今天我们学习的是如何在线程自己的范围内达到变量数据的共享,而各个线程之间又是互相独立开来,各自维护的,即我们说的ThreadLocal的作用。
一、概念
可以将每个线程用到的数据与对应的线程号存放到一个map集合中,使用数据时从这个集合中根据线程号获取对应线程的数据,就可以实现线程范围内共享相同的变量。
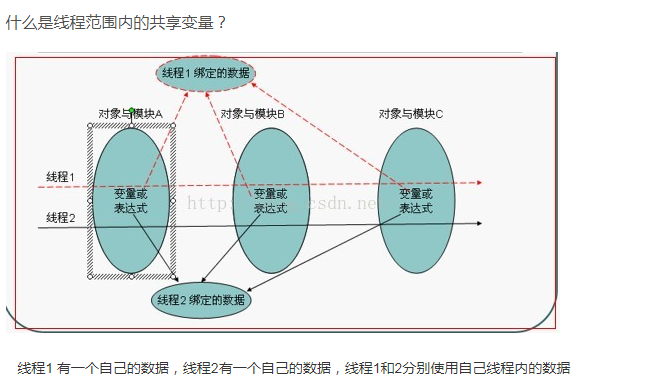
二、代码
Runnable中的run()方法里面执行Thread.currentThread()都会对应当前Runnable对应的线程,因此A、B中对应的Thread.currentThread()对应所在的Runnable对应的线程
public class ThreadScopeShareData { private static Map<Thread, Integer> threadData = new HashMap<Thread, Integer>(); public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0;i<2;i++){ new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { int data = new Random().nextInt(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " has put data :" + data); threadData.put(Thread.currentThread(), data); new A().get(); new B().get(); } }).start(); } } static class A{ public void get(){ int data = threadData.get(Thread.currentThread()); System.out.println("A from " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get data :" + data); } } static class B{ public void get(){ int data = threadData.get(Thread.currentThread()); System.out.println("B from " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get data :" + data); } } }
三、ThreadLocal
JDK1.5提供了ThreadLocal类来方便实现线程范围内的数据共享,它的作用就相当于前面中的Map(内部并不是Map),也就是让每个线程拥有自己的值
一个ThreadLocal对象只能记录一个线程内部的一个共享变量,需要记录多个共享数据,可以创建多个ThreadLocal对象,或者将这些数据进行封装,将封装后的数据对象存入ThreadLocal对象中。
线程结束后也可以自动释放相关的ThreadLocal变量,也可以调用ThreadLocal.remove()方法用来更快释放内存。
代码:
public class ThreadLocalTest { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Integer>(); public static void main(String[] args) { //启动两个线程 for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { //创建每个线程私有的变量 int data = new Random().nextInt(100); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" has put data: "+data); //往local里面设置值 threadLocal.set(data); new A().get(); new B().get(); } }).start(); } } static class A{ public void get(){ int data =threadLocal.get(); System.out.println("A from "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" has get data: "+data); } } static class B{ public void get(){ int data =threadLocal.get(); System.out.println("B from "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" has get data: "+data); } } }
假设需要保存不止一个值,可以把其他属性的值打包成一个类,然后将该类设置成ThreadLocal的值。
下面代码中,在类MyThreadLocalScopeDate里面定义了一个静态变量Map,用来保存所有线程创建的MyThreadLocalScopeDate,并使用单例使得不管多少线程都只创建一个MyThreadLocalScopeDate对象。
public class ThreadLocalTest { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Integer>(); public static void main(String[] args) { //启动两个线程 for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { //创建每个线程私有的变量 int data = new Random().nextInt(100); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" has put data: "+data); //往local里面设置值 threadLocal.set(data); //获取自己线程的MyThreadLocalScopeDate实例对象 MyThreadLocalScopeDate myData = MyThreadLocalScopeDate.getThreadInstance(); myData.setName("name"+data); myData.setAge(data); new A().get(); new B().get(); } }).start(); } } static class A{ public void get(){ int data =threadLocal.get(); System.out.println("A from "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" has get data: "+data); MyThreadLocalScopeDate myData = MyThreadLocalScopeDate.getThreadInstance(); System.out.println("A from "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" has get MyThreadLocalScopeDate name: "+myData.getName()+" , age: "+myData.getAge()); } } static class B{ public void get(){ int data =threadLocal.get(); System.out.println("B from "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" has get data: "+data); MyThreadLocalScopeDate myData = MyThreadLocalScopeDate.getThreadInstance(); System.out.println("B from "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" has get MyThreadLocalScopeDate name: "+myData.getName()+" , age: "+myData.getAge()); } } } class MyThreadLocalScopeDate{//单例模式 private MyThreadLocalScopeDate(){};//构造方法私有化 private static ThreadLocal<MyThreadLocalScopeDate> map = new ThreadLocal<MyThreadLocalScopeDate>();//封装MyThreadLocalScopeDate是线程实现范围内共享 //思考AB两个线程过来的情况 自己分析 AB都需要的自己的对象 没有关系 所以不需要同步 如果有关系就需要同步了 public static /*synchronized*/MyThreadLocalScopeDate getThreadInstance(){ MyThreadLocalScopeDate instance =map.get(); if(instance==null){ instance = new MyThreadLocalScopeDate(); map.set(instance); } return instance; } private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
参考资料:
《多线程视频》张孝祥