适配器模式
将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口,使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类能一起工作。
适配器模式分为类结构型模式和对象结构型模式两种,前者类之间的耦合度比后者高,且要求程序员了解现有组件库中的相关组件的内部结构,所以应用相对较少些。
该模式的主要优点如下。
- 客户端通过适配器可以透明地调用目标接口。
- 复用了现存的类,程序员不需要修改原有代码而重用现有的适配者类。
- 将目标类和适配者类解耦,解决了目标类和适配者类接口不一致的问题。
- 在很多业务场景中符合开闭原则。
其缺点是:
- 适配器编写过程需要结合业务场景全面考虑,可能会增加系统的复杂性。
- 增加代码阅读难度,降低代码可读性,过多使用适配器会使系统代码变得凌乱。
模式的实现
适配器模式(Adapter)包含以下主要角色。
- 目标(Target)接口:当前系统业务所期待的接口,它可以是抽象类或接口。
- 适配者(Adaptee)类:它是被访问和适配的现存组件库中的组件接口。
- 适配器(Adapter)类:它是一个转换器,通过继承或引用适配者的对象,把适配者接口转换成目标接口,让客户按目标接口的格式访问适配者。
类适配器模式的结构图如图:
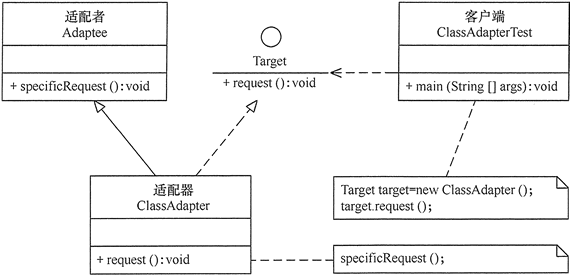
对象适配器模式的结构图如图:
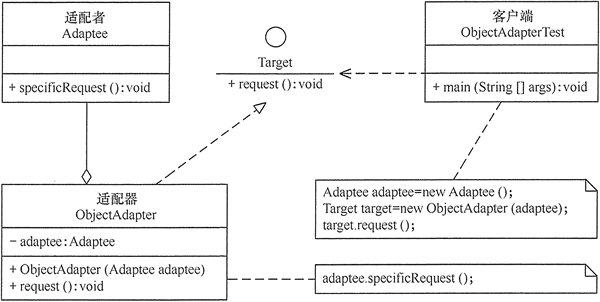
模式的实现
(1) 类适配器模式的代码如下。
// 目标接口
public interface Target {
void request();
}
// 适配者接口
public class Adaptee {
public void specificRequest(){
System.out.println("适配者中的业务代码被调用!");
}
}
// 类适配器
public class ClassAdapter extends Adaptee implements Target{
@Override
public void request() {
specificRequest();
}
}
// 客户端代码
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("类适配器模式测试");
Target target = new ClassAdapter();
target.request();
}
}
程序的运行结果如下:
类适配器模式测试
适配者中的业务代码被调用!
(2)对象适配器模式的代码如下。
// 目标接口
public interface Target {
public void request();
}
// 适配者接口
public class Adaptee {
public void specificRequest() {
System.out.println("适配者中的业务代码被调用!");
}
}
// 对象适配器类
public class ObjectAdapter extends Adaptee implements Target{
private Adaptee adaptee;
public ObjectAdapter(Adaptee adaptee) {
this.adaptee = adaptee;
}
@Override
public void request() {
specificRequest();
}
}
// 客户端代码
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("对象适配器模式测试:");
Adaptee adaptee = new Adaptee();
Target target = new ObjectAdapter(adaptee);
target.request();
}
}
程序的运行结果如下:
对象适配器模式测试:
适配者中的业务代码被调用!
双向适配器
适配器模式(Adapter)通常适用于以下场景。
- 以前开发的系统存在满足新系统功能需求的类,但其接口同新系统的接口不一致。
- 使用第三方提供的组件,但组件接口定义和自己要求的接口定义不同。
适配器模式(Adapter)可扩展为双向适配器模式,双向适配器类既可以把适配者接口转换成目标接口,也可以把目标接口转换成适配者接口,其结构图如图 :
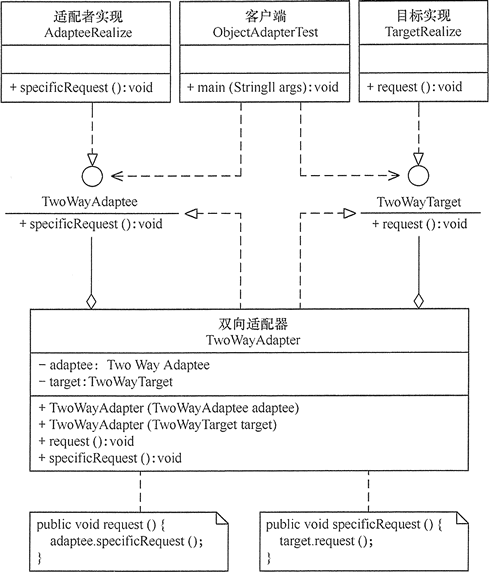
程序代码如下:
- 定义模板接口
public interface TwoWayTarget {
void request();
}
2) 适配者接口
public interface TwoWayAdaptor {
void specificRequest();
}
- 目标实现
public class TargetRealize implements TwoWayTarget{
@Override
public void request() {
System.out.println("目标代码被调用!");
}
}
- 适配者实现
public class AdaptorRealize implements TwoWayAdaptor{
@Override
public void specificRequest() {
System.out.println("适配者代码被调用!");
}
}
- 双向适配器实现
public class TwoWayAdapter implements TwoWayTarget, TwoWayAdaptor {
private TwoWayTarget target;
private TwoWayAdaptor adaptor;
public TwoWayAdapter(TwoWayTarget target) {
this.target = target;
}
public TwoWayAdapter(TwoWayAdaptor adaptor) {
this.adaptor = adaptor;
}
public void request() {
adaptor.specificRequest();
}
public void specificRequest() {
target.request();
}
}
- 客户端代码
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("目标通过双向适配器访问适配者:");
TwoWayAdaptor adaptor = new AdaptorRealize();
TwoWayTarget target = new TwoWayAdapter(adaptor);
target.request();
System.out.println("适配者通过双向适配器访问目标:");
target = new TargetRealize();
adaptor = new TwoWayAdapter(target);
adaptor.specificRequest();
}
}
程序的运行结果如下:
目标通过双向适配器访问适配者:
适配者代码被调用!
适配者通过双向适配器访问目标:
目标代码被调用!