spring容器源码分析(基于注解方式)
1、 一些概念
- 定义Bean的注解:
@Component : 基本注解, 标识了一个受 Spring 管理的组件
@Repository : 标识持久层组件
@Service : 标识服务层(业务层)组件
@Controller : 标识表现层组件Spring 能够从 classpath 下自动扫描, 实例化具有特定注解的组件。
2、初步
通过在applicationContext.xml中配置如下后,spring会自动扫描该路径下的所有bean。而如果Bean上面有相应的@Service,@Controller等注解,那么Spring的IOC容器将会帮我们实例对象,并设置属性。
<context:component-scan base-package="xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx">
<context:include-filter type="annotation"
expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Component" />
<context:include-filter type="annotation"
expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository" />
<context:include-filter type="annotation"
expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service" />
</context:component-scan>
3、spring如何实现注解驱动的呢?
好难搞 今天事情有点多,放一个大佬的认知 点击前往 下次在更
放一张流程注入图:
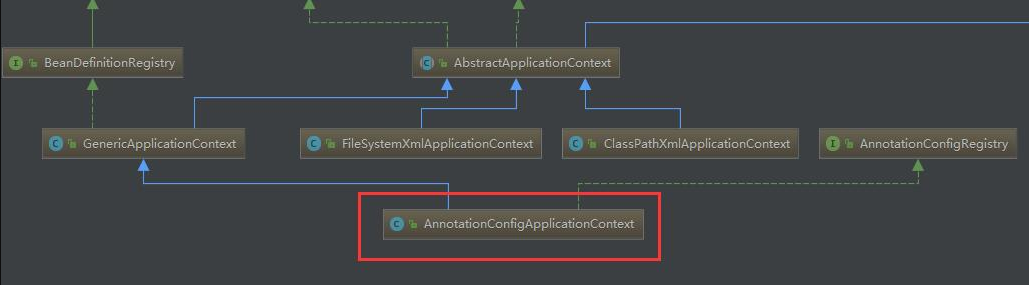
从父类 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext中入手:
/**
* Create a new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext, scanning for bean definitions
* in the given packages and automatically refreshing the context.
* @param basePackages the packages to check for annotated classes
*/
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(String... basePackages) {
this();
scan(basePackages);//扫描包
refresh();//调用AbstractApplicationContext中的refresh方法
}
可以从scan()函数再进一步分析
/**
* Perform a scan within the specified base packages.
* @param basePackages the packages to check for annotated classes
* @return number of beans registered
*/
public int scan(String... basePackages) {
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
doScan(basePackages);//扫描
// Register annotation config processors, if necessary.
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart);
}
很明显扫描的时候主要时进一步通过doScan()来实现的:
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {//遍历所有的包
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);//查找候选组件
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);//注册beandefinition
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
doScan()函数中遍历了所有的包,在通过相应的包查找候选组件 ,具体实在findCandidateComponents():
/**
* Scan the class path for candidate components.
* @param basePackage the package to check for annotated classes
* @return a corresponding Set of autodetected bean definitions
*/
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinition>();
try {
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + "/" + this.resourcePattern;//补充路径
Resource[] resources = this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (Resource resource : resources) {//遍历Resource
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {//通过asm获取class,暂且不研究asm
MetadataReader metadataReader = this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {//判断是否为候选组件
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setResource(resource);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {//判断是否为候选组件
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);//添加候选组件
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
}
在findCandidateComponents()中存在两个判断的条件
/**
* Determine whether the given bean definition qualifies as candidate.
* <p>The default implementation checks whether the class is concrete
* (i.e. not abstract and not an interface). Can be overridden in subclasses.
* @param beanDefinition the bean definition to check
* @return whether the bean definition qualifies as a candidate component
*/
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
return (beanDefinition.getMetadata().isConcrete() && beanDefinition.getMetadata().isIndependent());
}
/**
* Determine whether the given class does not match any exclude filter
* and does match at least one include filter.
* @param metadataReader the ASM ClassReader for the class
* @return whether the class qualifies as a candidate component
*/
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException {
for (TypeFilter tf : this.excludeFilters) {
// 默认为空
if (tf.match(metadataReader, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
return false;
}
}
// 默认有(见registerDefaultFilters方法)
for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
return isConditionMatch(metadataReader);
}
}
return false;
}
很自然的看到match()方法:
if (matchSelf(metadataReader)) {
return true;
}
protected boolean matchSelf(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
// 获取元注解
AnnotationMetadata metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
// AnnortationMetadata(当前类的注解)(annotationSet )
return metadata.hasAnnotation(this.annotationType.getName()) ||
// metaAnnotationMap(当前类的注解以及当前类的注解的派生注解)
(this.considerMetaAnnotations && metadata.hasMetaAnnotation(this.annotationType.getName()));
}
而matchSelf()中结构如下:
@Override
protected boolean matchSelf(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
AnnotationMetadata metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
return metadata.hasAnnotation(this.annotationType.getName()) ||
(this.considerMetaAnnotations && metadata.hasMetaAnnotation(this.annotationType.getName()));
}
查看hasAnnotation和 hasMetaAnnotation方法:
@Override
public boolean hasAnnotation(String annotationType) {
return this.annotationSet.contains(annotationType);
}
@Override
public boolean hasMetaAnnotation(String metaAnnotationType) {
Collection<Set<String>> allMetaTypes = this.metaAnnotationMap.values();
for (Set<String> metaTypes : allMetaTypes) {
if (metaTypes.contains(metaAnnotationType)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
PS:
metadata.hasAnnotation:例如如果当前类上的注解为@Service,那么元注解的annotationSet属性则为Service,不包含默认过滤器中的@Component和@named条件之一,返回false。
metadata.hasMetaAnnotation:例如如果当前类上的注解为@Service,那么元注解的metaAnotationMap则有@Service和@Component(@Service是@Component的派生属性),包含默认过滤器的@Component条件,则为true。
以上内容是针对性学习了 不迷烟火大佬
另外放一个Spring的基础复习链接 传送