Java错误和异常解析
错误和异常
在Java中, 根据错误性质将运行错误分为两类: 错误和异常. 在Java程序的执行过程中, 如果出现了异常事件, 就会生成一个异常对象. 生成的异常对象将传递Java运行时系统, 这一异常的产生和提交过程称为抛弃(throw)异常.当Java运行时系统得到一个异常对象时, 它将会沿着方法的调用栈逐层回溯, 寻找处理这一异常的代码. 找到能够处理这类异常的方法后, 运行时系统把当前异常对象交给这个方法进行处理, 这一过程称为捕获(catch)异常.
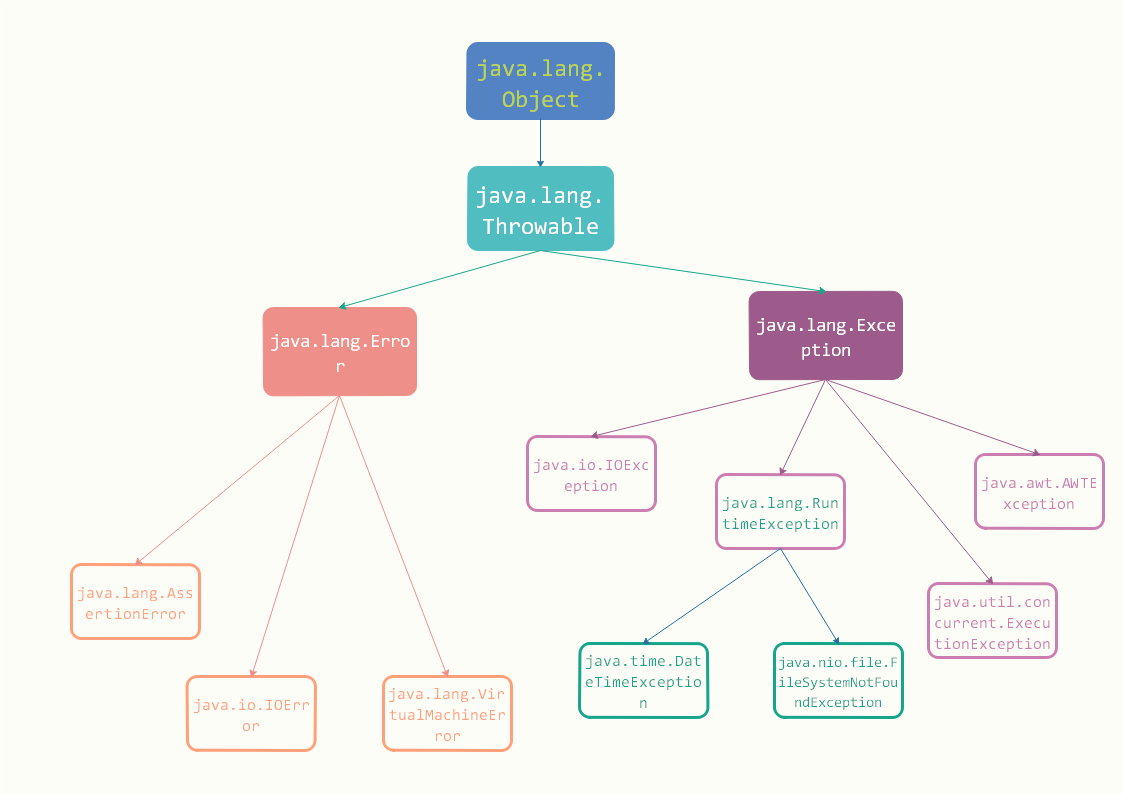
Throwable
类是 Java 语言中所有错误或异常的超类, 它的两个子类是Error和Exception
Error
是Throwable 的子类, 用于指示合理的应用程序不应该试图捕获的严重问题. 大多数这样的错误都是异常条件. 虽然 ThreadDeath 错误是一个"正规"的条件, 但它也是 Error 的子类, 因为大多数应用程序都不应该试图捕获它. 在执行该方法期间, 无需在其 throws 子句中声明可能抛出但是未能捕获的 Error 的任何子类, 因为这些错误可能是再也不会发生的异常条件. Error类包括一些严重的程序不能处理的系统错误类, 如内存溢出, 虚拟机错误, 栈溢出等. 这类错误一般与硬件有关, 与程序本身无关, 通常由系统进行处理, 程序本身无法捕获和处理.
1.OutOfMemoryError内存溢出一般是出现在申请了较多的内存空间没有释放的情形
//java.lang.OutOfMemoryError -Xmx150m
try {
byte[] b = new byte[1024*1024*600];
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
运行时,设置jvm最大的heap内存150m,此时申请600m的内存,因此会报error
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
2.StackOverflowError
堆栈溢出错误. 当一个应用递归调用的层次太深而导致堆栈溢出时抛出该错误.
public static void main(String[] args) {
method();
}
public static void method() {
while (true) {
method();
}
}
无限次的递归调用出现
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.StackOverflowError
Exception
类及其子类是 Throwable 的一种形式, 它指出了合理的应用程序想要捕获的条件. 有些异常在编写程序时无法预料的, 如中断异常, 非法存取异常等. 为了保证程序的健壮性, Java要求必须对这些可能出现的异常进行捕获, 并对其进行处理. Exception的除RuntimeException类的对象, 都是可检查的异常(Checked exception), Checked exception需要明确声明.
public class Exception extends Throwable
The class Exception and its subclasses are a form of Throwable that indicates conditions that a reasonable application might want to catch.
The class Exception and any subclasses that are not also subclasses of RuntimeException are checked exceptions. Checked exceptions need to be declared in a method or constructor's throws clause if they can be thrown by the execution of the method or constructor and propagate outside the method or constructor boundary.
RuntimeException
类是Exception类的子类. RuntimeException是那些可能在 Java 虚拟机正常运行期间抛出的异常的超类, 可能在执行方法期间抛出但未被捕获的RuntimeException 的任何子类都无需在 throws 子句中进行声明. 它是Exception的子类. 常见的运行时异常:
try {
String str = new String("AA");
str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("出现空指针的异常了");
}
try {
Object obj = new Date();
String str = (String) obj;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
System.out.println("出现类型转换的异常了");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("处理完异常后的逻辑");
}
try {
int i = 10;
System.out.println(i / 0);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("算术异常"+e.getMessage());
}
try {
int[] i = new int[10];
System.out.println(i[-10]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组下标越界的异常!");
}
IOExeption
类是Exception类的子类, 从一个不存在的文件中读取数据, 越过文件结尾继续读取, 连接一个不存在的URL
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(new File("hello1.txt"));
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) b);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e1) {
System.out.println("文件找不到了!");
} catch (IOException e1) {
System.out.println(e1.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
throws用来声明一种可能要抛出的异常类型, throw用来抛出一个异常对象. Exception体系包括RuntimeException体系和其他非RuntimeException的体系, RuntimeException是unchecked的, 而其他的Exception是checked, checked的意思就是可以通过try catch finally来捕获.
异常的打印发生后, 语句可以执行吗?
package com.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* RuntimeException, 发生了异常,就无法执行后续的代码
* 只要是非RuntimeException, 在exception块之外,发生异常仍然可以执行后续的代码,在exception之中,
* 无法执行,块就是指的包裹异常的部分
* https://www.cnblogs.com/wangyingli/p/5912269.html
* https://www.cnblogs.com/panxuejun/p/6837910.html
* https://blog.csdn.net/kingzone_2008/article/details/8535287
* https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_34319374/article/details/85889019
*/
public class MyException
{
/**
* 代码1
*/
private static List<String> ls = new ArrayList<>();
// 不需要,直接报错
public static void add(String element, List ll)
{
ll.add(element);
int size = ll.size();
if (size >= 2)
{
throw new RuntimeException("顺序表已满,无法添加");
// return; //无法执行
}
}
/**
* 代码2
*/
public static void test2() throws Exception
{
throw new Exception("参数越界。。。。。");
//System.out.println("异常后"); // 编译错误,「无法访问的语句」
}
public static void test3() throws Exception
{
/**
* 代码3
*/
if (true)
{
throw new Exception("参数越界33333333333");
// System.out.println("3,3,3,3,3"); // 不会执行, 抛出了 Exception声明, 整个方法都是块
}
System.out.println("异常后"); // 抛出异常,不会执行
}
public static void test4()
{
/**
* 代码4
*/
if (true)
{
try
{
throw new Exception("参数越界33333333333");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("4=========="); // 会执行, try,catch是它的块
}
System.out.println("异常后"); // 会执行
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 1
// add("xx", ls);
// add("xx", ls);
// add("xx", ls);
// System.out.println(1); // 无法执行
// 2
// try
// {
// test2();
// }
// catch (Exception e)
// {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// System.out.println(2); //可以执行
// 3
// try
// {
// test3();
// }
// catch (Exception e)
// {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// System.out.println(3);
// 4
try
{
test4();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(4);
}
}
ref:
1.详解Java异常Throwable、Error、Exception、RuntimeException的区别, 2.RuntimeException和Exception区别, 3.Throwable、Error、Exception、RuntimeException 区别 联系