1、引入依赖及配置
引入rabbitmq依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置文件application.yml
spring: application: name: rabbimq-springboot rabbitmq: host: 安装rabbit的主机 port: 运行端口 username: 登录用户 password: 登录密码 virtual-host: 虚拟主机(可在图形界面创建,/开头)
RabbiTemplate 用于简化操作rabbitmq,直接注入即可。
2、使用RabbiTemplate 操作rabbitmq
注入rabbitTemplate
// 注入rabbitTemplate @Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
1)直连模型

直连,不需要经过交换机,生产者直接将消息放进队列中
生产者:(生产者运行不会直接创建队列,必须先有消费者才会自动创建不存在的队列)
@Test void test() { /** * 参数说明: * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:发生消息,可直接发生对象 */ rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("hello","hello rabbitMq"); }
消费者:
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue("hello"))声明监听的队列
@RabbitHandler代表队列中取出的消息的回调函数
@Component @RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue("hello")) public class HelloCustomer { @RabbitHandler public void raceivel(String message){ System.out.println("massage = "+message); } }
需要设置队列属性时在消费者端声明队列时指定
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = "hello",declare = "true",autoDelete = "false",exclusive = "false"))
2)工作队列
同样不需要通过交换机,多个消费者
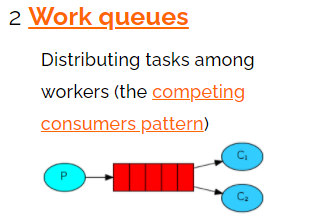
与Hello模型基本一致,多个消费者会平均消费消息。存在问题:两个消费者处理速度不同时,任然是平均分配。
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue("hello"))声明监听的队列注解直接注解在方法上时可以不用@RabbitHandler
生产者:
@Test void testWork() { /** * 参数说明: * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:发生消息,可直接发生对象 */ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("work","workQuque "+i); } }
消费者:
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = "work"))
public void work1(String massage){
System.out.println("work1 :massage = "+massage);
}
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = "work"))
public void work2(String massage){
System.out.println("work2 :massage = "+massage);
}
运行结果

3)发布订阅(广播模型)
该模式生产者生产的消息会广播给所有消费者
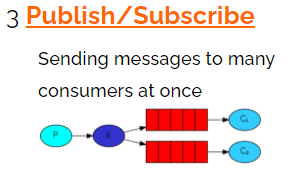
生产者:
@Test void testfanout() { /** * 参数说明: * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:路由key(该模式下该参数无意义) * 参数3:发送的消息 */ rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("log","","fanout 模型发生消息"); }
消费者:
消费者需生成临时队列,并绑定队列与路由交换机的关系
@RabbitListener(bindings = { @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, exchange = @Exchange(value = "log",type = "fanout") ) }) public void fanout1(String massage){ System.out.println("fanout1 massage = "+massage); } @RabbitListener(bindings = { @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, //不指定名称,生成临时队列 exchange = @Exchange(value = "log",type = "fanout") //交换机信息 ) }) public void fanout2(String massage){ System.out.println("fanout2 massage = "+massage); }
运行结果:

两个消费者绑定不同的临时队列,消费了相同的消息。
4)路由模式
与发布订阅不同的是可以指定不同的路由key,可指定特定想消费者消费。
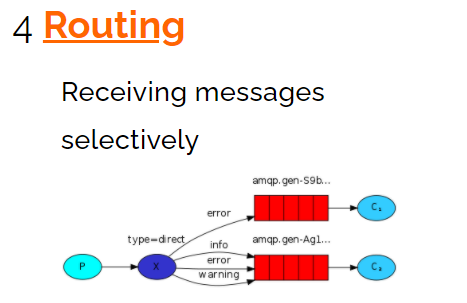
消费者:
@RabbitListener(bindings = { @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, exchange = @Exchange(value = "direct",type = "direct"), key = {"info","error"} ) }) public void route1(String massage){ System.out.println("route1 massage = "+massage); } @RabbitListener(bindings = { @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, //不指定名称,生成临时队列 exchange = @Exchange(value = "direct",type = "direct") ,//交换机信息, key = {"error"} ) }) public void route2(String massage){ System.out.println("route2 massage = "+massage); }
生产者:
@Test void testRoute() { /** * 参数说明: * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:路由key 用于指定哪些消费者可以消费 * 参数3:发送的消息 */ rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("direct","info","route 模型发生info消息"); }
输出:

由于生产者发生时指定路由key为info,只有绑定key为info的消费者可以消费
修改生产者
@Test void testRoute() { /** * 参数说明: * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:路由key 用于指定哪些消费者可以消费 * 参数3:发送的消息 */ rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("direct","error","route 模型发生error消息"); }
运行结果:

由于两个消费者都绑定了error可以,则两个消费者都能消费error消息
5)Topic模型
与路由模式基本相同,唯一不同是可以使用通配符指定消费者绑定的路由key。
通配符
-
#代表0个或多个单词
-
*代表一个单词
消费者:
@Component public class TopicCusomer { @RabbitListener(bindings = { @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, exchange = @Exchange(value = "topic",type = "topic"), key = {"user.#"} ) }) public void topic1(String massage){ System.out.println("topic1 massage = "+massage); } @RabbitListener(bindings = { @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, //不指定名称,生成临时队列 exchange = @Exchange(value = "topic",type = "topic") ,//交换机信息, key = {"user.*"} ) }) public void topic2(String massage){ System.out.println("topic2 massage = "+massage); } }
生产者:
@Test void testTopic() { /** * 参数说明: * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:路由key 用于指定哪些消费者可以消费 * 参数3:发送的消息 */ rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topic","user.order","topic 模型发生user.order消息"); }
结果:

两个消费者都消费了消息
修改生产者:
@Test void testTopic() { /** * 参数说明: * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:路由key 用于指定哪些消费者可以消费 * 参数3:发送的消息 */ rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topic","user.order.info","topic 模型发生user.order消息"); }
结果:

@Configuration public class TopicRabbitConfig { //路由key public final static String key= "topic.key"; //队列名称 public final static String key="queueName";
//交换机名称
public final static String exchangeName = "topicExchange";
//交换机 名称为topicExchange 类型为TOpic @Bean TopicExchange exchange() { return new TopicExchange(TopicRabbitConfig.exchangeName); } // 队列 @Bean public Queue testQueue() { return new Queue(TopicRabbitConfig.queueName); } @Bean Binding bindingExchangeMessage() { return BindingBuilder.bind(testQueue()).to(exchange()).with(TopicRabbitConfig.key); } }
生产者发送消息:
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map .put("messageId", messageId); map .put("messageData", messageData); map .put("createTime", createTime); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(TopicRabbitConfig.exchangeName,TopicRabbitConfig.key, map);
消费者消费消息:
@Component @RabbitListener(queues = "queueName") public class TopicReceiver { @RabbitHandler public void process(Map message) { System.out.println("消费者收到消息 : " + testMessage.toString()); } }