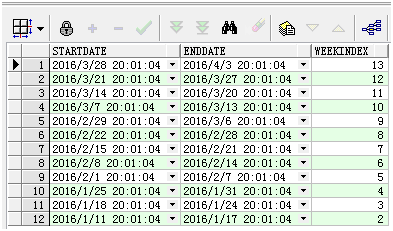
- d 表示一星期中的第几天
- iw 表示一年中的第几周
3.3 字符串分割,由一行变为多行
- 比如说分割01#02#03#04这种有规律的字符串
select REGEXP_SUBSTR('01#02#03#04', '[^#]+', 1, rownum) as newport from dual connect by rownum <= REGEXP_COUNT('01#02#03#04', '[^#]+');


4、省略prior关键字时数据的返回策略
构造一个结果集,其中包含两条数据;然后查询level为1,2,3层的数据。
select t.*, level from (select 1 as num from dual union select 2 as num from dual ) t connect by level <= 3;
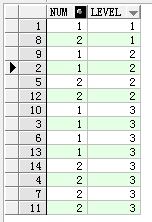
从上面截图的结果可以看出来省略prior关键字时第1层的数据就是初始结果集,第2层的数据是初始结果集的两倍,第3层的数据是初始结果集的3倍;假设初始结果集的记录为n条,查询m层的记录,则返回的记录数就是: 条记录。
在省略prior关键字对数据进行操作时需要特别注意,返回的数据不一定是你所期望的那样。
5、下面再看看几个例子,针对多条结果集当省略prior关键字时怎样获得正确的返回结果
5.1 有下面一个结果集
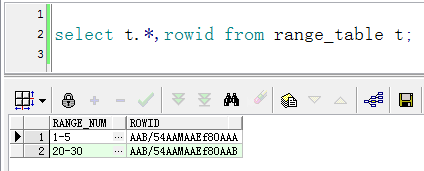
想要实现1-5,20-30的数据递增返回1、2、3、4、5、20、21、22、23、24、25、26、27、28、29、30总共16条记录。
SQL如下:
with temp0 as ( select t.range_num, REGEXP_SUBSTR(t.range_num, '[^-]+', 1, 1) minNum, --最小num REGEXP_SUBSTR(t.range_num, '[^-]+', 1, 2) maxNum --最大num from range_table t ) select t1.range_num ,t2.lv from temp0 t1 join ( select level lv from dual CONNECT BY LEVEL <= (select max(maxNum) from temp0 ) ) t2 on (t2.lv >=t1.minNum and t2.lv <=t1.maxNum);
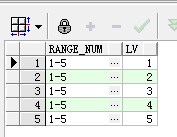
上面的sql中是先求出range_num的最大值与最小值,然后利用connect by 特性生成数值序列结果集,最后让两个结果集关联得到需要的结果。
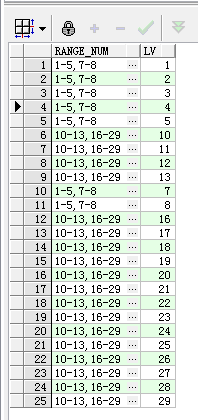
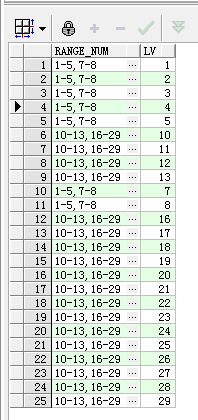
5.2 再看稍微复杂的结果集,输出结果格式跟上面一样
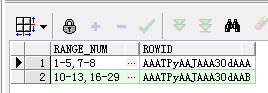
SQL如下:
with temp0 as ( select b.range_num, REGEXP_SUBSTR(b.range_num, '[^,]+', 1, c.lv) as newport, REGEXP_SUBSTR(REGEXP_SUBSTR(b.range_num, '[^,]+', 1, c.lv), '[^-]+', 1, 1) as minNum, REGEXP_SUBSTR(REGEXP_SUBSTR(b.range_num, '[^,]+', 1, c.lv), '[^-]+', 1, 2) as maxNum from (select regexp_count(a.range_num, '[^,]+') AS cnt, range_num from range_table a) b join (select LEVEL lv from dual CONNECT BY LEVEL <= 50) c --这里的50表示的是range_num通过,分割后的数量,这里写死了50也可以sql动态max出来 on c.lv <= b.cnt ) select t1.range_num,t2.lv from temp0 t1 join ( select level lv from dual CONNECT BY LEVEL <= ( select max(to_number(maxNum)) from temp0 ) ) t2 on ((t2.lv >=t1.minNum and t2.lv <=t1.maxNum));
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/wang_yunj/article/details/51040029