在第(四)节获取节点高度函数getHeight()函数的基础上,增添并测试更新节点高度函数和更新祖辈节点高度函数:updateHight()、updateAboveHei()。在上节中,每插入一个新节点,根结点以及新节点的其它祖辈节点的高度不增加,如今这已成为过去。在插入节点函数insertAsLC()、insertAsRC()函数中,分别添加updateAboveHei(),则每次插入新的节点,都会更新祖辈的节点高度。
节点类的代码,如第四节,不再增加。
树的定义代码如下:
#ifndef BINTREE #define BINTREE #include<binnode.h> template<typename T> class BinTree { public: int _size; BinNodePosi(T) _root;//根结点指针 int getHight(BinNodePosi(T) x) { int l_hight,r_hight; if(x==NULL) return -1; else if(!hasChild(*x)) { return 0; } else { l_hight = getHight(x->lc)+1; r_hight = getHight(x->rc)+1; } return l_hight>r_hight?l_hight:r_hight; } int max(int a,int b) { if(a>b) return a; else return b; } ///更新节点高度函数updateHeight() /// 以及更新祖辈节点高度函数updateAboveHeight() virtual int updateHeight(BinNodePosi(T) x)//更新节点x的高度 { return x->height=1+max(getHight(x->lc),getHight(x->rc)); } void updateAboveHeight(BinNode<T> *x)//跟新节点x及其祖先的高度 { while(x) { updateHeight(x);//先更新当前节点高度 x=x->parent;//然后更新祖辈节点高度 } } public: BinTree():_size(0),_root(NULL){} int size()const{return _size;}//获取树的规模,即共有多少个节点 bool empty(){return !_root;}//判断是否为空树 BinNodePosi(T) root()const{return _root;}//获取根结点指针 BinNodePosi(T) insertAsRoot(T const&e) { _size=1; return _root=new BinNode<T>(e); } BinNodePosi(T) insertAsLC(BinNodePosi(T) x,T const&e) { _size++;x->insertAsLC(e); // x->height =getHight(x);//将该语句替换为updateAboveHeight(x); updateAboveHeight(x); return x->lc; } BinNodePosi(T) insertAsRC(BinNodePosi(T) x,T const&e) { _size++;x->insertAsRC(e); updateAboveHeight(x); return x->rc; } }; #endif // BINTREE
在测试程序中的树形结构如图所示
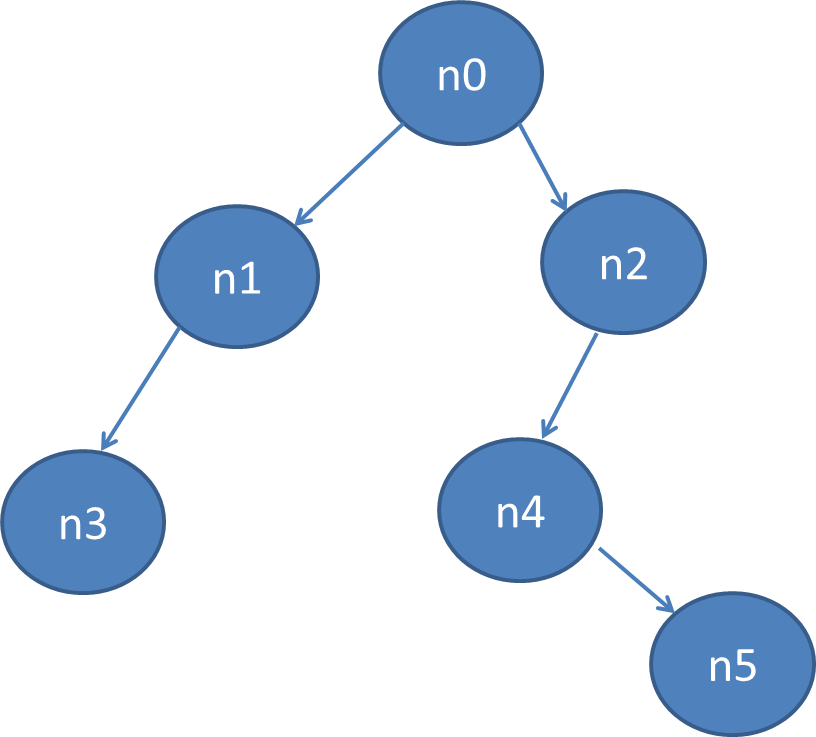
测试代码与第四节一样:
int main() { BinNode<string>* n[6];//数组指针 BinTree<string> bt; n[0]= bt.insertAsRoot("n0"); n[1]= bt.insertAsLC(n[0],"n1"); n[2]= bt.insertAsRC(n[0],"n2"); n[3]= bt.insertAsLC(n[1],"n3"); n[4]=bt.insertAsLC(n[2],"n4"); n[5]=bt.insertAsLC(n[4],"n5"); //测试根结点的高度 cout<<bt.getHight(n[2])<<endl; // bt.updateHeight(bt._root); cout<<bt._root->height<<endl; return 0; }
我们可以看到,随着新节点的插入,根结点的高度随之而增加。