一、前向传播
在caffe中,卷积层做卷积的过程被转化成了由卷积核的参数组成的权重矩阵weights(简记为W)和feature map中的元素组成的输入矩阵(简记为Cin)的矩阵乘积W * Cin。在进行乘积之前,需要对卷积核的参数和feature map作处理,以得到W和Cin。
下面用一个例子来说名上述两个过程。假设某一卷积层输入为c X h X w = 3 X 8 X 8的feature map,卷积核大小h1 X w1 = 2 X 2,个数c1 = 4,stride = 1,pad_h = pad_w = 0。
对feature map作处理,得到Cin的过程如下图(图中描述的是输入一个样本时的处理过程,在caffe中对一个batch_size的样本,也是在一个循环中一个一个地计算对输入的卷积)。

从图中可以看出,多层的feature map被转化成了一个矩阵,在caffe中,这个矩阵是以行优先的存储顺序存储在一个数组中。输出feature map的高、宽分别为
ho = (h + 2 * pad_h - h1)/stride + 1
wo = (w + 2 * pad_w - w1)/stride + 1
col_buff(即Cin)的维度为高 × 宽 = (c × h1 × w1) × (ho × wo)
对卷积核的参数作处理,得到W的过程如下图
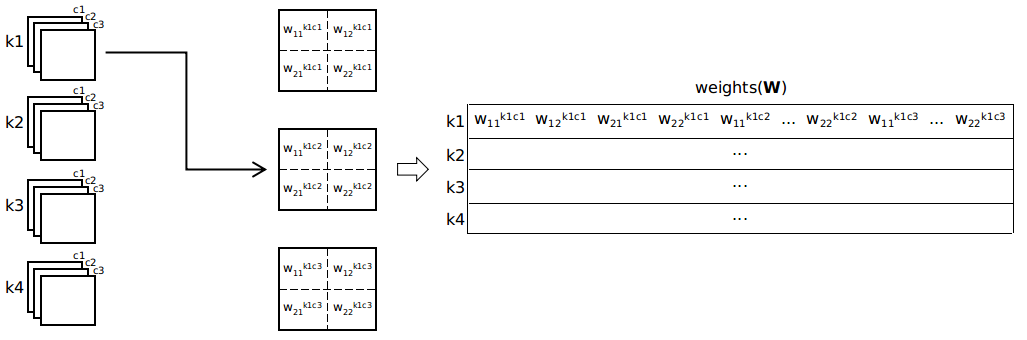
权重矩阵的维度为高 × 宽 = (c1) × (c × h1 × w1)。caffe中的数据存储采用Blob结构,其存储的优先顺序为样本数(num) × 通道数(c) × 高(h) × 宽(w),w优先级最低,即在w维度上相邻元素之间的地址差是最小的。所以卷积核的参数按照blob的存储结构恰好就是一个权重矩阵W,不需要作任何处理。
下面以caffe自带的例子LeNet为例,结合源代码,来分析代码的实现过程(代码注释中参数的值是batch_size=64,网络正向传播到conv2层时的值)
网络结构如下

name: "LeNet"
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include {
phase: TRAIN
}
transform_param {
scale: 0.00390625
}
data_param {
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb"
batch_size: 64
backend: LMDB
}
}
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include {
phase: TEST
}
transform_param {
scale: 0.00390625
}
data_param {
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_test_lmdb"
batch_size: 100
backend: LMDB
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "ip1"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "ip1"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 500
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "ip1"
top: "ip1"
}
layer {
name: "ip2"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "ip1"
top: "ip2"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 10
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "accuracy"
type: "Accuracy"
bottom: "ip2"
bottom: "label"
top: "accuracy"
include {
phase: TEST
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "ip2"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}
conv_layer.cpp
template <typename Dtype> void ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) { const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data(); for (int i = 0; i < bottom.size(); ++i) { // bottom_data is the pointer of input feature map. // top_data is the pointer of matrix Cout. const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[i]->cpu_data(); Dtype* top_data = top[i]->mutable_cpu_data(); // Every time just forward one single sample. for (int n = 0; n < this->num_; ++n) { // Compute Cout = W X Cin. this->forward_cpu_gemm(bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_, weight, top_data + n * this->top_dim_); if (this->bias_term_) { const Dtype* bias = this->blobs_[1]->cpu_data(); // Compute Cout = Cout + b X I. this->forward_cpu_bias(top_data + n * this->top_dim_, bias); } } } }
依次进入
this->forward_cpu_gemm(bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_, weight, top_data + n * this->top_dim_)
this->forward_cpu_bias(top_data + n * this->top_dim_, bias)
base_conv_layer.cpp
template <typename Dtype> void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::forward_cpu_gemm(const Dtype* input, const Dtype* weights, Dtype* output, bool skip_im2col) { const Dtype* col_buff = input; if (!is_1x1_) { if (!skip_im2col) { // Generating Cin by one single input feature map. conv_im2col_cpu(input, col_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data()); } // col_buff is the pointer of matrix Cin. col_buff = col_buffer_.cpu_data(); } // The following takes caffe's example mnist as example to explain the value of every parameter. // The value of these parameters are as follows when the solver forwarding into the conv2 layer. // group_ = 1(usually is 1) // conv_out_channels_ = c1 = 50 // conv_out_spatial_dim_ = ho * wo = 8 * 8 = 64 // kernel_dim_ = c(the number of channels of bottom) * h1 * w1 = 20 * 5 * 5 = 500 // weight_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * kernel_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 500 / 1 = 25000 // col_offset_ = kernel_dim_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 500 * 64 / 1 = 32000 // output_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 64 / 1 = 3200 // This function computes Cout = W X Cin. for (int g = 0; g < group_; ++g) { caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, conv_out_channels_ / group_, conv_out_spatial_dim_, kernel_dim_, (Dtype)1., weights + weight_offset_ * g, col_buff + col_offset_ * g, (Dtype)0., output + output_offset_ * g); } } template <typename Dtype> void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::forward_cpu_bias(Dtype* output, const Dtype* bias) { // The following takes caffe's example mnist as example to explain the value of every parameter. // The value of these parameters are as follows when the solver forwarding into the conv2 layer. // num_output_ = c1 = 50 // out_spatial_dim_ = ho * wo = 8 * 8 = 64 // bias_multiplier_ is the Blob of I(dimension h * w = 1 * out_spatial_dim_ = 1 * 64). // This function computes Cout = Cout + b X I. caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, num_output_, out_spatial_dim_, 1, (Dtype)1., bias, bias_multiplier_.cpu_data(), (Dtype)1., output); }
函数caffe_cpu_gemm
math_functions.cpp
template<> void caffe_cpu_gemm<float>(const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransA, const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransB, const int M, const int N, const int K, const float alpha, const float* A, const float* B, const float beta, float* C) { int lda = (TransA == CblasNoTrans) ? K : M; int ldb = (TransB == CblasNoTrans) ? N : K; cblas_sgemm(CblasRowMajor, TransA, TransB, M, N, K, alpha, A, lda, B, ldb, beta, C, N); }
参数说明参考该博客。
进入conv_im2col_cpu(input, col_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data())
base_conv_layer.hpp
// wrap im2col/col2im so we don't have to remember the (long) argument lists inline void conv_im2col_cpu(const Dtype* data, Dtype* col_buff) { if (!force_nd_im2col_ && num_spatial_axes_ == 2) { // Generating Cin by one single input feature map. im2col_cpu(data, conv_in_channels_, conv_input_shape_.cpu_data()[1], conv_input_shape_.cpu_data()[2], kernel_shape_.cpu_data()[0], kernel_shape_.cpu_data()[1], pad_.cpu_data()[0], pad_.cpu_data()[1], stride_.cpu_data()[0], stride_.cpu_data()[1], dilation_.cpu_data()[0], dilation_.cpu_data()[1], col_buff); } else { im2col_nd_cpu(data, num_spatial_axes_, conv_input_shape_.cpu_data(), col_buffer_shape_.data(), kernel_shape_.cpu_data(), pad_.cpu_data(), stride_.cpu_data(), dilation_.cpu_data(), col_buff); } }
最后进入im2col_cpu
im2col.cpp
// Function uses casting from int to unsigned to compare if value of // parameter a is greater or equal to zero and lower than value of // parameter b. The b parameter is of type signed and is always positive, // therefore its value is always lower than 0x800... where casting // negative value of a parameter converts it to value higher than 0x800... // The casting allows to use one condition instead of two. inline bool is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(int a, int b) { return static_cast<unsigned>(a) < static_cast<unsigned>(b); } template <typename Dtype> void im2col_cpu(const Dtype* data_im, const int channels, const int height, const int width, const int kernel_h, const int kernel_w, const int pad_h, const int pad_w, const int stride_h, const int stride_w, const int dilation_h, const int dilation_w, Dtype* data_col) { const int output_h = (height + 2 * pad_h - (dilation_h * (kernel_h - 1) + 1)) / stride_h + 1; const int output_w = (width + 2 * pad_w - (dilation_w * (kernel_w - 1) + 1)) / stride_w + 1; const int channel_size = height * width; for (int channel = channels; channel--; data_im += channel_size) { for (int kernel_row = 0; kernel_row < kernel_h; kernel_row++) { for (int kernel_col = 0; kernel_col < kernel_w; kernel_col++) { int input_row = -pad_h + kernel_row * dilation_h; for (int output_rows = output_h; output_rows; output_rows--) { if (!is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(input_row, height)) { for (int output_cols = output_w; output_cols; output_cols--) { // Pad up and below with 0 (the size of the two sides is identical). *(data_col++) = 0; } } else { int input_col = -pad_w + kernel_col * dilation_w; for (int output_col = output_w; output_col; output_col--) { if (is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(input_col, width)) { // Select all the elements corresponding to the same order in every // convolutional window and arrange them in a row successively. *(data_col++) = data_im[input_row * width + input_col]; } else { // Pad left and right with 0 (the size of the two sides is identical). *(data_col++) = 0; } input_col += stride_w; } } input_row += stride_h; } } } } }
二、反向传播
经过上面对前向传播的描述,可以将该过程简单地描述为权重矩阵(W)和输入矩阵(Cin)相乘最终得到输出矩阵(Cout)的过程,即W × Cin = Cout。反向传播的大体过程如下图(可以参考我写的前一章节)
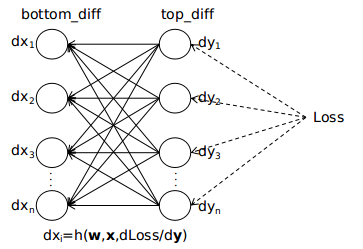
现在使用前向传播图示部分所使用的各种参数值为例,接着分析对应的反向传播的过程。
Loss对Cout的导数top_diff记为Tf

Tf另记为

反向传播的实质是在已知Tf的条件下求Loss对Cin的导数bottom_diff,我记为Bf,以及Loss对权重矩阵W的导数Wf.

Bf另记为
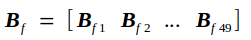
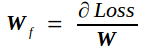
W另记为
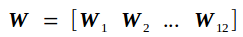
输入矩阵Cin另记为
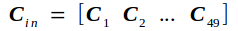
前向传播的过程如下图所示

根据链式求导法则,易知

同理,有
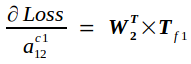
以此类推,有
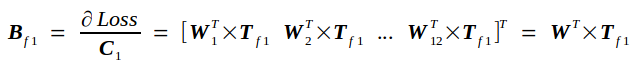
从而,有
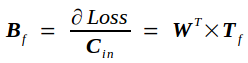
同理可推出Loss对权重矩阵的导数

若卷积核中带有偏置项,则前向传播的过程变为
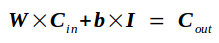
其中b的维度为(高 × 宽 = 4 × 1),I是一个维度为(高 × 宽 = 1 × 49)的元素全为1的矩阵
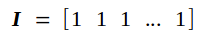
通过上述分析可知,此时Bf和Wf都没变,Loss对偏置项的导数为
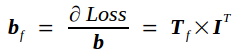
下面仍然以caffe自带的例子LeNet为例,结合源代码,来分析代码的实现过程(代码注释中参数的值是batch_size=64,网络反向传播到conv2层时的值)
conv_layer.cpp
template <typename Dtype> void ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top, const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) { // weight is the pointer of weight matrix W. // weight_diff is the pointer of matrix Wf // which is gradient with respect to weight. const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data(); Dtype* weight_diff = this->blobs_[0]->mutable_cpu_diff(); for (int i = 0; i < top.size(); ++i) { // top_diff point to data that is the derivative of Loss respect to the output // of the forward process of this layer (Cout), namely Tf. // bottom_data is Cin. // bottom_diff point to data that is the derivative of Loss respect to the input // of the forward process of this layer (Cin), namely Bf. const Dtype* top_diff = top[i]->cpu_diff(); const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[i]->cpu_data(); Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[i]->mutable_cpu_diff(); // Bias gradient, if necessary. if (this->bias_term_ && this->param_propagate_down_[1]) { // bias_diff is the pointer of matrix bf // which is gradient with respect to bias. Dtype* bias_diff = this->blobs_[1]->mutable_cpu_diff(); // Every time just backward one single sample, and then accumulate them. for (int n = 0; n < this->num_; ++n) { // Compute bf and accumulate them (accumulate bf of a batch samples). this->backward_cpu_bias(bias_diff, top_diff + n * this->top_dim_); } } if (this->param_propagate_down_[0] || propagate_down[i]) { for (int n = 0; n < this->num_; ++n) { if (this->param_propagate_down_[0]) { // Compute Wf and accumulate them (accumulate Wf of a batch samples). this->weight_cpu_gemm(bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_, top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, weight_diff); } if (propagate_down[i]) { // Compute Bf. this->backward_cpu_gemm(top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, weight, bottom_diff + n * this->bottom_dim_); } } } } }
依次进入
this->backward_cpu_bias(bias_diff, top_diff + n * this->top_dim_)
this->weight_cpu_gemm(bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_, top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, weight_diff)
this->backward_cpu_gemm(top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, weight, bottom_diff + n * this->bottom_dim_)
template <typename Dtype> void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::backward_cpu_bias(Dtype* bias, const Dtype* input) { // The following takes caffe's example mnist as example to explain the value of every parameter. // The value of these parameters are as follows when the solver backwarding into the conv2 layer. // num_output_ = c1 = 50 // out_spatial_dim_ = ho * wo = 8 * 8 = 64 // bias_multiplier_ is the Blob of I(dimension h * w = 1 * out_spatial_dim_ = 1 * 64). // This function computes bf = bf + Tf X I^T. caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, num_output_, out_spatial_dim_, 1., input, bias_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 1., bias); } template <typename Dtype> void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::weight_cpu_gemm(const Dtype* input, const Dtype* output, Dtype* weights) { const Dtype* col_buff = input; if (!is_1x1_) { // Generate Cin from input feature map. conv_im2col_cpu(input, col_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data()); // col_buff is the pointer of matrix Cin. col_buff = col_buffer_.cpu_data(); } for (int g = 0; g < group_; ++g) { // The following takes caffe's example mnist as example to explain the value of every parameter. // The value of these parameters are as follows when the solver backwarding into the conv2 layer. // group_ = 1(usually is 1) // conv_out_channels_ = c1 = 50 // kernel_dim_ = c(the number of channels of bottom) * h1 * w1 = 20 * 5 * 5 = 500 // conv_out_spatial_dim_ = ho * wo = 8 * 8 = 64 // output_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 64 / 1 = 3200 // col_offset_ = kernel_dim_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 500 * 64 / 1 = 32000 // weight_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * kernel_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 500 / 1 = 25000 // This function computes Wf = Wf + Tf X Cin^T. caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasTrans, conv_out_channels_ / group_, kernel_dim_, conv_out_spatial_dim_, (Dtype)1., output + output_offset_ * g, col_buff + col_offset_ * g, (Dtype)1., weights + weight_offset_ * g); } } template <typename Dtype> void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::backward_cpu_gemm(const Dtype* output, const Dtype* weights, Dtype* input) { // col_buff is the pointer of matrix Bf. Dtype* col_buff = col_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data(); if (is_1x1_) { col_buff = input; } for (int g = 0; g < group_; ++g) { // The following takes caffe's example mnist as example to explain the value of every parameter. // The value of these parameters are as follows when the solver backwarding into the conv2 layer. // group_ = 1(usually is 1) // kernel_dim_ = c(the number of channels of bottom) * h1 * w1 = 20 * 5 * 5 = 500 // conv_out_spatial_dim_ = ho * wo = 8 * 8 = 64 // conv_out_channels_ = c1 = 50 // weight_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * kernel_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 500 / 1 = 25000 // output_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 64 / 1 = 3200 // col_offset_ = kernel_dim_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 500 * 64 / 1 = 32000 // This function computes Bf = W^T X Tf. caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasTrans, CblasNoTrans, kernel_dim_, conv_out_spatial_dim_, conv_out_channels_ / group_, (Dtype)1., weights + weight_offset_ * g, output + output_offset_ * g, (Dtype)0., col_buff + col_offset_ * g); } if (!is_1x1_) { // This function is the reverse of conv_im2col_cpu. It transforms Bf into the form // which is the same as the input feature map. conv_col2im_cpu(col_buff, input); } }
函数caffe_cpu_gemv
math_functions.cpp
template <> void caffe_cpu_gemv<float>(const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransA, const int M, const int N, const float alpha, const float* A, const float* x, const float beta, float* y) { cblas_sgemv(CblasRowMajor, TransA, M, N, alpha, A, N, x, 1, beta, y, 1); }
参数说明参考该博客。
接着,进入conv_col2im_cpu(col_buff, input)
base_conv_layer.hpp
inline void conv_col2im_cpu(const Dtype* col_buff, Dtype* data) { if (!force_nd_im2col_ && num_spatial_axes_ == 2) { // This function is the reverse of conv_im2col_cpu. It transforms Bf into the form // which is the same as the input feature map. col2im_cpu(col_buff, conv_in_channels_, conv_input_shape_.cpu_data()[1], conv_input_shape_.cpu_data()[2], kernel_shape_.cpu_data()[0], kernel_shape_.cpu_data()[1], pad_.cpu_data()[0], pad_.cpu_data()[1], stride_.cpu_data()[0], stride_.cpu_data()[1], dilation_.cpu_data()[0], dilation_.cpu_data()[1], data); } else { col2im_nd_cpu(col_buff, num_spatial_axes_, conv_input_shape_.cpu_data(), col_buffer_shape_.data(), kernel_shape_.cpu_data(), pad_.cpu_data(), stride_.cpu_data(), dilation_.cpu_data(), data); } }
最后进入col2im_cpu
im2col.cpp
template <typename Dtype> void col2im_cpu(const Dtype* data_col, const int channels, const int height, const int width, const int kernel_h, const int kernel_w, const int pad_h, const int pad_w, const int stride_h, const int stride_w, const int dilation_h, const int dilation_w, Dtype* data_im) { caffe_set(height * width * channels, Dtype(0), data_im); const int output_h = (height + 2 * pad_h - (dilation_h * (kernel_h - 1) + 1)) / stride_h + 1; const int output_w = (width + 2 * pad_w - (dilation_w * (kernel_w - 1) + 1)) / stride_w + 1; const int channel_size = height * width; for (int channel = channels; channel--; data_im += channel_size) { for (int kernel_row = 0; kernel_row < kernel_h; kernel_row++) { for (int kernel_col = 0; kernel_col < kernel_w; kernel_col++) { int input_row = -pad_h + kernel_row * dilation_h; for (int output_rows = output_h; output_rows; output_rows--) { if (!is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(input_row, height)) { // Skip these addresses, because they are corresponding to padding zone(up and below). data_col += output_w; } else { int input_col = -pad_w + kernel_col * dilation_w; for (int output_col = output_w; output_col; output_col--) { if (is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(input_col, width)) { // This expression is the reverse of the corresponding one in im2col_cpu. data_im[input_row * width + input_col] += *data_col; } // Skip these addresses, because they are corresponding to padding zone(left and right). data_col++; input_col += stride_w; } } input_row += stride_h; } } } } }
