CODE: https://github.com/pxjw/Principles-of-Compiler/tree/master/consDFA
原题:
1、自己定义一个简单语言或者一个右线性正规文法
示例如(仅供参考) G[S]:S→aU|bV U→bV|aQ
V→aU|bQ Q→aQ|bQ|e
2、构造其有穷确定自动机,如
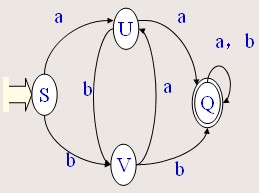
3、利用有穷确定自动机M=(K,Σ,f,
S,Z)行为模拟程序算法,来对于任意给定的串,若属于该语言时,该过程经有限次计算后就会停止并回答“是”,若不属于,要么能停止并回答“不是”
K:=S; c:=getchar; while c<>eof do {K:=f(K,c); c:=getchar; }; if K is in Z then return (‘yes’) else return (‘no’)
开始编程!
1.状态转换式构造类:
current——当前状态
next——下一状态
class TransTile { public: char current; char next; char input; TransTile(char C,char I,char Ne){ current = C; next = Ne; input = I; } };
2.DFA的构造类
此处包括DFA的数据集,字母表,以及过程P的定义。
包括了初始化,遍历转换,以及最终的字符串识别。
class DFA { public: //构造状态集各个元素 string States; char startStates; string finalStates; string Alphabets; vector <TransTile> Tile; DFA(){ init(); } void init() { cout << "输入有限状态集S:" << endl; cin >> States; cout << "输入字符集A:" << endl; cin >> Alphabets; cout << "输入状态转换式(格式为:状态-输入字符-下一状态,输入#结束):" << endl; cout << "例如:1a1 1a0 2a1 #" << endl; int h = 0; //while (cin>>input){ // TransTile transval(input[0], input[1], input[2]); // Tile.push_back(transval); //} while(true){ char input[4]; cin>>input; if(strcmp(input,"#")==0) break; TransTile transval(input[0],input[1],input[2]); Tile.push_back(transval); } cout << "输入初态:" << endl; cin >> startStates; cout << "输入终态:" << endl; cin >> finalStates; } //遍历转换表 char move(char P,char I){ for (int i = 0; i < Tile.size(); i++){ if (Tile[i].current == P&&Tile[i].input == I){ return Tile[i].next; } } return 'E'; } //识别字符串函数 void recognition(){ string str; cout << "输入需要识别的字符串:" << endl; cin >> str; int i = 0; char current = startStates; while (i < str.length()){ current = move(current, str[i]); if (current == 'E'){ break; } i++; } if (finalStates.find(current) != finalStates.npos){ cout << "该自动机识别该字符串!" << endl; } else { cout << "该自动机不能识别该字符串!" << endl; } } };
3.测试
Main函数
int main(){ DFA dfa; bool tag; while(1){ cout<<"你想要继续吗?是请输入1,否输入0:"<<endl; cin>>tag; if(tag){ dfa.recognition(); }else break; } return 0; }