每一趟从待排序的数据元素中选出最小(或最大)的一个元素,顺序放在已排好序的数列的最后,直到全部待排序的数据元素排完。 选择排序是不稳定的排序方法。
一. 算法描述
选择排序:比如在一个长度为N的无序数组中,在第一趟遍历N个数据,找出其中最小的数值与第一个元素交换,第二趟遍历剩下的N-1个数据,找出其中最小的数值与第二个元素交换......第N-1趟遍历剩下的2个数据,找出其中最小的数值与第N-1个元素交换,至此选择排序完成。
以下面5个无序的数据为例:
56 12 80 91 20(文中仅细化了第一趟的选择过程)
第1趟:12 56 80 91 20
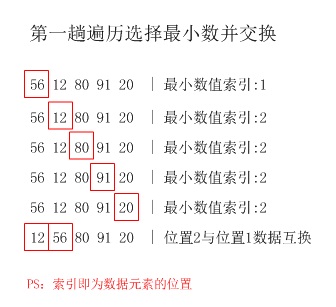
第2趟:12 20 80 91 56
第3趟:12 20 56 91 80
第4趟:12 20 56 80 91
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
int array[] = {12,2, 6, 9, 8, 5, 7, 1, 4};
//为了增加可移植性(采取sizeof())计算数组元素个数count
int count = sizeof(array) /sizeof(array[0]);
//
for (int i = 0; i < count - 1; i++) { //比较的趟数
int minIndex = i;//查找最小值
for (int j = minIndex +1; j < count; j++ ) {
if (array[minIndex] > array[j]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
//如果没有比较到最后还剩余一个数,那么就执行下面的操作
if (minIndex != i) {
//交换数据
int temp = 0;
temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[minIndex];
array[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
printf("[%2d]: %d ", i, array[i]);
}
return 0;
}