For the request and response:
request -----> HttpServletRequest
response -----> HttpServletResponse
Every request send by browser will create a new request object, when the response ends, the response object will be destroyed.
And the request and response object are created by the server.
The function of request and response:
request: handle the http request, get the http request information.
response: handle the http response, set the http response information.

The response structure:
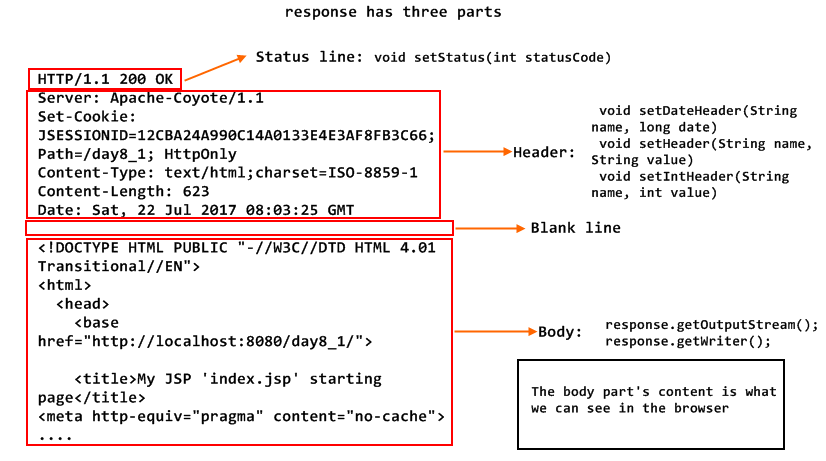
Redirect:
We can use response object to redirect the resource:
1. set the status code : response.setStatus(302);
2. set the response header : response.setHeader("location","/index.jsp");

But in actual developing:
response.sendRedirect(String location);
Set the header and control the browser to jump to the specific page in some time:
response.setHeader("refresh","5;url=/day8_1/refresh.html");
But in actual developing, we seldom use the server to control the jump in some time, usually accomplish in browser, we can do it via javascript:
<head>
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="5;url=/day8_1/index.jsp">
<script type="text/javascript">
var time = 5;
function change(){
var span = getElementById("s");
span.innerHTML = time;
time--;
setTimeout("change()",1000);
}
</sctipt>
</head>
<body onload="chang()">
The page will jump to the other page in <span id="s"></span> second.
</body>
We usually forbid the cache in jsp, but if you want to forbid it in server, you can use the code:
response.setHeader("pragma","no-cache");
response.setHeader("cache-control","no-cache");
response.setDateHeader("expires",-1);
The body part in response is what we see in the browser. And if we want to handle the response body content, we should use response object to get the output stream object.
PrintWriter getWriter();
ServletOutputStream getOutputStream();
When we use getWriter() and when we use getOutputStream()?
If you want to get the original file and don't do any modification, we can use getOutputStream();
If you wan to manipulate your defined information, we can use getWriter().
The PrintWriter has two features:
1. it could auto-refresh.
2. it could print the information in original type.
Notice:
1.When you get the output stream via response, the PrintWriter and ServletOutputStream can't use both at the same time, you can only use one of them.
2.When you use the PrinWirter or ServletOutputStream, close the stream is not necessary, the server will close the stream automatically.
The encoding of response:
1. response.setContentType(String mimeType); -----> it can not only set the response's encoding but also set the browser's text encoding
2. response.setHeader("Content-Type","text/html;charset=utf-8"); -----> it has the same function of the setContentType()
3. response.setEncoding("utf-8"); -----> it can only set the response's encoding, can't set the browser's encoding, to avoid encoding problems, we should change the setting of browser.
HttpServletRequest:
Request object could get the http request infomation.
What's the difference of post and get request method?
1. post could submit big data and the get request could only submit the data less than 1kb
2. the data submited by post could not be displayed on the browser, while the data submited by get will be displayed on the browser.
3. the post request's paramter located in the request body, while the get request's parameter located in the resource path.

Get the request parameter via request object(very important) :
1. String getParameter(String name);
returns the value of the name.
2.String[] getParameterValues(String name);
returns the value array of the name.
3.Enumeration getParameterNames();
returns the enumeration of the parameter names.
4.Map<String,String[]> getParameterMap();
returns the map of parameters, in the map, the key represents the parameter name, the value represents the value names.
key -----> String
value -----> String[]
for example:
Map<String,String[]> map = request.getParameterMap();
for( String key : map.keySet() ){
String[] value = map.get(key);
String str = (key+"="+Arrays.toString(value)).replace("[","").replace("]","");
System.out.println(str);
}
After we get the parameter of request, we should calibrate the parameter, this is server's calibration.
1. calabrate the parameter is empty or not.
parameter.trim().length()>0;
2. regex calibration.
The encoding problems:
There are some parts need to be modified before you handle the encoding problems:
1. set the browser's encoding as utf-8
2. set the myeclipse encoding as utf-8
3. set the web.xml encoding as utf-8
The best way to handle the encoding problem is : (whenever GET or POST submit method):
// we can see from the web.xml of tomcat server, that the server's encoding is iso8859-1.
String param = request.getParameter("param name");
param = new String(param.getBytes("iso8859-1"), "utf-8" );
There is another way to handle the encoding problem, if the submit method is POST, we can:
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String param = request.getParameter("param name");

Request domain object:
The request life circle:
1. the request object will be created when a request was send.
2. the request object will be destroyed the when the response object ends.
Every request is a new request object.
We should remember that the domain object such as ServleContext, ServletRequest ... has the setAttribute(), getAttribute() and removeAttribute method.
Request's important method:
request.getReqeustDispatcher("/").forward(request,response);
return; // this is a good habbit
After the request.getRequestDispatcher("/").forward(request, response); the request and response will go to the next servlet, and the response buffer will be cleared.
Also when the response.sendRedirect(); method completed, the response buffer will also be cleared. Any operation related with buffer will not work anymore.
We should add the "return;" after we use forward() or sendRedirect().

The difference of sendRedirect() and forward() ?

1. Forward is operated in the server, from one servlet jump to another servlet. There is one request and one response.
Redirect will send two requests and returns two response, the two requests and responses are different.
2. Forward is the operation in server and it will not change the URL path.
Redirect has two requests, and the URL path will change.
3. Forward can jump to other resource which stays at the web application.
Redirect can jump to the resource out of the web application, such as http://www.baidu.com
4. Forward: request.getRequestDispatcher("/").forward();
Redirect: response.sendRedirect();
5. Forward: "/" represents the path : http://localhost:8080/app/
Redirect: "/" represents the path: http://localhost:8080
6. Forward: it has request domain.
Redirect: it doesn't has domain.
The difference of getParamter() and getAttribute():
The two methods are all called by request:
request.getParameter(); get the information from request, such as the data submited by html file.
request.getAttribute(); get the data from request domain, if you want to get the attribute, you should setAttribute() first.