一图甚千言,这张图真的是耽搁我太多时间了:

下面的tomcat架构设计代码分析,和这张图息息相关.
使用maven搭建本次的环境,贴出pom.xml完整内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>groupId</groupId> <artifactId>JavaWebDemo</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId> <version>2.5</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat-catalina</artifactId> <version>8.0.14</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> </project>
至此,环境已经准备就绪,就可以愉快看代码了.
tomcat的Server是由org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina来管理的,Catalina是tomcat的管理类可以通过反射加载查看代码:
Catalina类中有很多方法,他们具有不同的含义,其中
public void load() {... public void start() {... public void stop() {...
这些方法用于管理tomcat的生命周期,其中load方法:
load方法重要前半部分:
public void load() { long t1 = System.nanoTime(); this.initDirs(); this.initNaming(); Digester digester = this.createStartDigester(); InputSource inputSource = null; InputStream inputStream = null; File file = null; try { file = this.configFile(); inputStream = new FileInputStream(file); inputSource = new InputSource(file.toURI().toURL().toString());
load方法重要后半部分:
this.getServer().setCatalina(this); this.getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile()); this.getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile()); this.initStreams(); try { this.getServer().init();
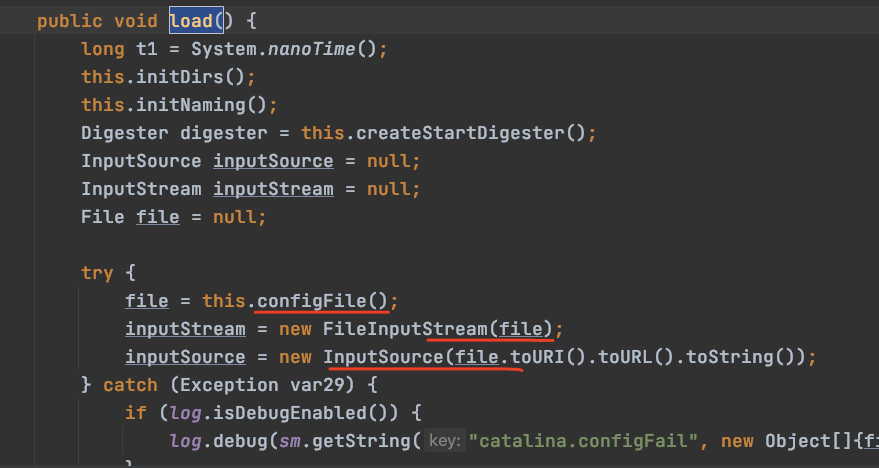

其中load方法是根据创建conf/server.xml文件来创建Server,并调用Server的init方法进行初始化
start和stop方法暂定,下面会讲到.这三个方法都会按照容器结构逐层调用相应的方法.
不过tomcat的入口main方法并不在Catalina类里,而是在org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap类中,这样做的好处是tomcat管理类和入口类实现分离
Bootstrap是tomcat的入口,正常情况下启动tomcat就是调用Bootstrap类的main方法,代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) { if (daemon == null) {
//新建一个bootstrap Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); try {
//初始化 bootstrap.init(); } catch (Throwable var3) { handleThrowable(var3); var3.printStackTrace(); return; } //赋值给daemon daemon = bootstrap; } else { Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(daemon.catalinaLoader); } try { String command = "start"; if (args.length > 0) { command = args[args.length - 1]; } if (command.equals("startd")) { args[args.length - 1] = "start"; daemon.load(args); daemon.start(); } else if (command.equals("stopd")) { args[args.length - 1] = "stop"; daemon.stop(); } else if (command.equals("start")) { daemon.setAwait(true); daemon.load(args); daemon.start(); } else if (command.equals("stop")) { daemon.stopServer(args); } else if (command.equals("configtest")) { daemon.load(args); if (null == daemon.getServer()) { System.exit(1); } System.exit(0); } else { log.warn("Bootstrap: command "" + command + "" does not exist."); } } catch (Throwable var4) { Throwable t = var4; if (var4 instanceof InvocationTargetException && var4.getCause() != null) { t = var4.getCause(); } handleThrowable(t); t.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1); } }
Bootstrap类中的main方法只干两件事情,(1):新建一个bootstrap,并执行init方法初始化,初始化后赋值给daemon,然后处理main方法传入进来的命令,来判断执行对应的方法,比如传入start,执行start方法,如果传入错误的命令,直接告警command不存在.
在main方法中,daemon调用了好几个方法,当main方法传入的命令是start的时候,会自动调用setAwait(true),load()和start()方法:
} else if (command.equals("start")) { daemon.setAwait(true); daemon.load(args); daemon.start();
跟进start方法:
org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap#182:
public void start() throws Exception { if (this.catalinaDaemon == null) { this.init(); } Method method = this.catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class[])null); method.invoke(this.catalinaDaemon, (Object[])null); }
首先会判断你的catalinaDaemon是否为空,不为空,再用反射调用start方法,然后实例化类.
所以上面的daemon.start相当于:(Catalina)catalinaDaemon.start()
同理,其他的方法如setAwait(true)和load方法也是通过反射调用,这里不在展示代码.
从前面的分析,我们知道tomcat入口类会调用tomcat管理类的start,load,setAwait方法:
tomcat入口类Bootstarp和tomcat管理类Catalina是相辅相成的:
Catalina的启动主要是调用setAwait,load和start方法来完成的,setAwait方法用于设置Server启动完成后是否进入等待状态的标志,如果为true就进入,否则讲究不进入
load方法会自动加载server.xml配置文件,创建并初始化Server [getServer.init()]
start方法用于启动服务器
下面一个个看下这些方法:
首先来看setAwait方法:
org.apache.startup.Catalina:
public void setAwait(boolean b) { this.await = b; }

这个方法就是设置await的属性值,await属性会在start方法中的服务器启动完成之后,使用它来判断是否进入等待状态:
查看load方法,文章开头已经讲了load方法,load方法中会根据conf/server.xml创建Server对象,并调用server的init方法来初始化
Catalina的start方法查看:
public void start() { if (this.getServer() == null) { this.load(); } if (this.getServer() == null) { log.fatal("Cannot start server. Server instance is not configured."); } else { long t1 = System.nanoTime(); try {
//调用Server的start方法启动服务器 this.getServer().start(); } catch (LifecycleException var7) { log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.serverStartFail"), var7); try { this.getServer().destroy(); } catch (LifecycleException var6) { log.debug("destroy() failed for failed Server ", var6); } return; } long t2 = System.nanoTime(); if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("Server startup in " + (t2 - t1) / 1000000L + " ms"); } if (this.useShutdownHook) { if (this.shutdownHook == null) { this.shutdownHook = new Catalina.CatalinaShutdownHook(); } Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook); LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager(); if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) { ((ClassLoaderLogManager)logManager).setUseShutdownHook(false); } } //判断等待状态 if (this.await) { this.await(); this.stop(); } } }
start方法主要调用了server的start方法启动服务器,并根据等待状态判断是否让程序进行等待状态
这里首先判断getServer是否存在,如果不存在就启动server的load方法进行初始化Server.然后调用Server的start方法来启动服务器,注册判断await属性.在tomcat入口类Bootstrap类中,设置await为true,所以需要进入等待状态,跟进逻辑判断的await方法,静态调试进入:
org.apache.catalina.core.StandServer:
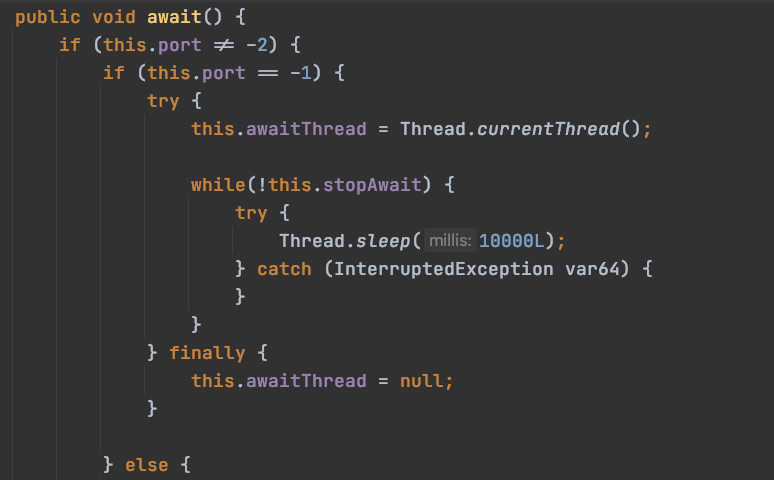
发现await方法内部会执行一个while循环,这样程序就会停到awit方法,当await方法里的while循环退出时,就会执行stop方法,从而关闭服务器.
通过上面的学习,我们简单梳理了tomcat的入口类Bootstrap类和tomcat的管理类Catalina
继续学习往下突进:
Server接口的默认实现是org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer,可通过反射加载进入查看代码:
public final class StandardServer extends LifecycleMBeanBase implements Server {
StandardServer类继承自LifecycleMBeanBase类,跟进LifecycleMBeanBase类:
org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleMBeanBase:
LifecycleMBeanBase类又继承自LifecycleBase:
org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase:

查看LifecycleBase类的init和start方法:
org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase:
public final synchronized void init() throws LifecycleException { if (!this.state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) { this.invalidTransition("before_init"); } this.setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZING, (Object)null, false); try { this.initInternal(); } catch (Throwable var2) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(var2); this.setStateInternal(LifecycleState.FAILED, (Object)null, false); throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.initFail", new Object[]{this.toString()}), var2); } this.setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED, (Object)null, false); }
发现init方法会调用initInternal方法:

initInternal是一个模块方法,需要其子类去实现此方法.
LifecycleBase类start方法:
截取部分:
public final synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException { if (!LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(this.state) && !LifecycleState.STARTING.equals(this.state) && !LifecycleState.STARTED.equals(this.state)) { if (this.state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) { this.init(); } else if (this.state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) { this.stop(); } else if (!this.state.equals(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED) && !this.state.equals(LifecycleState.STOPPED)) { this.invalidTransition("before_start"); } this.setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP, (Object)null, false); try { this.startInternal(); } catch (Throwable var2) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(var2); this.setStateInternal(LifecycleState.FAILED, (Object)null, false); throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.startFail", new Object[]{this.toString()}), var2); }
会调用this.startInternal();方法:

startInternal方法也是模块方法,需要其子类去具体实现方法:
我们的StandardServer类和LifecycleMBeanBase类都是继承自LifecycleBase,都是LifecycleBase的子类,都可以去实现方法的.
回到StandardServer类,查看initInternal方法实现:
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer:
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.initInternal(); this.onameStringCache = this.register(new StringCache(), "type=StringCache"); MBeanFactory factory = new MBeanFactory(); factory.setContainer(this); this.onameMBeanFactory = this.register(factory, "type=MBeanFactory"); this.globalNamingResources.init(); if (this.getCatalina() != null) {
..................
查看startInternal方法具体实现:
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { this.fireLifecycleEvent("configure_start", (Object)null); this.setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); this.globalNamingResources.start(); synchronized(this.servicesLock) { for(int i = 0; i < this.services.length; ++i) { this.services[i].start(); } } }
除了startInternal和initInternal方法,StandardServer中还实现了await方法,Catalina中就是调用它让服务器进入等待状态的:
public void await() { if (this.port != -2) { if (this.port == -1) { try { this.awaitThread = Thread.currentThread(); while(!this.stopAwait) { try { Thread.sleep(10000L); } catch (InterruptedException var64) { } } } finally { this.awaitThread = null; } } else { try { this.awaitSocket = new ServerSocket(this.port, 1, InetAddress.getByName(this.address)); } catch (IOException var67) { log.error("StandardServer.await: create[" + this.address + ":" + this.port + "]: ", var67); return; } boolean var32 = false; ServerSocket serverSocket; try { var32 = true; this.awaitThread = Thread.currentThread(); while(true) { if (this.stopAwait) { var32 = false; break; } serverSocket = this.awaitSocket; if (serverSocket == null) { var32 = false; break; } Socket socket = null; StringBuilder command = new StringBuilder(); label603: { label602: { try { label618: { long acceptStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); InputStream stream; try { socket = serverSocket.accept(); socket.setSoTimeout(10000); stream = socket.getInputStream(); } catch (SocketTimeoutException var69) { log.warn(sm.getString("standardServer.accept.timeout", new Object[]{System.currentTimeMillis() - acceptStartTime}), var69); continue; } catch (AccessControlException var70) { log.warn("StandardServer.accept security exception: " + var70.getMessage(), var70); continue; } catch (IOException var71) { if (this.stopAwait) { break label602; } log.error("StandardServer.await: accept: ", var71); break label618; } int expected; for(expected = 1024; expected < this.shutdown.length(); expected += this.random.nextInt() % 1024) { if (this.random == null) { this.random = new Random(); } } while(true) { if (expected <= 0) { break label603; } boolean var8 = true; int ch; try { ch = stream.read(); } catch (IOException var66) { log.warn("StandardServer.await: read: ", var66); ch = -1; } if (ch < 32) { break label603; } command.append((char)ch); --expected; } } } finally { try { if (socket != null) { socket.close(); } } catch (IOException var63) { } } var32 = false; break; } var32 = false; break; } boolean match = command.toString().equals(this.shutdown); if (match) { log.info(sm.getString("standardServer.shutdownViaPort")); var32 = false; break; } log.warn("StandardServer.await: Invalid command '" + command.toString() + "' received"); } } finally { if (var32) { ServerSocket serverSocket = this.awaitSocket; this.awaitThread = null; this.awaitSocket = null; if (serverSocket != null) { try { serverSocket.close(); } catch (IOException var62) { } } } } serverSocket = this.awaitSocket; this.awaitThread = null; this.awaitSocket = null; if (serverSocket != null) { try { serverSocket.close(); } catch (IOException var65) { } } } } }
StandardServer类中的await实现代码很长,他大概率的处理逻辑是这样的:
首先判断port端口号,port=多少就进入哪个逻辑判断:
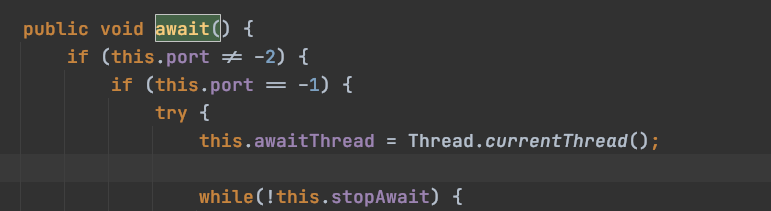
port为-1就进入一个while循环:

代码中没有break语句,只有在调用stop的时候,当stopAwait为true,才会退出循环
当port为其他值得时候,走else语句:

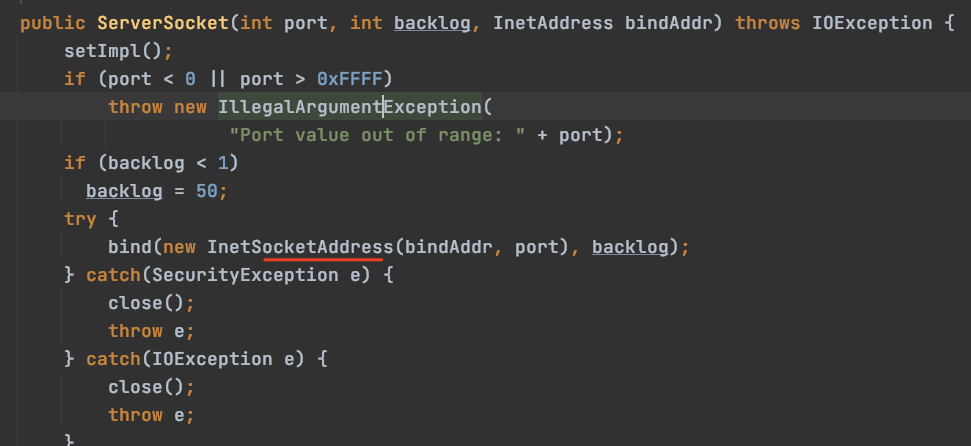
创建ServerSocket对象,跟进代码,发现是个绑定操作,绑定地址和端口:
往下看代码,等待接收消息,它会把等待接收消息的数据存储到StringBuilder command中:
StringBuilder command = new StringBuilder(); label603: { label602: { try { label618: { long acceptStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); InputStream stream; try { socket = serverSocket.accept(); socket.setSoTimeout(10000); stream = socket.getInputStream(); } catch (SocketTimeoutException var69) { log.warn(sm.getString("standardServer.accept.timeout", new Object[]{System.currentTimeMillis() - acceptStartTime}), var69); continue; } catch (AccessControlException var70) { log.warn("StandardServer.accept security exception: " + var70.getMessage(), var70); continue; } catch (IOException var71) { if (this.stopAwait) { break label602; } log.error("StandardServer.await: accept: ", var71); break label618; } int expected; for(expected = 1024; expected < this.shutdown.length(); expected += this.random.nextInt() % 1024) { if (this.random == null) { this.random = new Random(); } } while(true) { if (expected <= 0) { break label603; } boolean var8 = true; int ch; try { ch = stream.read(); } catch (IOException var66) { log.warn("StandardServer.await: read: ", var66); ch = -1; } if (ch < 32) { break label603; } command.append((char)ch); --expected; }
继续往下看代码,就是把监听接收到的命令和shutdown匹配,如果匹配上,就break退出循环:
//检查在指定端口接收到的命令是否和shutdown匹配 boolean match = command.toString().equals(this.shutdown); if (match) { log.info(sm.getString("standardServer.shutdownViaPort")); var32 = false; break; }
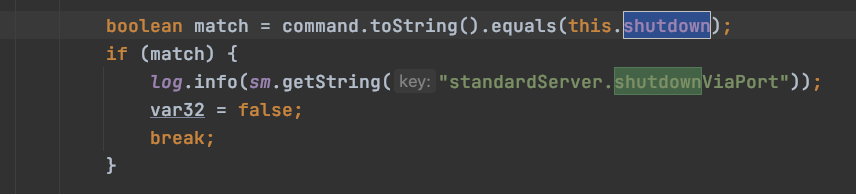
这里的shutdown和port对应的是conf/server.xml文件中的:

这时程会在8005端口监听shutdown命令,如果接收到就关闭tomcat. 对接收到的数据,tomcat也是有要求的:
int ch; try { ch = stream.read(); } catch (IOException var66) { log.warn("StandardServer.await: read: ", var66); ch = -1; } if (ch < 32) { break label603; }
接收到的数据ascii<32,会自动截断掉摒弃.
现在已经讲完了Server的启动过程,以及上面讲的tomcat管理类和tomcat入口类,继续冲
Service的启动过程:
Service的默认实现类是:org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService

StandardService和StandardServer一样,都继承自LifecycleMBeanBase,而LifecycleMBeanBase继承自LifecycleBase:
所以StandardService也是会调用initInternal和startInternal方法:
来看下这两个方法:
先看initInternal方法:
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.initInternal(); if (this.container != null) { this.container.init(); } Executor[] arr$ = this.findExecutors(); int len$ = arr$.length; int len$; for(len$ = 0; len$ < len$; ++len$) { Executor executor = arr$[len$]; if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) { ((JmxEnabled)executor).setDomain(this.getDomain()); } executor.init(); } this.mapperListener.init(); synchronized(this.connectorsLock) { Connector[] arr$ = this.connectors; len$ = arr$.length; for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) { Connector connector = arr$[i$]; try { connector.init(); } catch (Exception var9) { String message = sm.getString("standardService.connector.initFailed", new Object[]{connector}); log.error(message, var9); if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE")) { throw new LifecycleException(message); } } } } }
可以发现StandardService类的initInternl方法先调用父类型的initInternl方法,然后开始调用this.container.init(); executor.init();connector.init();
完整代码:
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", new Object[]{this.name})); } this.setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); if (this.container != null) { synchronized(this.container) { this.container.start(); } } synchronized(this.executors) { Iterator i$ = this.executors.iterator(); while(true) { if (!i$.hasNext()) { break; } Executor executor = (Executor)i$.next(); executor.start(); } } this.mapperListener.start(); synchronized(this.connectorsLock) { Connector[] arr$ = this.connectors; int len$ = arr$.length; for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) { Connector connector = arr$[i$]; try { if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) { connector.start(); } } catch (Exception var8) { log.error(sm.getString("standardService.connector.startFailed", new Object[]{connector}), var8); } } } }
可以发现StandardService类的startInternl方法,主要调用了: this.container.start(); executor.start();this.mapperListener.start();connector.start();
mapperListener是Mapper的监听器,可以监听container容器的变化,executors是用在connectors中管理线程的线程池
在server.xml配置文件中有参考用法,不过默认是注释掉的:
内容如下:
<Service name="Catalina"> <!--The connectors can use a shared executor, you can define one or more named thread pools--> <!-- <Executor name="tomcatThreadPool" namePrefix="catalina-exec-" maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="4"/> -->
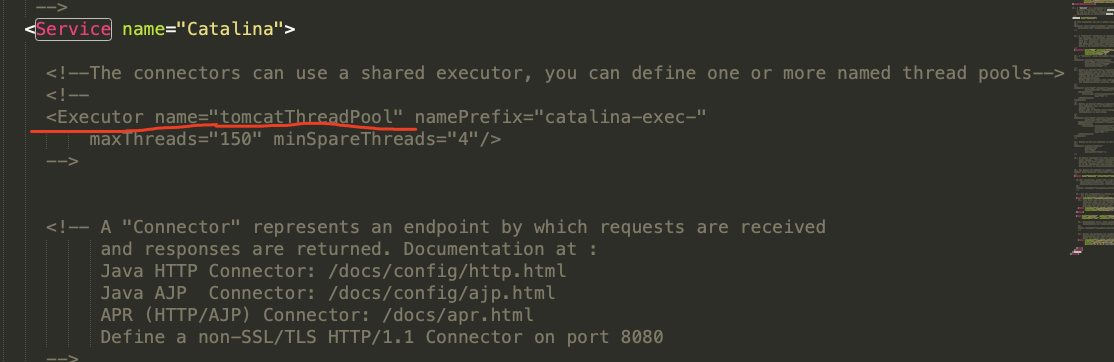
这样Connector就配置了一个tomcatThreadPool线程池,最多可以同时启动150个线程,最少4个可用线程
整个tomcat的启动流程如下:
tomcat 入口类:Bootstrap---->tomcat 管理类:Calalina----->Sever实现类:StandardServer ----->Service实现类:StandardSercice ----->MapperListencer----->Executor----->Connector