A Battle of Network Structures: An Empirical Study of CNN, Transformer, and MLP
【GiantPandaCV导语】ViT的兴起挑战了CNN的地位,随之而来的是MLP系列方法。三种架构各有特点,为了公平地比较几种架构,本文提出了统一化的框架SPACH来对比,得到了具有一定insight的结论。
背景
近期Transformer MLP系列模型的出现,增加了CV领域的多样性,MLP-Mixer的出现表明卷积或者注意力都不是模型性能优异的必要条件。不同架构的模型进行比较的过程中,会使用不同的正则化方法、训练技巧等,为了比较的公平性,本文提出了SPACH的统一框架,期望对几种架构进行对比,同时探究他们各自的特点。
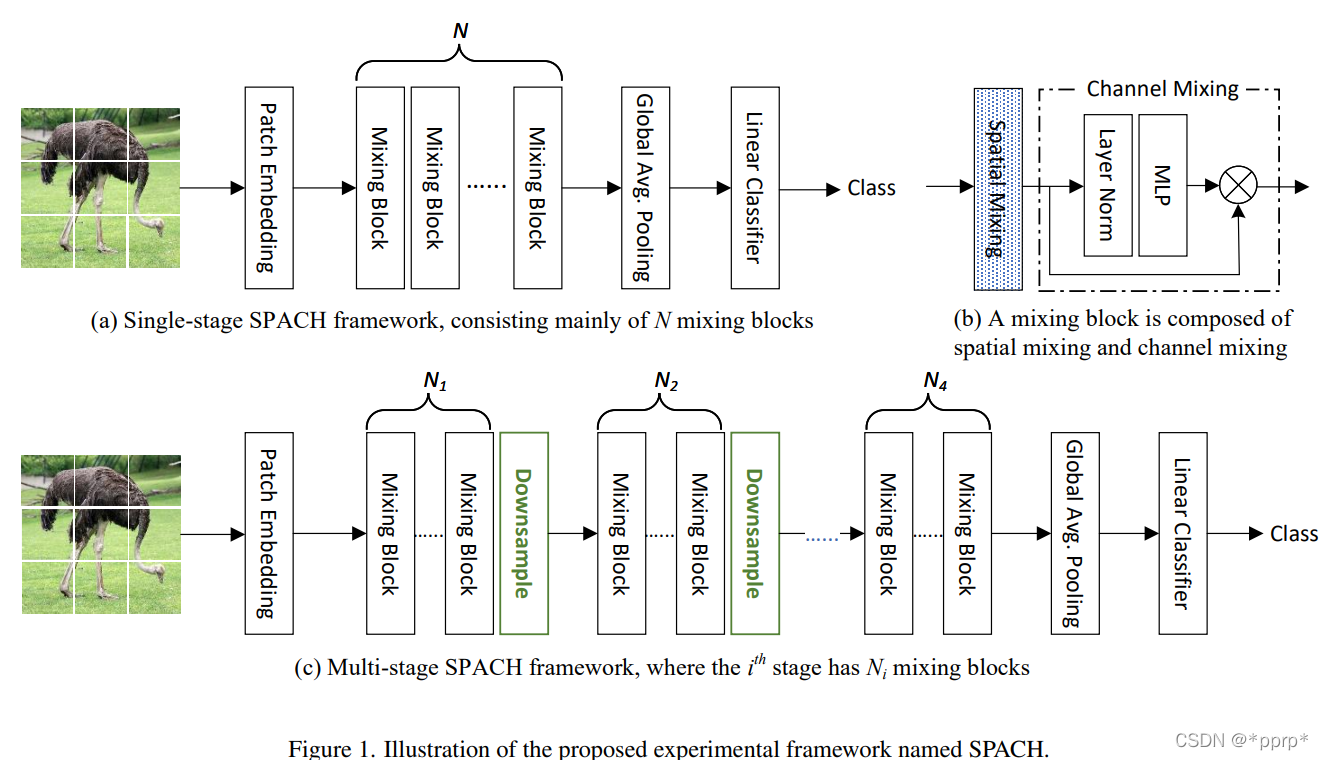
这个框架总体来说有两种模式:多阶段和单阶段。每个阶段内部采用的是Mixing Block,而该Mixing Block可以是卷积层、Transformer层以及MLP层。
经过实验发现了以下几个结论:
- 多阶段框架效果优于单节段框架(通过降采样划分阶段)
- 局部性建模具有高效性和重要性。
- 通过使用轻量级深度卷积(depth wise conv),基于卷积的模型就可以取得与Transformer模型类似的性能。
- 在MLP和Transformer的架构的支路中使用一些局部的建模可以在有效提升性能同时,只增加一点点参数量。
- MLP在小型模型中具有非常强的性能表现,但是模型容量扩大的时候会出现过拟合问题,过拟合是MLP成功路上的拦路虎。
- 卷积操作和Transformer操作是互补的,卷积的泛化性能更强,Transformer结构模型容量更大。通过灵活组合两者可以掌控从小到大的所有模型。
统一框架
本文提出一统MLP、Transformer、Convolution的框架:SPACH
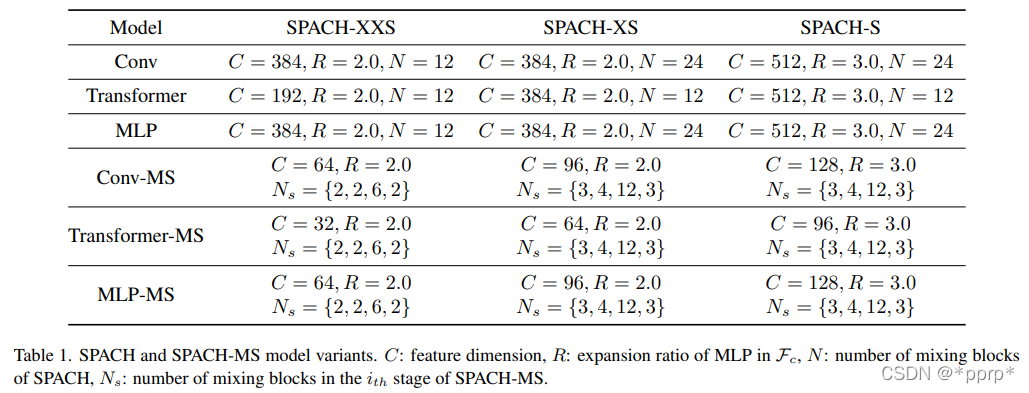
下表展示的是各个模块中可选的参数,并提出了三种变体空间。
其中各个模块设计如下:
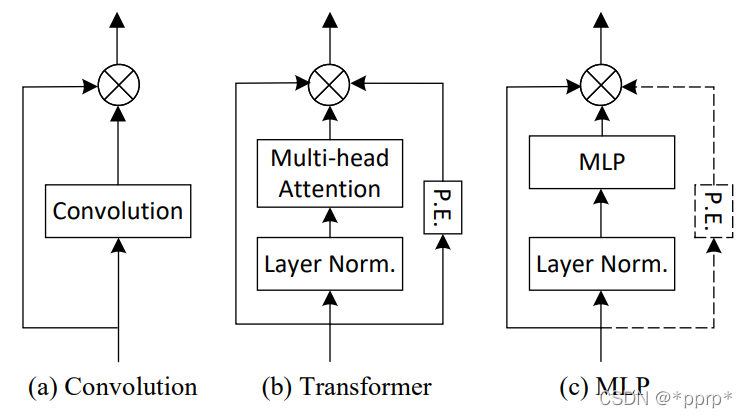
- (a)展示的是卷积部分操作,使用的是3x3深度可分离卷积。
- (b)展示的是Transformer模块,使用了positional embedding(由于目前一些研究使用absolute positional embedding会导致模块模型的平移不变性,因此采用Convolutional Position Encoding(CPE)。
- (c)展示的是MLP模块,参考了MLP-Mixer的设计,虽然MLP-Mixer中并没有使用Positional Embedding,但是作者发现通过增加轻量级的CPE能够有效提升模型性能。
注:感觉这三种模块的设计注入了很多经验型设计,比如卷积并没有用普通卷积,用深度可分离卷积其实类似MLP中的操作,此外为MLP引入CPE的操作也非常具有技巧性。
三种模块具有不同的属性:

所谓dynamic weight是Transformer中可以根据图片输入的不同动态控制权重,这样的模型的容量相较CNN更高。CNN中也有这样的趋势,dynamic network的出现也是为了实现动态权重。(感谢zzk老师的讲解)Transformer侧重是关系的学习和建模,不完全依赖于数据,CNN侧重模板的匹配和建模,比较依赖于数据。
| Transformer | CNN |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Attention | Multi-scale Features by multi-stage |
| Global Context Fusion | Shift,scale and distortion invariance |
| Better Generalization(学习关系,不完全依赖数据) | Local Spatial Modeling |
实验
实验设置:
- 数据集选择ImageNet-1K
- 输入分辨率224x224
- 训练设置参看DeiT
- AdamW优化器训练300个epoch
- weight decay: 0.05 (T用的weight decay更小)
- learning rate:0.005 对应 512 batch size(T用的lr更小)
结论1:multi-stage 要比 single-stage性能更好
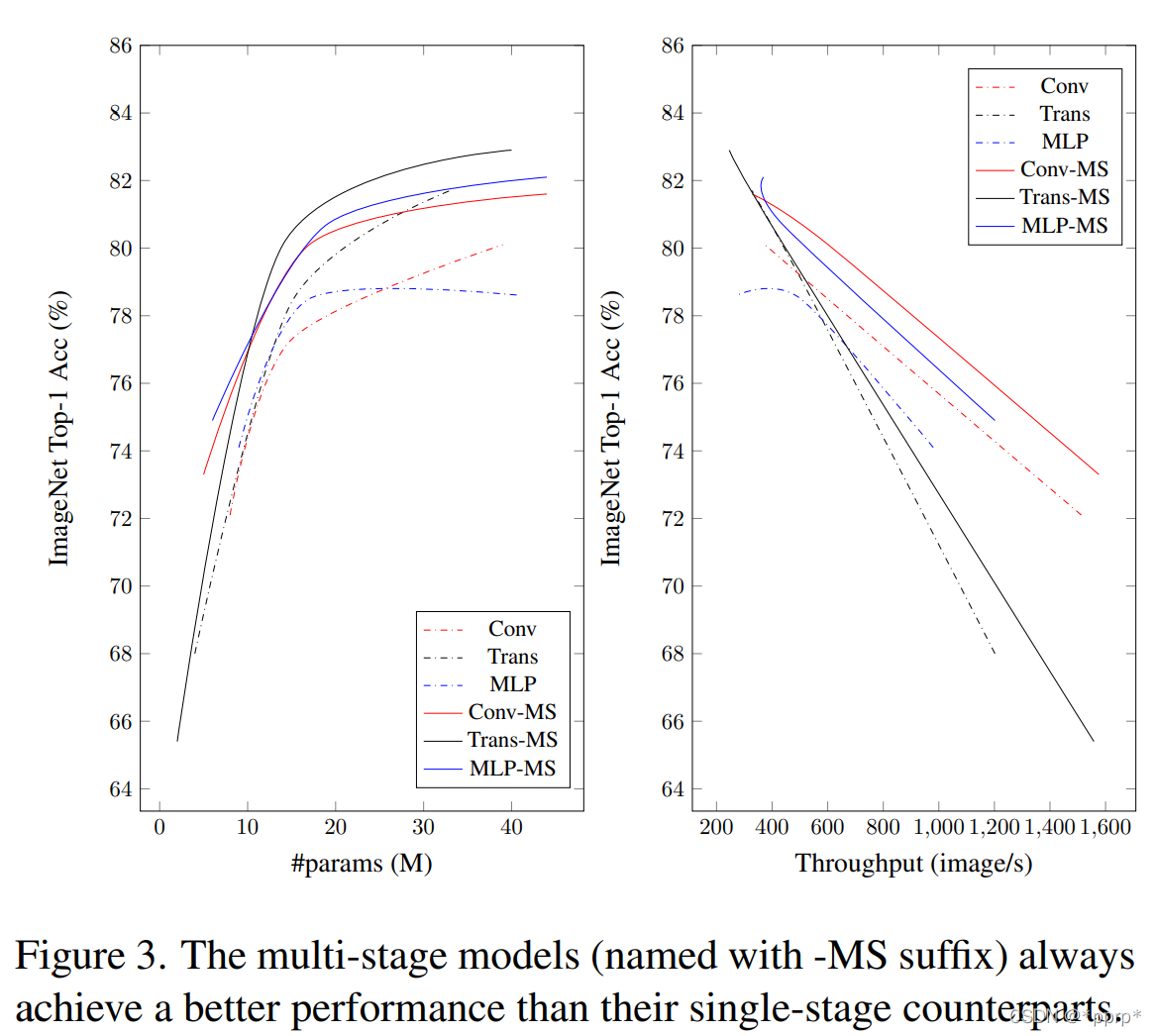
具体性能如下表所记录,Multi-Stage能够显著超过Single Stage的模型。
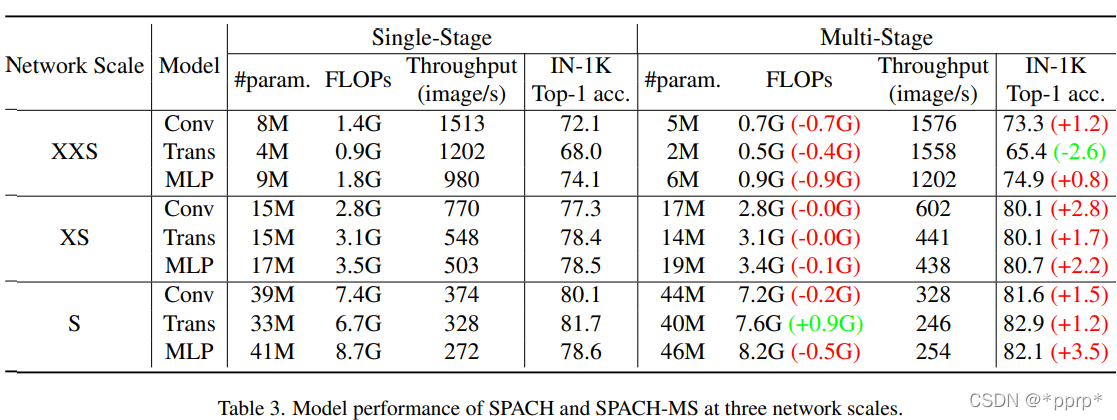
可以发现,有一个例外,在xxs尺度下,Transformer进度损失了2.6个百分点,因为多阶段模型恰好只有单阶段模型一半的参数量和Flops。
随着参数量的增加,模型最高精度先后由MLP、Conv、Transformer所主导。
结论2:局部建模非常重要
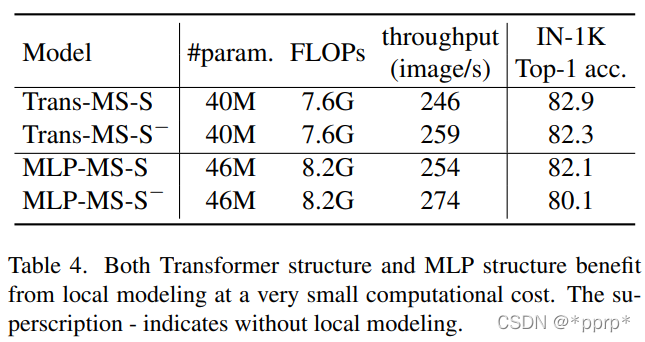
上表展示了具有局部建模以及去除局部建模的效果,可以发现使用卷积旁路的时候吞吐量略微降低,但是精度有显著提高。
结论3:MLP的细节分析
MLP性能不足主要源自于过拟合问题,可以使用两种机制来缓解这个问题。
- Multi-Stage的网络机制,可以从以上实验发现,multi-stage能够有效降低过拟合,提高模型性能。
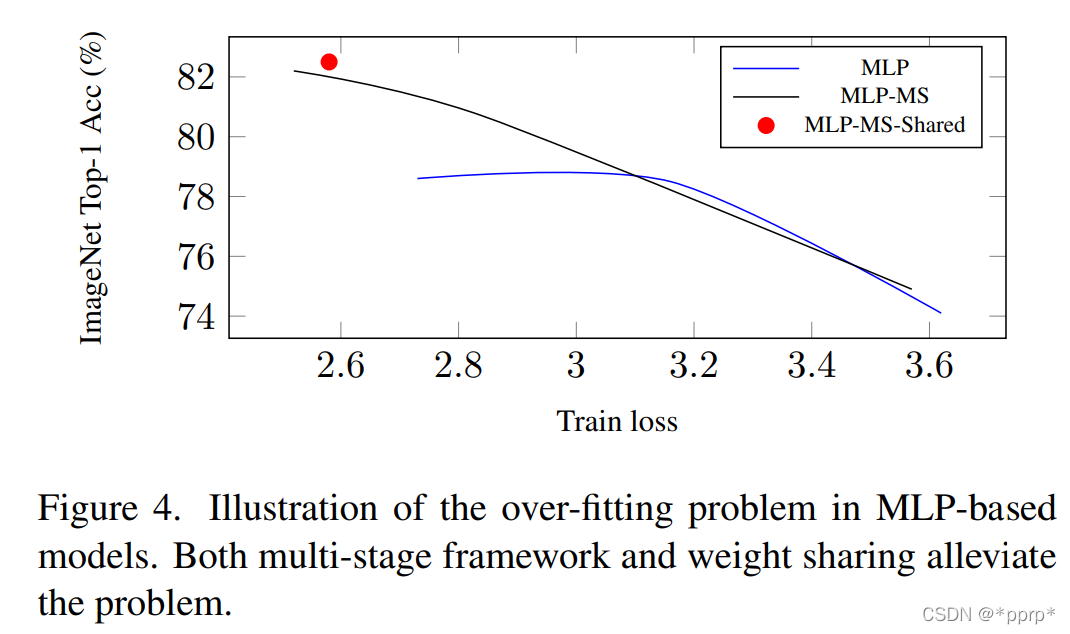
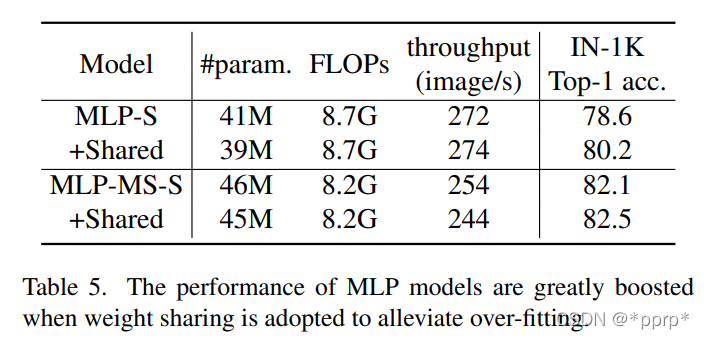
- 权重共享机制,MLP在模型参数量比较大的情况下容易过拟合,但是如果使用权重共享可以有效缓解过拟合问题。具体共享的方法是对于某个stage的所有Mixing Block均使用相同的MLP进行处理。
结论4:卷积与Transformer具有互补性
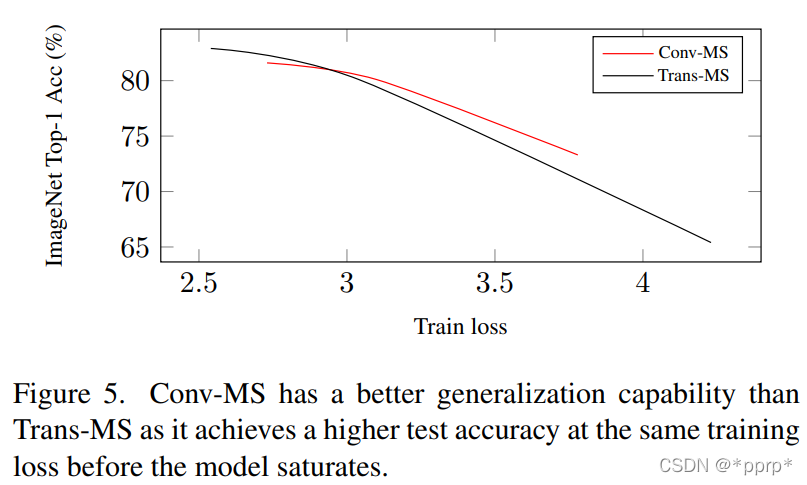
作者认为卷积具有的泛化能力更强,而Transformer具有更大的模型容量,如下图所示,在Loss比较大的情况下,整体的准确率是超过了Transformer空间的。
结论5: 混合架构的模型
在multi-stage的卷积网络基础上将某些Mixing Block替换为Transformer的Block, 并且处于对他们建模能力的考量,选择在浅层网络使用CNN,深层网络使用Transformer,得到两种模型空间:

SOTA模型比较结果:
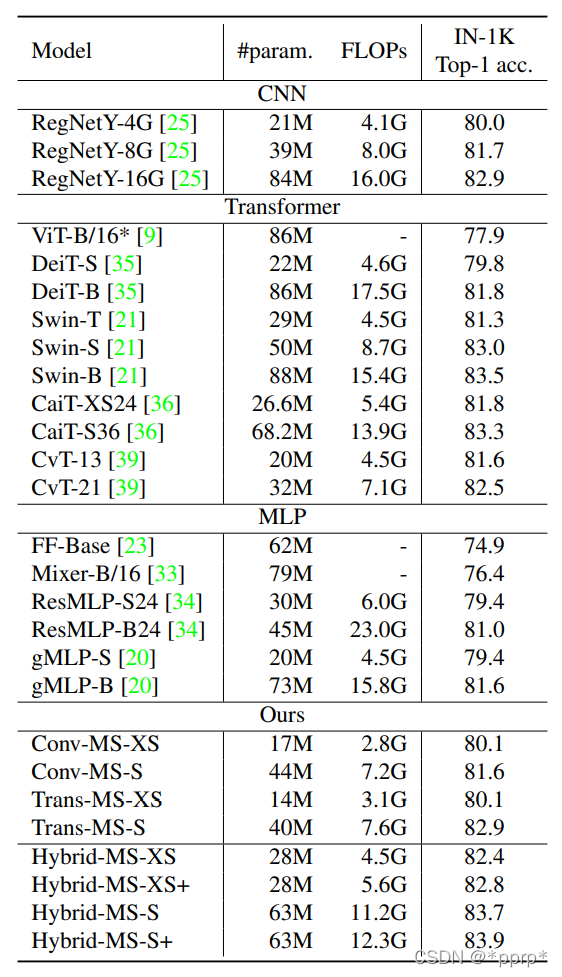
整体结论是:
- Transformer能力要比MLP强,因此不考虑使用MLP作为混合架构
- 混合Transformer+CNN的架构性能上能够超越单独的CNN架构或者Transformer架构
- FLOPS与ACC的权衡做的比较出色,能够超越Swin Transformer以及NAS搜索得到的RegNet系列。
最后作者还向读者进行提问:
- MLP性能欠佳是由于过拟合带来的,能够设计高性能MLP模型防止过拟合呢?
- 目前的分析证明卷积或者Transformer并不是一家独大,如何用更好的方式融合两种架构?
- 是否存在MLP,CNN,Transformer之外的更有效地架构呢?
代码
对照下图逐步给出各个Mixing Block:
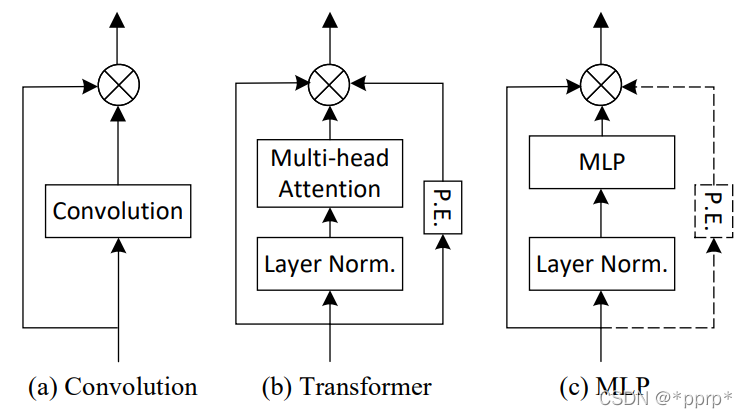
(a)卷积模块 ,kernel为3的深度可分离卷积
class DWConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, kernel_size=3):
super(DWConv, self).__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
self.net = nn.Sequential(Reshape2HW(),
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size, 1, padding, groups=dim),
Reshape2N())
def forward(self, x):
x = self.net(x)
return x
(b)Transformer
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
"""Spatial Attention"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, qkv_bias=False, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0., **kwargs):
super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x)
qkv = rearrange(qkv, "b n (three heads head_c) -> three b heads n head_c", three=3, heads=self.num_heads)
q, k, v = qkv[0] * self.scale, qkv[1], qkv[2]
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) # B, head, N, N
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
out = (attn @ v) # B, head, N, C
out = rearrange(out, "b heads n head_c -> b n (heads head_c)")
out = self.proj(out)
out = self.proj_drop(out)
return out
(c)MLP模块,分为channel mlp和spatial mlp,与MLP-Mixer保持一致
class ChannelMLP(nn.Module):
"""Channel MLP"""
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0., **kwargs):
super(ChannelMLP, self).__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
self.hidden_features = hidden_features
self.out_features = out_features
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
"""Spatial Attention"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, qkv_bias=False, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0., **kwargs):
super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x)
qkv = rearrange(qkv, "b n (three heads head_c) -> three b heads n head_c", three=3, heads=self.num_heads)
q, k, v = qkv[0] * self.scale, qkv[1], qkv[2]
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) # B, head, N, N
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
out = (attn @ v) # B, head, N, C
out = rearrange(out, "b heads n head_c -> b n (heads head_c)")
out = self.proj(out)
out = self.proj_drop(out)
return out
SPACH骨干网络的构建: MixingBlock
class MixingBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim,
spatial_func=None, scaled=True, init_values=1e-4, shared_spatial_func=False,
norm_layer=partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6), act_layer=nn.GELU, drop_path=0., cpe=True,
num_heads=None, qkv_bias=False, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0., # attn
in_features=None, hidden_features=None, drop=0., # mlp
channel_ratio=2.0
):
super(MixingBlock, self).__init__()
spatial_kwargs = dict(act_layer=act_layer,
in_features=in_features, hidden_features=hidden_features, drop=drop, # mlp
dim=dim, num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=proj_drop # attn
)
self.valid_spatial_func = True
if spatial_func is not None:
if shared_spatial_func:
self.spatial_func = spatial_func
else:
self.spatial_func = spatial_func(**spatial_kwargs)
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
if scaled:
self.gamma_1 = nn.Parameter(init_values * torch.ones(1, 1, dim), requires_grad=True)
else:
self.gamma_1 = 1.
else:
self.valid_spatial_func = False
self.channel_func = ChannelMLP(in_features=dim, hidden_features=int(dim*channel_ratio), act_layer=act_layer,
drop=drop)
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.cpe = cpe
if cpe:
self.cpe_net = DWConv(dim)
def forward(self, x):
in_x = x
if self.valid_spatial_func:
x = x + self.drop_path(self.gamma_1 * self.spatial_func(self.norm1(in_x)))
if self.cpe:
x = x + self.cpe_net(in_x)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.channel_func(self.norm2(x)))
return
SPACH构建:
class Spach(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
num_classes=1000,
img_size=224,
in_chans=3,
hidden_dim=384,
patch_size=16,
net_arch=None,
act_layer=nn.GELU,
norm_layer=partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6),
stem_type='conv1',
scaled=True, init_values=1e-4, drop_path_rate=0., cpe=True, shared_spatial_func=False, # mixing block
num_heads=12, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0., # attn
token_ratio=0.5, channel_ratio=2.0, drop_rate=0., # mlp
downstream=False,
**kwargs
):
super(Spach, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.downstream = downstream
self.stem = STEM_LAYER[stem_type](
img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=in_chans, embed_dim=hidden_dim, downstream=downstream)
self.norm1 = norm_layer(hidden_dim)
block_kwargs = dict(dim=hidden_dim, scaled=scaled, init_values=init_values, cpe=cpe,
shared_spatial_func=shared_spatial_func, norm_layer=norm_layer, act_layer=act_layer,
num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=proj_drop, # attn
in_features=self.stem.num_patches, hidden_features=int(self.stem.num_patches * token_ratio), channel_ratio=channel_ratio, drop=drop_rate) # mlp
self.blocks = self.make_blocks(net_arch, block_kwargs, drop_path_rate, shared_spatial_func)
self.norm2 = norm_layer(hidden_dim)
if not downstream:
self.pool = Reduce('b n c -> b c', reduction='mean')
self.head = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, self.num_classes)
self.init_weights()
def make_blocks(self, net_arch, block_kwargs, drop_path, shared_spatial_func):
if shared_spatial_func:
assert len(net_arch) == 1, '`shared_spatial_func` only support unitary spatial function'
assert net_arch[0][0] != 'pass', '`shared_spatial_func` do not support pass'
spatial_func = SPATIAL_FUNC[net_arch[0][0]](**block_kwargs)
else:
spatial_func = None
blocks = []
for func_type, depth in net_arch:
for i in range(depth):
blocks.append(MixingBlock(spatial_func=spatial_func or SPATIAL_FUNC[func_type], drop_path=drop_path,
**block_kwargs))
return nn.Sequential(*blocks)
def init_weights(self):
for n, m in self.named_modules():
_init_weights(m, n)
def forward_features(self, x):
x = self.stem(x)
x = reshape2n(x)
x = self.norm1(x)
x = self.blocks(x)
x = self.norm2(x)
return x
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.pool(x)
x = self.head(x)
return x
参考
https://github.com/microsoft/SPACH