NIO主要包括Channel,Buffer,Selector三个核心元素组成。
Channel即通道,l和Buffer有好几种类型。下面是JAVA NIO中的一些主要Channel的实现:
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
正如你所看到的,这些通道涵盖了UDP 和 TCP 网络IO,以及文件IO。
Buffer有IntBuffer,CharBuffer,FloatBuffer。。。。。
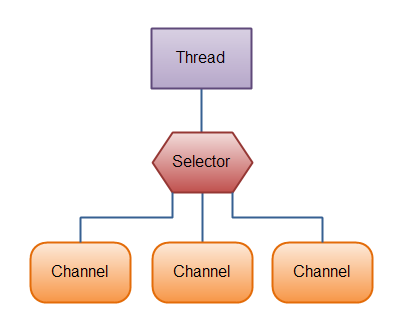
可以在Selector上注册通道。
Selector所在线程负责处理监听,待所关注的事件到达时,将事件分发给在Selector上注册的channel作异步处理,如下图所示。
Buffer的基本用法
使用Buffer读写数据一般遵循以下四个步骤:
- 调用channel的read()方法,将channel中的数据写入到Buffer中。
- 调用
flip()方法flip方法将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式。调用flip()方法会将position设回0,并将limit设置成之前position的值。
换句话说,position现在用于标记读的位置,limit表示之前写进了多少个byte、char等 —— 现在能读取多少个byte、char等。
public final Buffer flip() { limit = position; position = 0; mark = -1; return this; }
- 调用channel的write()方法,将Buffer中的数据写入channel中。
- 调用
clear()方法或者compact()方法
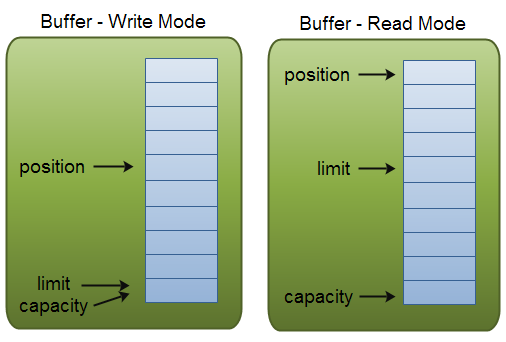
为了理解Buffer的工作原理,需要熟悉它的三个属性:
- capacity
- position
- limit
position和limit的含义取决于Buffer处在读模式还是写模式。不管Buffer处在什么模式,capacity的含义总是一样的。
这里有一个关于capacity,position和limit在读写模式中的说明,详细的解释在插图后面。
capacity
作为一个内存块,Buffer有一个固定的大小值,也叫“capacity”.你只能往里写capacity个byte、long,char等类型。一旦Buffer满了,需要将其清空(通过读数据或者清除数据)才能继续写数据往里写数据。
position
当你写数据到Buffer中时,position表示当前的位置。初始的position值为0.当一个byte、long等数据写到Buffer后, position会向前移动到下一个可插入数据的Buffer单元。position最大可为capacity – 1.
当读取数据时,也是从某个特定位置读。当将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式,position会被重置为0. 当从Buffer的position处读取数据时,position向前移动到下一个可读的位置。
limit
在写模式下,Buffer的limit表示你最多能往Buffer里写多少数据。 写模式下,limit等于Buffer的capacity。
当切换Buffer到读模式时, limit表示你最多能读到多少数据。因此,当切换Buffer到读模式时,limit会被设置成写模式下的position值。换句话说,你能读到之前写入的所有数据(limit被设置成已写数据的数量,这个值在写模式下就是position)
使用JAVA NIO编写一个客户端与服务端通信的例子。
Server
1 package com.nio; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.net.InetSocketAddress; 5 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 6 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; 7 import java.nio.channels.Selector; 8 import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; 9 import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; 10 import java.util.Iterator; 11 import java.util.Set; 12 13 public class Server { 14 private Selector selector; 15 private ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(100); 16 17 public void start() throws IOException { 18 ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open(); 19 ssc.configureBlocking(false); 20 ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8002)); 21 selector = Selector.open(); 22 ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); 23 while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { 24 selector.select(); 25 Set selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); 26 Iterator iterator = selectedKeys.iterator(); 27 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 28 SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) iterator.next(); 29 if (!key.isValid()) { 30 continue; 31 } 32 if (key.isAcceptable()) { 33 accept(key); 34 } else if (key.isReadable()) { 35 read(key); 36 } 37 } 38 iterator.remove(); 39 } 40 } 41 42 private void read(SelectionKey key) throws IOException { 43 SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); 44 this.readBuffer.clear(); 45 int readNum = 0; 46 try { 47 readNum = socketChannel.read(this.readBuffer); 48 } catch (IOException e) { 49 key.cancel(); 50 socketChannel.close(); 51 return; 52 } 53 if (readNum > 0) { 54 byte[] newBytes = new byte[readNum]; 55 System.arraycopy(readBuffer.array(), 0, newBytes, 0, readNum); 56 String message = new String(newBytes); 57 System.out.println(message); 58 message = "你好,已收到你发的消息:" + message; 59 readBuffer.flip(); 60 readBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes()); 61 socketChannel.write(readBuffer); 62 } 63 } 64 65 private void accept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException { 66 ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); 67 SocketChannel clientChanel = ssc.accept(); 68 clientChanel.configureBlocking(false); 69 clientChanel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); 70 System.out.println("a new client connected..."); 71 } 72 73 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 74 new Server().start(); 75 } 76 }
Client
1 package com.nio; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.net.InetSocketAddress; 5 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 6 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; 7 import java.nio.channels.Selector; 8 import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; 9 import java.util.Iterator; 10 import java.util.Scanner; 11 import java.util.Set; 12 13 public class Client { 14 private void start() throws IOException { 15 SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open(); 16 sc.configureBlocking(false); 17 sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8002)); 18 Selector selector = Selector.open(); 19 sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT ); 20 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 21 while (true) { 22 selector.select(); 23 Set selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); 24 Iterator iterator = selectedKeys.iterator(); 25 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 26 SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) iterator.next(); 27 if (key.isConnectable()) { 28 sc.finishConnect(); 29 sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); 30 System.out.println("server connected"); 31 break; 32 } else if (key.isWritable()) { 33 System.out.println("please input message"); 34 String message = scanner.nextLine(); 35 ByteBuffer writebufBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes()); 36 sc.write(writebufBuffer); 37 sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); 38 }else if(key.isReadable()){ 39 ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); 40 int readNum = sc.read(readBuffer); 41 byte[] newBytes = new byte[readNum]; 42 System.arraycopy(readBuffer.array(), 0, newBytes, 0, readNum); 43 String message = new String(newBytes); 44 System.out.println(message); 45 sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); 46 } 47 } 48 iterator.remove(); 49 } 50 } 51 52 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 53 new Client().start(); 54 } 55 }
Client端输入abc后,Server端会将收到的信息返回到Client端,打印"你好,已收到......"

Server端也会打印出Client端发送的消息。