在对车牌识别过程中,常用的方法有:基于形状、基于色调、基于纹理、基于文字特征等方法。首先基于形状,在车牌中因为车牌为形状规格的矩形,所以目的转化为寻找矩形特征,常常是利用车牌长宽比例特征、占据图像的比例等。基于色调,国内的车牌往往是蓝底白字,可以采用图像的色调或者饱和度特征,进入生成二值图,定位车牌位置。基于纹理特征自己还没有基础到。基于文字特征往往是根据文字轮廓特征进行识别,原理是基于相邻文字轮廓特征、比例进行定位车牌位置。
一、图像二值化
正如前面文章所言,首先进行获取图像二值化特征,本文采取了根据图像亮度特征,提高对比度,进行可以清晰获取文字的图像,为下一步的文字轮廓识别打好基础。
1.1 算法流程
伪代码
1、图像转化为HSV图像,获取V通道图像
2、提高对比度
3、V图像高斯滤波,去除噪声
4、图像二值化
程序源码:
def get_colorvalue(image): height, width, shape = image.shape image_hsv = np.zeros((height,width), np.uint8) image_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV) image_hue, image_saturation, image_value = cv2.split(image_hsv) return image_value def enhance_contrast(image): kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3,3)) img_tophat = cv2.morphologyEx(image, cv2.MORPH_TOPHAT,kernel) img_blackhat = cv2.morphologyEx(image, cv2.MORPH_BLACKHAT, kernel) image_plus_tophat = cv2.add(image, img_tophat) image_plus_blackhat_minus_blackhat = cv2.subtract(image_plus_tophat, img_blackhat) return image_plus_blackhat_minus_blackhat def preprocess(srcimage): image_value = get_colorvalue(srcimage) image_enhance = enhance_contrast(image_value) image_blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(image_enhance, (5,5), 0) # _, image_binary = cv2.threshold(image_blur, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
_, image_binary = cv2.threshold(image_blur, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY ) cv2.imwrite('image_binary.png',image_binary) return image_binary
1.2 算法分析
在实验中在获取通道图像时,发现可以利用图像饱和度图像进行定位。
1、通道图像提取
image_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
image_hue, image_saturation, image_value = cv2.split(image_hsv)
上面分别为src、hue、saturation、value四副图像,在其中saturatio中可以清晰获取车牌相对于背景的饱和度大,则提取较value图像则可视为灰度图像,能保留图像大部分图像特征。
关于hsv的介绍可以参考这篇文章学习Opencv笔记(二)————hsv色系:文章简单介绍hsv体系内容。
2、图像对比度增强
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3,3)) img_tophat = cv2.morphologyEx(image, cv2.MORPH_TOPHAT,kernel) img_blackhat = cv2.morphologyEx(image, cv2.MORPH_BLACKHAT, kernel) image_plus_black = cv2.add(image, img_blackhat) image_plus_blackhat_minus_blackhat = cv2.subtract(image_plus_black, img_tophat)
(img_tophat) (img_blackhat)
 (ima_plus_top_hat) (img_plus_black_top_hat)
(ima_plus_top_hat) (img_plus_black_top_hat)
图像增强的目的是提高图像的对比度,亮度地方更亮,暗的地方更暗。在形态学处理中,顶帽操作往往用来分离比邻近点亮一些的板块,在一幅图像具有大幅背景而微小物品比较有规律的情况下,可以使用顶帽运算进行背景提取。黑帽运算后的效果图突出了比原图轮廓周围的区域更暗的区域,这一操作也与选择的核尺寸有关。
流程就是,加上黑帽,减去顶冒,其实通过实验结果发现,貌似作用不大。
形态学处理详细介绍可以参考:数字图像处理-形态学研究:对形态学各种操作和理论进行了详细的介绍
3.二值化
在获取单通道图像后,进行了图像二值化操作,其中网上有个文章推荐使用adaptiveThreshold,其实真的不好用,我也采用了ostu算法,经过试验验证也不是很好用,经过多次验证,初步定阈值为80,效果比较良好。
二、图像位置初步定位
由于车辆图像背景比较复杂,所以应该根据车牌的特征进行初次筛选,其特征还是根据中国车牌大小、比例等关系进行筛选。
 上图是自己找的关于车牌的标准,我们可以清晰知道宽:高 = 3.5 所以程序设置的最小比例是2,最大是5,然后就是根据图像大小设定的面积,长宽等大小。
上图是自己找的关于车牌的标准,我们可以清晰知道宽:高 = 3.5 所以程序设置的最小比例是2,最大是5,然后就是根据图像大小设定的面积,长宽等大小。
2.1、算法源码
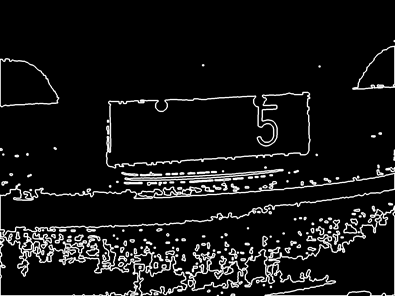
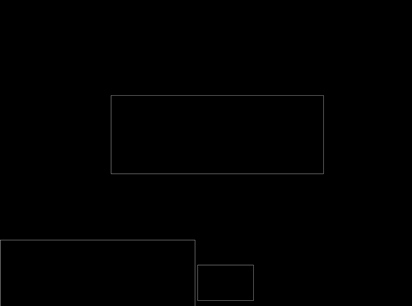
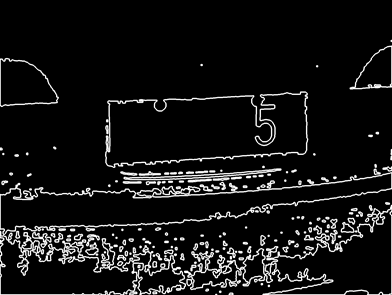
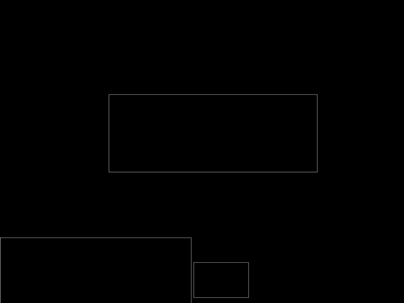
#contants for plate contour MIN_CONTOUR_WIDTH = 80 MIN_CONTOUR_HEIGHT = 30 MIN_CONTOUR_RATIO = 1.5 MAX_CONTOUR_RATIO = 5 MIN_CONTOURL_AREA = 1500 def get_external_contours(image_thresh): # Construct display images and display contours in images height, width = image_thresh.shape image_contour1 = np.zeros((height, width),np.uint8) image_contour2 = np.zeros((height, width),np.uint8) ## Custom 3*3 nuclei undergo expansion corrosion in the X direction kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3)) image_dilate= cv2.dilate(image_thresh,kernel,iterations =2) image_erode= cv2.erode(image_dilate, kernel, iterations = 4) image_dilate= cv2.dilate(image_erode,kernel,iterations = 2) # _, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(image_dilate, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) contour_filter = [] cv2.drawContours(image_contour1, contours, -1,(255, 255, 255 ),3) # choose the suite contour by the feature of special scence for contour in contours: contour_possible = PossibleContour(contour) if(check_external_contour(contour_possible)): cv2.rectangle(image_contour2, (contour_possible.rectX, contour_possible.rectY), (contour_possible.rectX + contour_possible.rectWidth, contour_possible.rectY + contour_possible.rectHeight),255) contour_filter.append(contour_possible) print("the length of origin contours is %d " %len(contour_filter)) cv2.imwrite("1_1contours.png",image_contour1) cv2.imwrite("1_2contours.png",image_contour2) return contour_filter # #According to the license plate area size, length and width ratio, the primary screening is carried out def check_external_contour(contour): if (contour.area > MIN_CONTOURL_AREA and contour.rectWidth > MIN_CONTOUR_WIDTH and contour.rectHeight > MIN_CONTOUR_HEIGHT and contour.whratio > MIN_CONTOUR_RATIO and contour.whratio < MAX_CONTOUR_RATIO): return True else: return False
2 .2、算法分析
上述算法核心是利用了findcontours函数,即在图像中寻找目标轮廓,详细的介绍可以参考这篇文章:
OpenCV-Python教程(11、轮廓检测):文中很详细介绍函数参数含义及应用
在获取轮廓中,传入自己定义的类中,获取根据轮廓的矩形的面积、长宽等值,方便后续计算。
第二步就是根据上述理论分析,得到的函数。
上面四副图片分别展示了经过筛选后的结果,对contour根据限制条件进行选择,最终选择符合条件的候选区域,并保存在list中。
三、图像车牌精确定位
在中国车牌颜色为蓝底白字,所以蓝色数值会比较大,我们计算候选车牌区域蓝色数值(均值)的最大值,确定最终的车牌区域。
3.1 算法源码
def chack_plate_blueHue(contour_list, image_src): if len(contour_list) == 0: print('cannot find the plate contours') return None mean_list = [] # calculate the mean of each blue image and choose the max one,get the index for contour in contour_list: image = cv2.getRectSubPix(image_src, ( contour.rectWidth, contour.rectHeight),(contour.centerX, contour.centerY)) b , g, r = cv2.split(image) sum_pix = b.shape[0] * b.shape[1] b_mean = np.sum(np.array(b))/sum_pix mean_list.append(b_mean) index = np.argmax(np.array(mean_list)) contour_final = contour_list[index] return contour_final
3.2 算法分析
1、遍历轮廓数组,根据前期获取的候选车牌区域,通过getRectSubPix获取其图像
2、分离图像,获取blue通道图像
3、计算图像均值,并添加到list
4、寻找list的argmax,获取其index
5、返回list中准确的contour