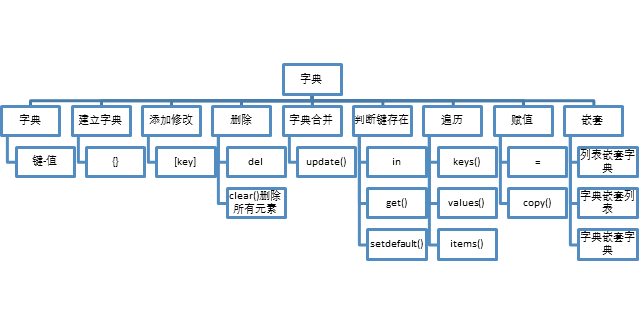
什么是字典?
像列表一样,但是不能想列表用下表索引,而是通过'键',键及其关联的值称为'键-值'对。字典经常会简写成dict
创建字典{}
例如:
>>> dict = {'one':1,'two':2,'three':3}
访问字典的值通过key
>>> dict = {'one':1,'two':2,'three':3}
>>> dict['one']
1
添加或修改字典[key]
>>> dict = {'one':1,'two':2,'three':3}
>>> dict['one']
1
>>> dict['four'] = 4
>>> dict
{'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
>>> dict['one'] = '一'
>>> dict
{'one': '一', 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
删除字典里元素 del
>>> del dict['four']
>>> dict
{'one': '一', 'two': 2, 'three': 3}
合并字典update()
>>> dict
{'one': '一', 'two': 2, 'three': 3}
>>> dict1 = {'four':4}
>>> dict.update(dict1)
>>> dict
{'one': '一', 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
使用clear()删除所有元素
>>> dict
{'one': '一', 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
>>> dict.clear()
>>> dict
{}
判断一个键是否存在in,get()方法,setdefault()方法
>>> dict={'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
>>> 'one' in dict
True
>>> 'five' in dict
False
get()方法,它有两个参数:要取的其值的键,以及如果该键不存在时,返回的备用值。
>>> dict
{'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
>>> dict.get('one')
1
>>> dict.get('five')
>>> print(dict.get('five'))
None
>>> dict.get('five',5)
5
>>> dict
{'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
setdefault()方法提供一种方式,传递给该方法的第一个参数,是要检查的键。第二个参数,如果该键不存在时要设置的值。如果该键存在,就会返回键的值。
>>> dict
{'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
>>> dict.setdefault('one',1)
1
>>> dict.setdefault('one','一')
1
>>> dict
{'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
>>> dict.setdefault('five',5)
5
>>> dict
{'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'five': 5, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
keys()、values()、items()方法
分别对应键、值、和键-值对
>>> for i in dict.keys():
print(i)
one
two
three
four
>>> for i in dict.values():
print(i)
1
2
3
4
>>> for a,b in dict.items():
print(a,b)
one 1
two 2
three 3
four 4
使用 = 赋值,使用copy()复制
= 和列表一样,改变其中一个变量,其他变量也会改变
>>> dict
{'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'five': 5, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
>>> dict1 = dict
>>> del dict1['five']
>>> dict1
{'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
>>> dict
{'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4}
使用copy()就可以避免这种情况
嵌套
列表中嵌套字典
>>> [{'one':1},{'two',2},{'three':3}]
[{'one': 1}, {2, 'two'}, {'three': 3}]
字典中嵌套列表
>>> {'one':[1,'yi','一','壹'],'two':[2,'二','贰']}
{'one': [1, 'yi', '一', '壹'], 'two': [2, '二', '贰']}
字典中嵌套字典
>>> {'number':{'one':1,'two':2,'three':3},'abc':{'a':'A','b':'B'}}
{'number': {'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3}, 'abc': {'a': 'A', 'b': 'B'}}