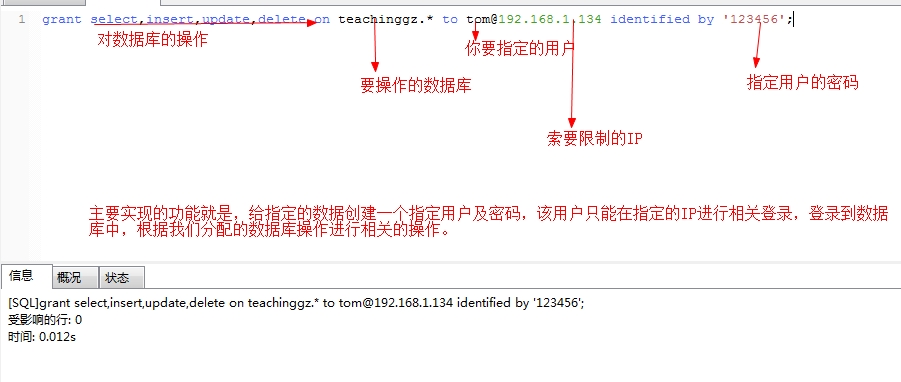
创建用户:
格式:grant select on 数据库.* to 用户名@登录主机 identified by '密码'
举例:
例 1:增加一个用户 test1 密码为 abc,让他可以在任何主机上登录,并对所有数据库有
查询、插入、修改、删除的权限。首先用以 root 用户连入 MySQL,然后键入以下命令:
grant select,insert,update,delete on *.* to root@localhost identified by 'mysql';
或者
grant all privileges on *.* to root@localhost identified by 'mysql';
然后刷新权限设置。
flush privileges;
例 2:如果你不想 root 有密码操作数据库“mydb”里的数据表,可以再打一个命令将密码消掉。
grant select,insert,update,delete on mydb.* to root@localhost identified by '';
#注意:此处的"localhost",是指该用户只能在本地登录,不能在另外一台机器上远程登录。
如果想远程登录的话,将"localhost"改为"%",
表示在任何一台电脑上都可以登录。也可以指定某台机器可以远程登录。
2、修改密码
用UPDATE直接编辑user表
mysql -u root
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> UPDATE user SET Password = PASSWORD('newpass') WHERE user = 'root';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
在丢失root密码的时候,可以这样
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables&
mysql -u root mysql
mysql> UPDATE user SET password=PASSWORD("new password") WHERE user='root';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
3、修改登录的ip,让那个ip可以登录
数据库可以远程连接或者说用IP地址可以访问
可能是你的帐号不允许从远程登陆,只能在localhost。 这个时候只要在localhost的那台电脑,登入mysql后, 更改 "mysql" 数据库里的 "user" 表里的 "host" 项, 从"localhost"改称"%" mysql -u root -p mysql>use mysql;
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'192.168.1.100' IDENTIFIED BY 'password' WITH GRANT OPTION;
mysql> flush privileges; #刷新数据库(不要然,重启才可以看到效果)
mysql> select host, user from user; #查看
4. 删除用户
@>mysql -u root -p
@>密码
mysql>Delete FROM user Where User='test' and Host='localhost';
mysql>flush privileges;
mysql>drop database testDB; //删除用户的数据库
删除账户及权限:>drop user 用户名@'%';
>drop user 用户名@ localhost;
5. 列出所有数据库
mysql>show database;
6. 切换数据库
mysql>use '数据库名';
7. 列出所有表
mysql>show tables;
8. 显示数据表结构
mysql>describe 表名;
9. 删除数据库和数据表
mysql>drop database 数据库名;
mysql>drop table 数据表名;
10.表操作
备注:操作之前使用“use <数据库名>”应连接某个数据库。
建表
命令:create table <表名> (<字段名 1> <类型 1> [,..<字段名 n> <类型 n>]);
例子:
mysql> create table MyClass(
> id int(4) not null primary key auto_increment,
> name char(20) not null,
> sex int(4) not null default '0',
> degree double(16,2));
获取表结构
命令: desc 表名,或者show columns from 表名
例子:
mysql> describe MyClass
mysql> desc MyClass;
mysql> show columns from MyClass;
删除表
命令:drop table <表名>
例如:删除表名为 MyClass 的表
mysql> drop table MyClass;
插入数据
命令:insert into <表名> [( <字段名 1>[,..<字段名 n > ])] values ( 值 1 )[, ( 值 n )]
例子:
mysql> insert into MyClass values(1,'Tom',96.45),(2,'Joan',82.99), (2,'Wang', 96.59);
查询表中的数据
查询所有行
mysql> select * from MyClass;
查询前几行数据
例如:查看表 MyClass 中前 2 行数据
mysql> select * from MyClass order by id limit 0,2;
或者
mysql> select * from MyClass limit 0,2;
删除表中数据
命令:delete from 表名 where 表达式
例如:删除表 MyClass 中编号为 1 的记录
mysql> delete from MyClass where id=1;
修改表中数据
命令:update 表名 set 字段=新值,... where 条件
mysql> update MyClass set name='Mary' where id=1;
在表中增加字段
命令:alter table 表名 add 字段 类型 其他;
例如:在表 MyClass 中添加了一个字段 passtest,类型为 int(4),默认值为 0
mysql> alter table MyClass add passtest int(4) default '0'
更改表名
命令:rename table 原表名 to 新表名;
例如:在表 MyClass 名字更改为 YouClass
mysql> rename table MyClass to YouClass;
更新字段内容
命令:update 表名 set 字段名 = 新内容
update 表名 set 字段名 = replace(字段名, '旧内容', '新内容');
例如:文章前面加入 4 个空格
update article set content=concat(' ', content);
原文https://www.cnblogs.com/lemon-flm/p/7597879.html
