一、Github项目地址
https://github.com/PIPIYing/wc
二、项目概况
项目描述
Word Count
1. 实现一个简单而完整的软件工具(源程序特征统计程序)。
2. 进行单元测试、回归测试、效能测试,在实现上述程序的过程中使用相关的工具。
3. 进行个人软件过程(PSP)的实践,逐步记录自己在每个软件工程环节花费的时间。
项目要求
wc.exe 是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。这个项目要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有wc.exe 的功能,并加以扩充,给出某程序设计语言源文件的字符数、单词数和行数。
实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
项目功能
具体功能要求
程序处理用户需求的模式为:wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
基本功能
1. 支持-c参数:返回文件 file.c 的字符数(实现)
2. 支持-w参数:返回文件 file.c 的词的数目(实现)
3. 支持-l参数:返回文件 file.c 的行数(实现)
基本功能列表:
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数
拓展功能
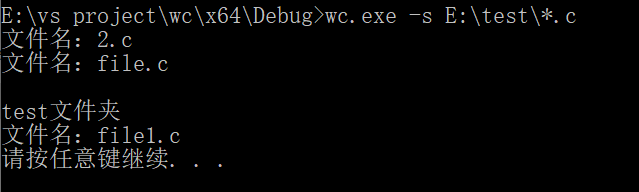
1. 支持-s参数:递归处理目录下符合条件的文件(实现)
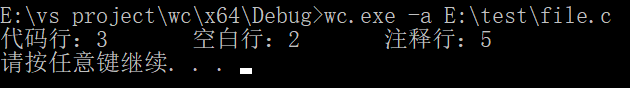
2. 支持-a参数:返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)(实现)
3. 支持*,?参数:可以处理一般通配符(实现)
空行:本行全部是空格或格式控制字符,如果包括代码,则只有不超过一个可显示的字符,例如“{”。
代码行:本行包括多于一个字符的代码。
注释行:本行不是代码行,并且本行包括注释。一个有趣的例子是有些程序员会在单字符后面加注释:
} //注释
在这种情况下,这一行属于注释行。
[file_name]: 文件或目录名,可以处理一般通配符。
高级功能
1. 支持-x参数:程序显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息(未实现)
2. 支持-s、-a和一般通配符(*,?)参数:返回当前目录及子目录中所有*.c 文件的代码行数、空行数、注释行数(实现)
-x 参数。这个参数单独使用。如果命令行有这个参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。
需求举例:
wc.exe -s -a *.c
返回当前目录及子目录中所有*.c 文件的代码行数、空行数、注释行数。
三、解题思路
看完题目描述和项目要求,明确这是一个cmd下的命令行系统,通过在cmd界面输入命令行来执行相关功能。
由于本人还没有学过Java,所以本次项目采用了C语言来完成。其中主要用到了头文件stdio.h定义的关于文件的函数,再基于各个功能模块进行分析。
四、设计实现过程
通过分析功能,将每个功能写成一个接口,再通过main函数接收命令行来调用相关功能的接口,实现功能并在cmd打印相关信息。
基本接口如下:
int countChar(char path[N], char file[N]);
功能:统计文件字符数
设计:把基本路径和文件名拼接,调用函数fopen_s读取文件
1. 若文件不存在,打印信息
2. 若文件存在,则统计字符数(不包括中文字)和中文字(包括中文字符,其中中文字和中文字符各占2个字符位),打印字符数和中文字数
int countWord(char path[N], char file[N]);
功能:统计文件单词数
设计:把基本路径和文件名拼接,调用函数fopen_s读取文件
1. 若文件不存在,打印信息
2. 若文件存在,则通过统计空格数来统计单词数,打印单词数
int countLine(char path[N], char file[N]);
功能:统计文件行数
设计:把基本路径和文件名拼接,调用函数fopen_s读取文件
1. 若文件不存在,打印信息
2. 若文件存在,则通过函数fgets按行读取字符的特性,统计行数,打印行数
int countElse(char path[N], char file[N]);
功能:统计文件代码行数、空行数和注释行数
设计:把基本路径和文件名拼接,调用函数fopen_s读取文件
1. 若文件不存在,打印信息
2. 若文件存在,则三种行数的判断规则如下:
a.代码行:调用函数fgets按行读取字符,除去空格、换行、\t之外都计入字符数,最后字符数>1即为代码行
b.空行:调用函数fgets按行读取字符,除去空格、换行、\t之外都计入字符数,最后字符数<1即为空行
c.注释行:分为//和/* */。前者读取到两个’/’即为注释行,后者读取到开始符号/*和结束符号*/之间的行均为注释行
3. 最后打印代码行数、空行数和注释行数
int searchFile(char path[N],char mode[N],int tag);
功能:递归查找符合条件的文件
设计:通过拼接文件的查找路径,根据需求,调用函数_findfirst获取文件句柄
1. 若文件句柄=-1,则文件不存在
2. 根据文件句柄遍历文件并打印符合需求的文件名;有子目录则返回该函数,进行递归操作
int splitPath(char path[N],char mode[N]);
功能:拆分在cmd下输入的完整路径
设计:检查最后一个’/’后是不是文件名或一般通配符,并标记
1. 路径符合要求,返回基本路径和文件名或一般通配符
2. 路径不符合要求,则打印错误信息
五、代码说明
统计字符数
1 //统计字符数 2 int countChar(char path[N], char file[N]) 3 { 4 FILE* fp = NULL; 5 errno_t err; 6 //英文字符计数器和中文字符计数器 7 int n = 0, nC = 0; 8 int c[M]; 9 int i = 0; 10 char filePath[N] = { 0 }; 11 12 strcpy_s(filePath, path); 13 strcat_s(filePath, file); 14 15 err = fopen_s(&fp, filePath, "r"); 16 if (fp == NULL) 17 { 18 printf("该文件不存在。\n"); 19 return -1; 20 } 21 else { 22 for (i = 0; i < M; i++) { 23 c[i] = fgetc(fp); 24 if (feof(fp)) break; 25 else { 26 if (c[i] > 127) { 27 //每个中文字和中文符号各占2个字符位 28 c[i + 1] = fgetc(fp); 29 i += 2; 30 //统计中文字 31 nC++; 32 } 33 else if (c[i] < 0) 34 break; 35 //统计字符数(包括字母、数字、英文符号、空格、换行,不包括中文字符) 36 else n++; 37 } 38 } 39 n -= 1; 40 printf("字符数:%d\t中文字:%d\n", n,nC); 41 } 42 43 fclose(fp); 44 return n; 45 }
统计单词数
1 //统计单词数 2 int countWord(char path[N], char file[N]) { 3 FILE* fp = NULL; 4 errno_t err; 5 int c; 6 //计数器 7 int n = 0; 8 char filePath[N] = { 0 }; 9 10 strcpy_s(filePath, path); 11 strcat_s(filePath, file); 12 13 err = fopen_s(&fp, filePath, "r"); 14 if (fp == NULL) 15 { 16 printf("该文件不存在。\n"); 17 return -1; 18 } 19 do 20 { 21 c = fgetc(fp); 22 if (feof(fp)) break; 23 //通过空格来统计单词数 24 else if (c == ' ') n++; 25 } while (1); 26 27 printf("单词数:%d\n", n); 28 29 return n; 30 }
统计行数
1 //统计行数 2 int countLine(char path[N], char file[N]) { 3 FILE* fp = NULL; 4 errno_t err; 5 char b[N]; 6 //计数器 7 int n = 0; 8 char filePath[N] = { 0 }; 9 10 strcpy_s(filePath, path); 11 strcat_s(filePath, file); 12 13 err = fopen_s(&fp, filePath, "r"); 14 if (fp == NULL) 15 { 16 printf("该文件不存在。\n"); 17 return -1; 18 } 19 do { 20 //fgets()函数按行读取字符,每读一次为一行,以此计数 21 if (fgets(b, N, fp)) n++; 22 else break; 23 } while (1); 24 25 printf("行数:%d\n", n); 26 27 return n; 28 }
统计代码行、空行和注释行
1 //统计代码行、空行和注释行 2 int countElse(char path[N], char file[N]) { 3 FILE* fp = NULL; 4 errno_t err; 5 char b[N]; 6 //记录代码行数,记录空行数,记录注释行,记录数组长度,记录字符长度,记录两种注释行数(//和/* */),记录三种行的总数 7 int codeLine = 0, blankLine = 0, commentLine = 0, length = 0, count_char = 0, countC1 = 0, countC2 = 0, sum = 0; 8 int i, j; 9 //tag是查找/* */注释符号的前半部分的标记,查找成功记为1,查找失败记为0 10 int tag = 0; 11 char filePath[N] = { 0 }; 12 13 strcpy_s(filePath, path); 14 strcat_s(filePath, file); 15 16 err = fopen_s(&fp, filePath, "r"); 17 if (fp == NULL) 18 { 19 printf("该文件不存在。\n"); 20 return -1; 21 } 22 do { 23 //fgets()函数按行读取字符 24 if (fgets(b, N, fp)) { 25 length = strlen(b); 26 for (i = 0, count_char = 0; i < length; i++) { 27 if (b[i] != ' ' && b[i] != '\n' && b[i] != '\t') 28 //在一行中,除去空格、换行、\t之外都计入字符数 29 count_char++; 30 if (b[i] == '/' && b[i + 1] == '/') { 31 //第一种注释情况,读入的一行为注释行,跳出循环 32 countC1++; 33 //注释行不属于代码行 34 if (count_char > 1) codeLine--; 35 //注释行不属于空行 36 else blankLine--; 37 break; 38 } 39 if (tag == 1) { 40 countC2++; 41 //在该行查找注释的结束符号 42 for (j = i; j < length; j++) { 43 if (b[j] == '*' && b[j + 1] == '/') { 44 //查找结束符号成功,该行为注释行 45 //注释行不属于代码行 46 if (count_char > 1) codeLine--; 47 //注释行不属于空行 48 else blankLine--; 49 //现查找注释行前半部分失败 50 tag = 0; 51 break; 52 } 53 } 54 //tag=0说明该行是完整的注释行,同行查找结束符号成功 55 if (tag == 0) break; 56 //否则同行查找结束符号失败,把tag置为1 57 else { 58 //注释行不属于代码行 59 if (count_char > 1) codeLine--; 60 //注释行不属于空行 61 else blankLine--; 62 break; 63 } 64 } 65 if (b[i] == '/' && b[i + 1] == '*' && tag == 0) { 66 countC2++; 67 tag = 1; 68 //第二种注释情况,读入的一行为注释行,同行查找结束符号 69 for (j = i + 2; j < length - 2; j++) { 70 if (b[j] == '*' && b[j + 1] == '/') { 71 //查找结束符号成功,该行为注释行 72 countC2++; 73 //注释行不属于代码行 74 if (count_char > 1) codeLine--; 75 //注释行不属于空行 76 else blankLine--; 77 //现查找注释行前半部分失败 78 tag = 0; 79 break; 80 } 81 } 82 //tag=0说明该行是完整的注释行,同行查找结束符号成功 83 if (tag == 0) break; 84 //否则同行查找结束符号失败,把tag置为1 85 else { 86 //注释行不属于代码行 87 if (count_char > 1) codeLine--; 88 //注释行不属于空行 89 else blankLine--; 90 break; 91 } 92 } 93 } 94 //字符数大于1为代码行,否则为空行 95 if (count_char > 1) codeLine++; 96 else blankLine++; 97 } 98 else break; 99 } while (1); 100 101 commentLine = countC1 + countC2; 102 sum = codeLine + blankLine + commentLine; 103 104 printf("代码行:%d\t", codeLine); 105 printf("空白行:%d\t", blankLine); 106 printf("注释行:%d\n", commentLine); 107 108 //返回注释行,作为单元测试的内容 109 return commentLine; 110 }
递归查找符合条件的文件
1 //递归查找符合条件的文件 2 int searchFile(char path[N],char mode[N],int tag) { 3 //文件句柄 4 intptr_t Handle1; 5 intptr_t Handle2; 6 //文件结构体 7 struct _finddata_t fileInfo1; 8 struct _finddata_t fileInfo2; 9 //特定文件查找路径、所有文件的查找路径、递归路径 10 char nowPath_file[N] = { 0 }; 11 char nowPath_folder[N] = { 0 }; 12 char nowPath_re[N] = { 0 }; 13 //查找文件和文件夹的通识符 14 char mode_N[N] = { "*.*" }; 15 int i, num = 0; 16 //标记文件夹 17 int mark = 0; 18 19 //基本路径 20 strcpy_s(nowPath_file, path); 21 strcpy_s(nowPath_folder, path); 22 strcpy_s(nowPath_re, path); 23 //拼接特定文件和所有文件的查找路径 24 strcat_s(nowPath_file, mode); 25 strcat_s(nowPath_folder, mode_N); 26 27 //根目录的文件句柄 28 Handle1 = _findfirst(nowPath_folder, &fileInfo1); 29 //.c类型文件的文件句柄 30 Handle2 = _findfirst(nowPath_file, &fileInfo2); 31 32 if ((Handle2 = _findfirst(nowPath_file, &fileInfo2)) == -1L) 33 printf("该目录中没有这种类型的文件。\n"); 34 else { 35 //查找文件后缀名. 36 for (i = 0; i < strlen(fileInfo2.name); i++) { 37 if (fileInfo2.name[i] == '.') { 38 mark = 1; 39 break; 40 } 41 } 42 //只打印文件名,不打印文件夹名 43 if (mark == 1 && strcmp(fileInfo2.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileInfo2.name, "..") != 0) { 44 printf("文件名:%s\n", fileInfo2.name); 45 //单元测试的参数 46 num = num + 1; 47 //实现指令的功能 48 if (tag == 1) { 49 countChar(nowPath_re, fileInfo2.name); 50 } 51 else if (tag == 2) { 52 countWord(nowPath_re, fileInfo2.name); 53 } 54 else if (tag == 3) { 55 countLine(nowPath_re, fileInfo2.name); 56 } 57 else if (tag == 4) { 58 countElse(nowPath_re, fileInfo2.name); 59 } 60 else; 61 mark = 0; 62 } 63 //_findnext是以_findfirst为开始接着查找以下符合H2(.c)的文件并打印 64 while (_findnext(Handle2, &fileInfo2) == 0) { 65 //查找文件后缀名. 66 for (i = 0; i < strlen(fileInfo2.name); i++) { 67 if (fileInfo2.name[i] == '.') { 68 //标记文件夹 69 mark = 1; 70 break; 71 } 72 } 73 //只打印文件名,不打印文件夹名 74 if (mark == 1 && strcmp(fileInfo2.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileInfo2.name, "..") != 0) { 75 printf("文件名:%s\n", fileInfo2.name); 76 //单元测试参数 77 num = num + 1; 78 //实现指令的功能 79 if (tag == 1) { 80 countChar(nowPath_re, fileInfo2.name); 81 } 82 else if (tag == 2) { 83 countWord(nowPath_re, fileInfo2.name); 84 } 85 else if (tag == 3) { 86 countLine(nowPath_re, fileInfo2.name); 87 } 88 else if (tag == 4) { 89 countElse(nowPath_re, fileInfo2.name); 90 } 91 else; 92 } 93 mark = 0; 94 } 95 _findclose(Handle2); 96 } 97 98 if ((Handle1 = _findfirst(nowPath_folder, &fileInfo1)) == -1L) 99 printf("该目录中没有文件。\n"); 100 else { 101 do { 102 if (fileInfo1.attrib & _A_SUBDIR) { 103 //判断是否为"."当前目录,".."上一层目录,查找子目录的文件 104 if ((strcmp(fileInfo1.name, ".") != 0) && (strcmp(fileInfo1.name, "..") != 0)) 105 { 106 printf("\n%s文件夹\n", fileInfo1.name); 107 //拼接子目录的路径,进行递归查找 108 strcat_s(nowPath_re, fileInfo1.name); 109 strcat_s(nowPath_re, "\\"); 110 //单元测试参数 111 num += searchFile(nowPath_re, mode, tag); 112 } 113 } 114 //循环该目录中所有文件 115 } while (_findnext(Handle1, &fileInfo1) == 0); 116 _findclose(Handle1); 117 } 118 //返回单元测试参数 119 return num; 120 }
拆分在cmd下输入的完整路径
1 //拆分在cmd下输入的完整路径 2 int splitPath(char path[N],char mode[N]) { 3 int i, j, k, len; 4 //1表示到符合输入要求的路径 5 int mark = 0; 6 len = strlen(path); 7 8 for (i = len; i >= 0; i--) { 9 if (path[i] == '\\') { 10 for (j = i; j < len; j++) { 11 //是文件/通配符的标志 12 if (path[j] == '.' || path[j] == '*') { 13 for (k = 0; i < len; i++, k++) { 14 mode[k] = path[i + 1]; 15 path[i + 1] = '\0'; 16 } 17 mark = 1; 18 } 19 if (mark == 1) break; 20 } 21 if (mark == 1) break; 22 } 23 } 24 if (mark == 1) return 1; 25 else printf("输入文件路径有误,请重新输入!\n例:E:\\test\\file.c\n"); 26 return -1; 27 }
主函数
1 //主函数 2 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { 3 //char path[N] = { "E:\\vs project\\wcTest\\" }; 4 //char mode[N] = { "*.*" }; 5 //char file[N] = { "test.c" }; 6 char path[N] = { "E:\\test" }; 7 char mode[N] = { 0 }; 8 //1是-c,2是-w,3是-l,4是-a 9 int tag = 0; 10 11 //统计 12 if (strcmp(argv[1], "-c") == 0) { 13 strcpy_s(path, argv[2]); 14 if (splitPath(path, mode) == 1) countChar(path, mode); 15 } 16 else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-w") == 0) { 17 strcpy_s(path, argv[2]); 18 if (splitPath(path, mode) == 1) countWord(path, mode); 19 } 20 else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-l") == 0) { 21 strcpy_s(path, argv[2]); 22 if (splitPath(path, mode) == 1) countLine(path, mode); 23 } 24 else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-a") == 0) { 25 strcpy_s(path, argv[2]); 26 if (splitPath(path, mode) == 1) countElse(path, mode); 27 } 28 //拓展功能 29 else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-s") == 0 && strcmp(argv[2], "-c") == 0) { 30 tag = 1; 31 strcpy_s(path, argv[3]); 32 if (splitPath(path, mode) == 1) searchFile(path, mode, tag); 33 } 34 else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-s") == 0 && strcmp(argv[2], "-w") == 0) { 35 tag = 2; 36 strcpy_s(path, argv[3]); 37 if (splitPath(path, mode) == 1) searchFile(path, mode, tag); 38 } 39 else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-s") == 0 && strcmp(argv[2], "-l") == 0) { 40 tag = 3; 41 strcpy_s(path, argv[3]); 42 if (splitPath(path, mode) == 1) searchFile(path, mode, tag); 43 } 44 else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-s") == 0 && strcmp(argv[2], "-a") == 0) { 45 tag = 4; 46 strcpy_s(path, argv[3]); 47 if (splitPath(path, mode) == 1) searchFile(path, mode, tag); 48 } 49 //批处理同类型文件 50 else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-s") == 0) { 51 strcpy_s(path, argv[2]); 52 if (splitPath(path, mode) == 1) searchFile(path, mode, tag); 53 } 54 else printf("指令有误,请重新输入!\n"); 55 56 system("pause"); 57 58 return 0; 59 }
六、测试运行
测试运行分为三个模块:单元测试、回归测试、运行测试
1. 单元测试
单元测试分为三部分测试:
TestMethod1:统计字符数、单词数、行数、其他行数的测试,通过返回值确定函数是否正确
TestMethod2:递归文件的测试,通过目录(包括子目录)中的文件个数确定函数是否正确
TestMethod3:拆分路径的测试,通过返回值确定函数是否正确
测试结果如下图:

小结:单元测试通过,编写的各个接口可用
2. 回归测试
回归测试分为五部分测试,如下所示。
空文件测试:
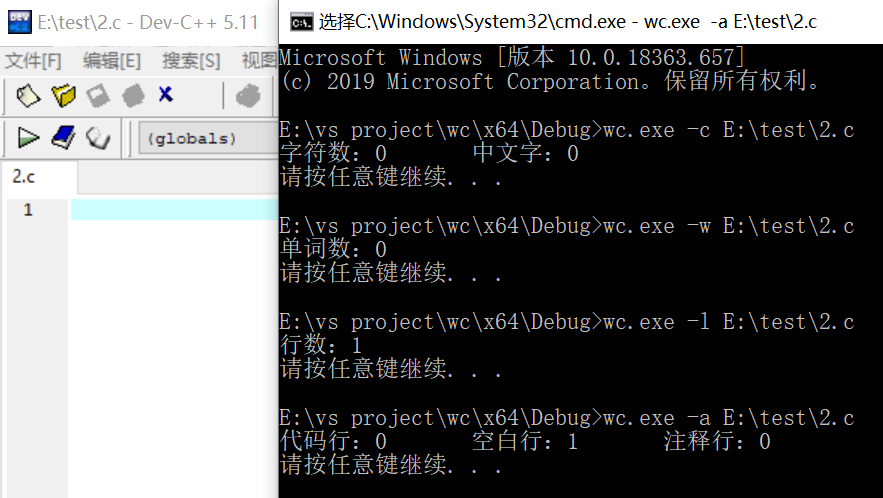
只有一个字符的文件测试:
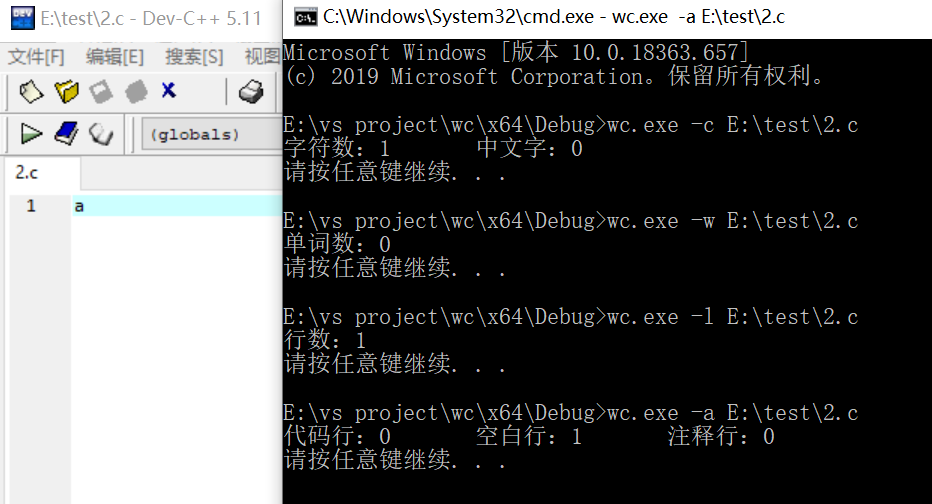
只有一个词的文件测试:
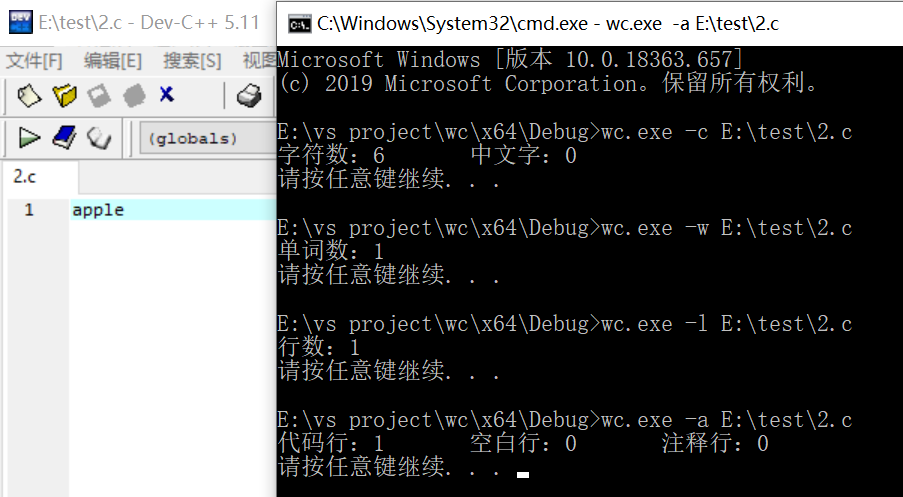
只有一行的文件测试:
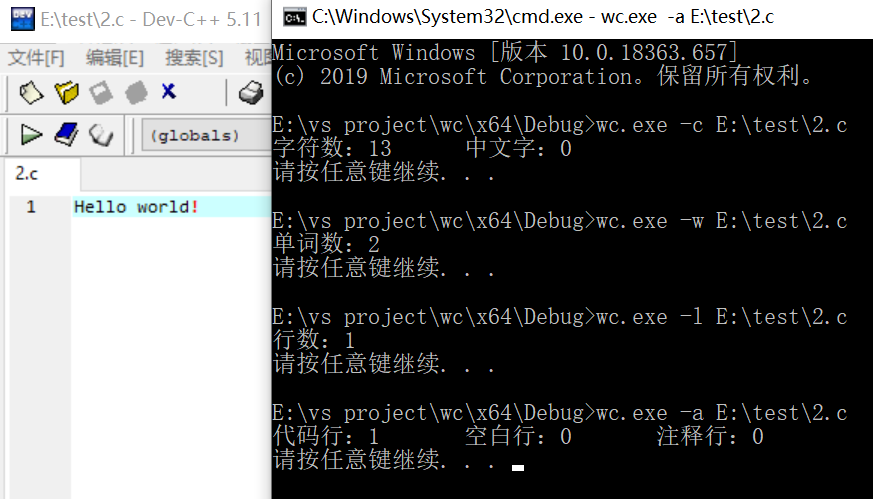
一个典型的源文件测试:
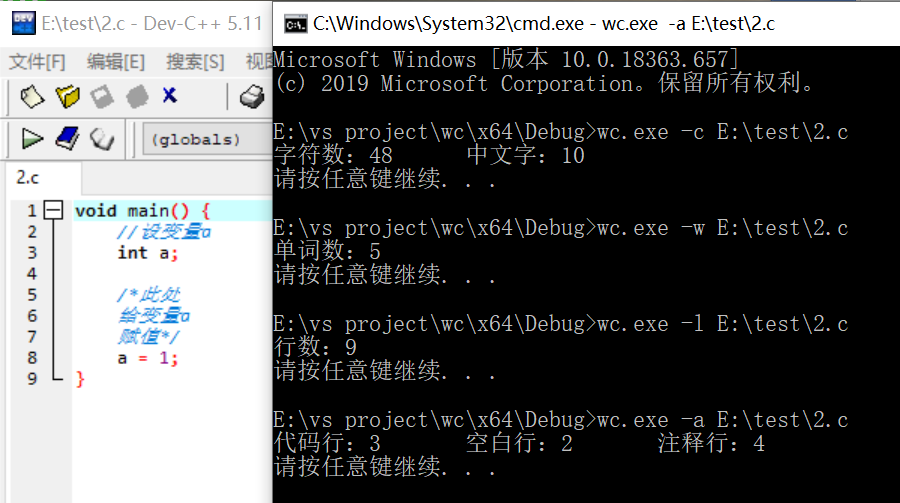
小结:回归测试通过
3. 运行测试
运行需求中的各条命令行,并展示运行测试结果如下。
基本功能
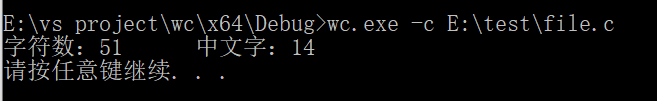
wc.exe –c E:\test\file.c
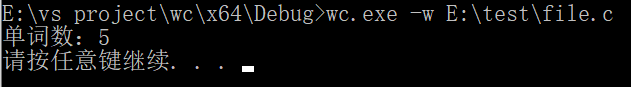
wc.exe –w E:\test\file.c
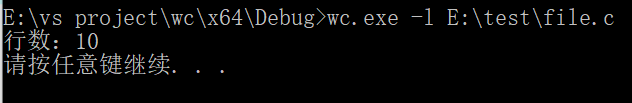
wc.exe –l E:\test\file.c
拓展功能
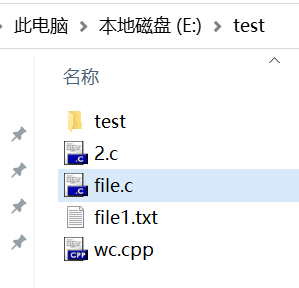
测试文件夹如图所示
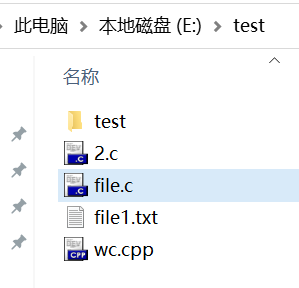
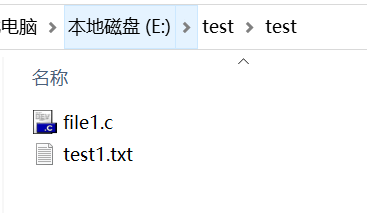
wc.exe –s E:\test\*.c
wc.exe –a E:\test\file.c
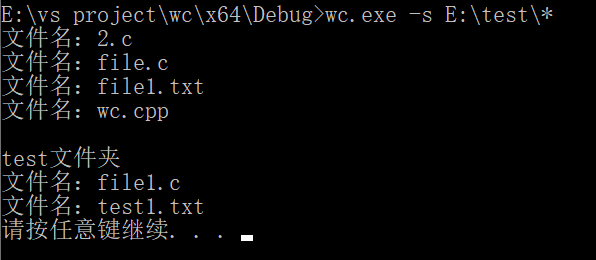
wc.exe –s E:\test\*
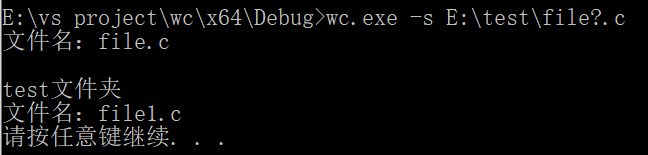
wc.exe –s E:\test\file?.c
高级功能
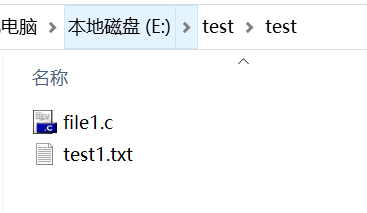
测试文件夹如图所示
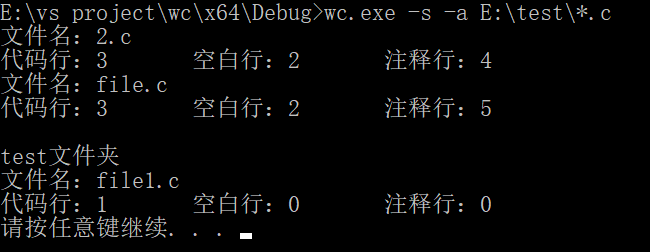
wc.exe –s –a E:\test\*.c
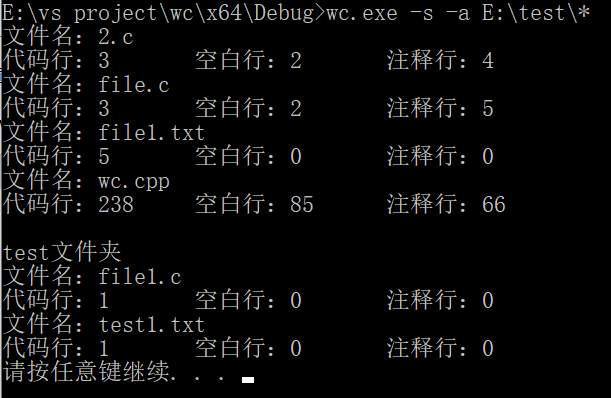
wc.exe –s –a E:\test\*
七、PSP表格
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
||
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
300 |
360 |
|
Development |
开发 |
||
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
10 |
30 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
10 |
20 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
10 |
10 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
5 |
5 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
30 |
40 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
180 |
240 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
60 |
50 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
120 |
90 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
||
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
60 |
40 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
20 |
20 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
15 |
|
合计 |
535 |
560 |
八、项目小结
1. 本次项目采用C语言完成,编码过程较为复杂,同时也学习到了C语言的一些补充知识。
2. 结合PSP表格可以认识到自己在预想和实际开发中的不足之处。
3. 要学习更多的语言来便捷地进行项目的开发
九、学习进度条
|
第N周 |
新增代码(行) |
累计代码(行) |
本周学习耗时(小时) |
累计学习耗时(小时) |
重要成长 |
|
2 |
451 |
451 |
9 |
9 |
了解了c语言头文件stdio.h中的其他函数 |