本文代码基于SpringBoot,文末有代码连接 。首先是一些在Spring Boot的一些配置和概念,然后跟随代码看下五种模式
MQ两种消息传输方式,点对点(代码中的简单传递模式),发布/订阅(代码中路由模式)。要是你熟悉RabbitMQ SpringBoot配置的话,就是simple和direct。
MQ安装指南:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_19006223/article/details/89421050
0.消息队列运转过程
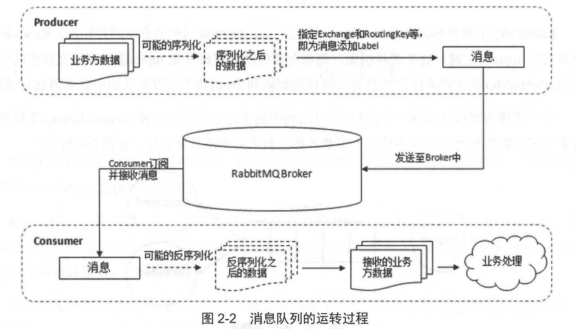
生产者生产过程:
(1)生产者连接到 RabbitMQ Broker 建立一个连接( Connection) ,开启 个信道 (Channel)
(2) 生产者声明一个交换器 ,并设置相关属性,比如交换机类型、是否持久化等
(3)生产者声明 个队列井设置相关属性,比如是否排他、是否持久化、是否自动删除等
(4)生产者通过路由键将交换器和队列绑定起来。
(5)生产者发送消息至 RabbitMQ Broker ,其中包含路由键、交换器等信息。
(6) 相应的交换器根据接收到的路由键查找相匹配的队列 如果找到 ,则将从生产者发送过来的消息存入相应的队列中。
(7) 如果没有找到 ,则根据生产者配置的属性选择丢弃还是回退给生产者
(8) 关闭信道。
(9) 关闭连接。
消费者接收消息的过程:
(1)消费者连接到 RabbitMQ Broker ,建立一个连接(Connection ,开启 个信道(Channel)
(2) 消费者向 RabbitMQ Broker 请求消费相应队列中的消息,可能会设置相应的回调函数, 以及做 些准备工作。
(3)等待 RabbitMQ Broker 回应并投递相应队列中的消息, 消费者接收消息。
(4) 消费者确认 ack) 接收到的消息
(5) RabbitMQ 从队列中删除相应己经被确认的消息
(6) 关闭信道。
(7)关闭连接。
1.项目结构

common是工具,receiver是消费者,sender是生产者
具体各自的pom.xml文件请看项目,都有注释。
2.sender(生产者的配置)

#确认机制
publisher-confirms: true 消息有没有到达MQ(会返回一个ack确认码)
publisher-returns: true 消息有没有找到合适的队列
主要是为了生产者和mq之间的一个确认机制,当消息到没到mq,会提供相应的回调,在项目中 RabbitSender 这个类中进行了相应的配置

1 private final RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback confirmCallback = (correlationData, ack, s) -> { 2 if (ack) { 3 System.out.println(correlationData.getId()); 4 } else { 5 log.error("ConfirmCallback消息发送失败: {}", s); 6 } 7 }; 8 9 private final RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback returnCallback = (message, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey) 10 -> log.error("ReturnCallback消息发送失败: {}", new String(message.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); 11 12 13 public <T> void sendMsg(String exchangeName, String routingKeyName, T content) { 14 // 设置每个消息都返回一个确认消息 15 this.rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true); 16 // 消息确认机制 17 this.rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(confirmCallback); 18 // 消息发送失败机制 19 this.rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(returnCallback); 20 // 异步发送消息 21 CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(); 22 correlationData.setId("123"); 23 this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, routingKeyName, content, correlationData); 24 }
还可以根据需求设置发送时CorrelationData 的值
#mandatory
参数设为 true 时,交换器无法根据自身的类型和路由键找到一个符合条件 的队列,那么 RabbitM 会调用 Basic.Return 命令将消息返回给生产者。
默认为false,直接丢弃
3.receiver(消费者配置)

这里主要说一下 listerner 的相关配置
一共有两种模式:simple和direct模式
simple主要包括两种工作模式,direct主要包括四种,待会代码会详解。
先说主要配置(以direct为例)
#acknowledge-mode: manual
手动确认模式,推荐使用这种。就是说当消息被消费者消费时,需要手动返回信息告诉mq。如果是自动的话,mq会自动确认,不管你消费者是否完成消费(比如说抛出异常)
#prefetch: 1
一个消费者一次拉取几条消息,本demo一条一条来。
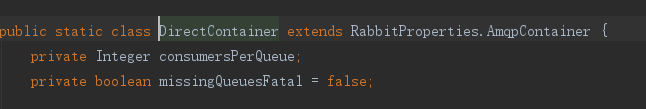
#consumers-per-queue: 2
一个队列可以被多少消费者消费(这个配置,我测试的时候没测试出来,如果有朋友了解的话,可以评论下。)
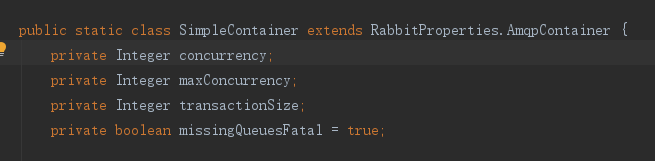
还有其他配置,看下源码,两种模式共有的
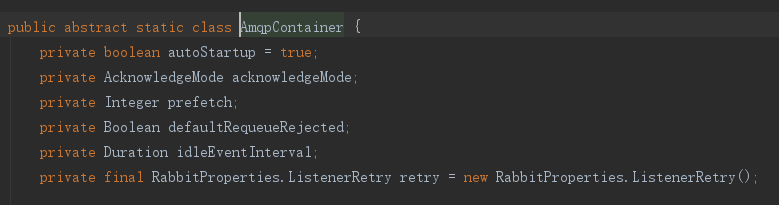
simple特有的
direct特有的
4.各种模式详解
---------simple方式下的两种
打开上面的listener配置
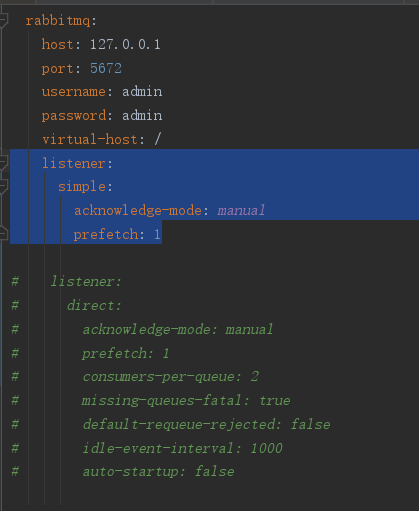
4.1 simple
一个生产者,一个消费者
生产者发送消息都在SenderTest里面
生产者:
/**简单模式*/
@Test
public void senderSimple() throws Exception {
String context = "simple---> " + new Date();
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple", context);
}
消费者
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple")
public void simple(Message message, Channel channel){
String messageRec = new String(message.getBody());
System.out.println("simple模式接收到了消息:"+messageRec);
try {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("报错了------------------"+e.getMessage());
}
}
输出
simple模式接收到了消息:simple---> Sat Apr 20 20:40:16 CST 2019
4.2 work 模式
一个生产者,多个消费者
生产者
private static final List<Integer> ints = Arrays.asList(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
/**work模式*/
@Test
public void senderWork() throws Exception {
ints.forEach((i)->{
String context = "work---> " + i;
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("work", context);
});
}
消费者
@RabbitListener(queues = "work")
public void work1(Message message, Channel channel){
try{
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
String messageRec = new String(message.getBody());
System.out.println("work1接收到了消息:"+messageRec);
try {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("work1报错了------------------"+e.getMessage());
}
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "work")
public void work2(Message message, Channel channel){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
String messageRec = new String(message.getBody());
System.out.println("work2接收到了消息:"+messageRec);
try {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("work2报错了------------------"+e.getMessage());
}
}
输出
work1接收到了消息:work---> 2 work2接收到了消息:work---> 0 work1接收到了消息:work---> 1 work1接收到了消息:work---> 4 work2接收到了消息:work---> 3 work1接收到了消息:work---> 6 work1接收到了消息:work---> 7 work2接收到了消息:work---> 5 work1接收到了消息:work---> 8 work1接收到了消息:work---> 10 work2接收到了消息:work---> 9
-----direct方式下的
切换listener配置

4.3direct交换机
生产者发送消息给指定交换机,绑定的某个队列。
消费者通过监听某交换机绑定的某个队列接受消息。
生产者
/**direct交换机*/
@Test
public void senderDirect() throws Exception {
rabbitSender.sendMsg("direct","directKey1","directContent1");
rabbitSender.sendMsg("direct","directKey2","directContent2");
}
消费者
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(exchange = @Exchange("direct"), key = "directKey1"
, value = @Queue(value = "directQueue1", durable = "true", exclusive = "false", autoDelete = "false")))
public void direct1(String str, Channel channel, Message message) throws IOException {
try {
System.out.println("directQueue1接收到了:"+str);
}catch (Exception e){
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false,false);
}
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(exchange = @Exchange("direct"), key = "directKey2"
, value = @Queue(value = "directQueue2", durable = "true", exclusive = "false", autoDelete = "false")))
public void direct2(String str, Channel channel, Message message) throws IOException {
try {
System.out.println("directQueue2接收到了:"+str);
}catch (Exception e){
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false,false);
}
}
输出
directQueue1接收到了:directContent1 directQueue2接收到了:directContent2
4.4 topic交换机
指定主题
# :匹配一个或者多级路径
*: 匹配一级路径
生产者
@Test
public void senderTopic() throws Exception {
String contexta = "topic.a";
rabbitSender.sendMsg("topic","topicKey.a",contexta);
String contextb = "topic.b";
rabbitSender.sendMsg("topic","topicKey.b",contextb);
String contextc = "topic.c";
rabbitSender.sendMsg("topic","topicKey.c",contextc);
String contextz = "topic.z";
rabbitSender.sendMsg("topic","topicKey.c.z",contextz);
}
消费者
/**
* topic交换机
* */
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(exchange = @Exchange(name = "topic",type = "topic"), key = "topicKey.#"
, value = @Queue(value = "topicQueue", durable = "true", exclusive = "false", autoDelete = "false")))
public void topicQueue(String str, Channel channel, Message message) throws Exception {
try {
System.out.println("topicQueue接收到了:"+str);
}catch (Exception e){
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false,false);
}
}
输出
topicQueue接收到了:topic.a
4.5 Fanout 交换机
广播模式,一个消息可以给多个消费者消费
生产者
/**Fanout 交换机*/
@Test
public void senderFanout() throws Exception {
String contexta = "Fanout";
rabbitSender.sendMsg("fanout","fanoutKey1",contexta);
//写不写KEY都无所谓
}
消费者
/**
* Fanout 交换机
* */
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(exchange = @Exchange(name = "fanout",type = "fanout"), key = "fanoutKey1"
, value = @Queue(value = "fanoutQueue1", durable = "true", exclusive = "false", autoDelete = "false")))
public void fanoutQueue1(String str, Channel channel, Message message) throws Exception {
try {
System.out.println("fanoutQueue1接收到了:"+str);
}catch (Exception e){
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false,false);
}
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(exchange = @Exchange(name = "fanout",type = "fanout"), key = "fanoutKey2"
, value = @Queue(value = "fanoutQueue2", durable = "true", exclusive = "false", autoDelete = "false")))
public void fanoutQueue2(String str, Channel channel, Message message) throws Exception {
try {
System.out.println("fanoutQueue2接收到了:"+str);
}catch (Exception e){
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false,false);
}
}
输出
fanoutQueue2接收到了:Fanout
fanoutQueue1接收到了:Fanout
4.6 Headers 交换机
代码:https://github.com/majian1994/rabbitMQ_Study
