problem :A 第一个类
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
class Thing
{
private:
string name;
public:
Thing(){}
Thing(string n):name(n) {cout << "" << name << endl;}
~Thing(){ cout << "Destroy a thing" << " " << name << endl;}
};
int main()
{
Thing A("Car");
string str;
cin>>str;
Thing B(str);
return 0;
}
problem b:建造一间教室
description:
一间教室包括很多物品。这里只考虑灯(Light)和椅子(Chair)。定义Light类,只有一个int类型的参数,表示灯的瓦数;定义Chair类,只有一个字符串类型的参数,表示椅子的颜色。定义ClassRoom类,包括四个属性:两个int类型的属性,分别为灯的个数和椅子的个数。一个Light类的对象和一个Chair类的对象,分别为教室中灯的种类和椅子的种类。
input:
输入有6行,第1行是一个正整数,表示灯的瓦数。第2行是一个不含空白符的字符串,表示椅子的颜色。第3、4行表示教室中灯的个数和椅子的数量。第5行是一个正整数,表示教室中灯的瓦数,第6行是一个不含空白符的字符串,表示教室中椅子的颜色。
sample input:
20
blue
16
100
25
red
sample output:

代码示例:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <iomanip>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <cmath>
5 using namespace std;
6 class Light
7 {
8 private:
9 int w;
10 public:
11 Light(){ }
12 Light(int ww):w(ww){ cout << "A " << w << "w light is created." << endl; }
13 ~Light(){ cout << "A " << w << "w light is erased." << endl;}
14 int getw() const { return w; }
15 };
16 class Chair
17 {
18 private:
19 string cl;
20 public:
21 Chair(){ }
22 Chair(string c):cl(c){ cout << "A " << cl << " chair is created." << endl; }
23 ~Chair(){ cout << "A " << cl << " chair is created." << endl;}
24 string getcl() const { return cl; }
25 };
26
27 class ClassRoom
28 {
29 private:
30 int lnum, cnum;
31 Light lig;
32 Chair cha;
33 public:
34 ClassRoom(){ }
35 ClassRoom(int ln,int cn,int w,string c ): lig(w), cha(c),lnum(ln), cnum(cn)
36 {
37 cout << "A classroom having " << lnum << " lights and " << cnum << " chairs is created." << endl;
38 }
39 ~ClassRoom(){ cout << "A classroom having " << lnum << " lights and " << cnum << " chairs is erased." << endl;}
40 };
41
42 int main()
43 {
44 int nl, nc;
45 int w;
46 string color;
47 cin>>w>>color;
48 Light light(w);
49 Chair chair(color);
50 cin>>nl>>nc;
51 cin>>w>>color;
52 ClassRoom room(nl, nc, w, color);
53 return 0;
54 }
problem c: 是否回文数?
description :
定义Data类,有一个int类型的属性。定义其构造函数、setValue函数和isPalindrome函数,其中setValue函数用于设置属性值,isPalindrome用于判断该属性值是否为回文数。判断回文数时,不考虑数的符号。
输入:
若干个int类型范围内的整数
输出:
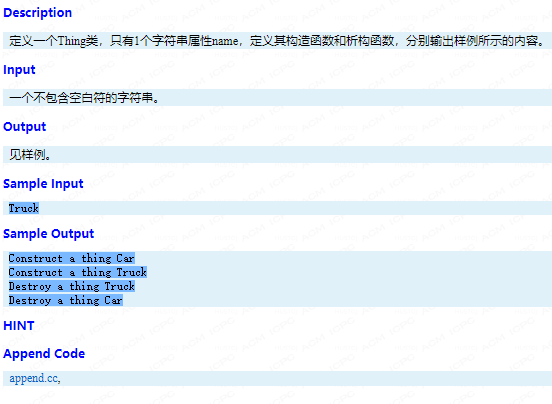
每个输入对应一行输出,如果对应的输入是回文数,则输出Yes,否则输出No。
代码演绎:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <iomanip> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cmath> 5 using namespace std; 6 class Data 7 { 8 private: 9 int data; 10 public: 11 Data(int d = 0) : data(d) { } 12 ~Data(){ } 13 public: 14 void setValue(int v) { data = v; } 15 bool isPalindrome() const 16 { 17 int temp; 18 temp = data; 19 if(data < 0 ) temp = -temp; 20 int tt[100]; 21 int i = 0; 22 while(temp != 0) 23 { 24 tt[i] = temp % 10; 25 temp /= 10; 26 i++; 27 } 28 for(int j = 0, k = i-1; j < i;j++,k-- ) 29 if(tt[j] != tt[k]) 30 return false; 31 return true; 32 } 33 }; 34 int main() 35 { 36 Data data; 37 int v; 38 while (cin>>v) 39 { 40 data.setValue(v); 41 if (data.isPalindrome()) 42 cout<<"Yes"<<endl; 43 else 44 cout<<"No"<<endl; 45 } 46 return 0; 47 }
problem d:Base 与 Derived
description:
定义Base和Derived类,Derived类是Base类的子类,两个类都只有1个int类型的属性。定义它们的构造函数和析构函数,输出信息如样例所示。
input;
输入2个整数。
output:
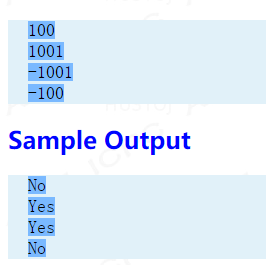
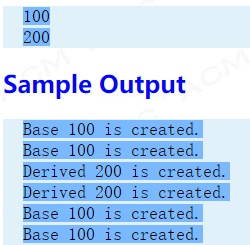
见样例
代码样例:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <iomanip>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <cmath>
5 using namespace std;
6 class Base
7 {
8 private:
9 int bs;
10 public:
11 Base(int b = 0):bs(b) { cout << "Base " << bs << " is created." << endl; }
12 ~Base() { cout << "Base " << bs << " is created." << endl;}
13 };
14 class Derived:public Base
15 {
16 private:
17 int de;
18 public:
19 Derived(int x, int y):Base(x),de(y) { cout << "Derived " << de << " is created." << endl; }
20 ~Derived(){ cout << "Derived " << de << " is created." << endl; }
21 };
22 int main()
23 {
24 int a, b;
25 cin>>a>>b;
26 Base base(a);
27 Derived derived(a, b);
28 return 0;
29 }
problem e: 类模板sample
description:
定义类模板Sample,设模板参数为T,则Sample类只有一个T类型的属性。定义其构造函数、拷贝构造函数,输出与样例类似的信息。定义show函数,用于显示属性值(只输出属性值)。定义add函数,将当前对象与Sample类的另一个对象的属性值相加,和仍存入当前对象。
input:
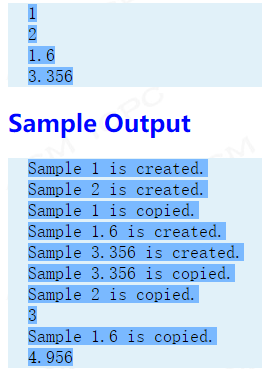
输入2个int类型整数、2个double类型实数。
代码示例:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <iomanip>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <cmath>
5 using namespace std;
6 template <class T>
7 class Sample
8 {
9 private:
10 T t;
11 public:
12 Sample(T tt) : t(tt){ cout << "Sample " << t << " is created." << endl; }
13 Sample(const Sample & s):t(s.t) { cout << "Sample " << t << " is copied." << endl;}
14 ~Sample() { }
15 public:
16 void show()const{ cout << t << endl; }
17 void add(Sample s){ t += s.t; }
18 };
19
20
21 int main()
22 {
23 int a, b;
24 double c, d;
25 cin>>a>>b>>c>>d;
26 Sample<int> s1(a), s2(b), s3(s1);
27 Sample<double> s4(c), s5(d), s6(s5);
28 s1.add(s2);
29 s1.show();
30 s5.add(s4);
31 s5.show();
32 return 0;
33 }