前言
栈和队列是算法的一个基本的知识点之一。这篇文章主要介绍三道有关栈和队列的算法题。因为篇幅所限,只介绍push和pop这两种方法的实现
-
用栈实现队列
-
用队列实现栈
-
循环队列的实现
用栈实现队列
入队列的功能我们可以用栈的入栈的功能替代。但问题在于出队列的功能怎么实现。
这里有一个问题,就是栈是后入先出的,队列是先进先出的,两者出入的方式不一样。
那么怎么实现方向的一致呢? 我们可以使用两个栈,一个栈用于输入,一个栈用于输出。当发现输出栈为空的时候,把排列的数据从输入栈一个个弹出,“倒入”到 输出栈中,这样的话,数据排列的方向就刚好被逆转过来了,原本在输入栈中处于栈底的数据被置换到输出栈的栈顶,这时候对它出栈也就同时完成了队列的出列的功能。
下面是具体的图示
1.入队列操作: 等同于对入队列进行入栈操作,图示如下
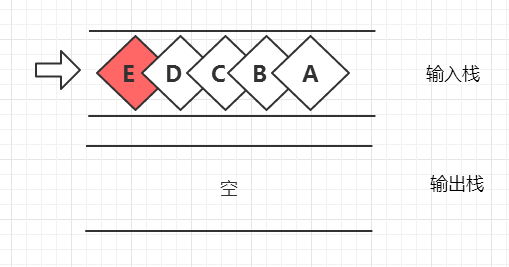
2.出队列操作: 判断当输出栈为空时,先把输入栈的数据依次弹出并加入到输出栈中
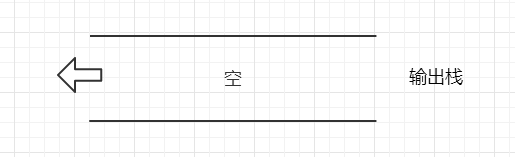
步骤1
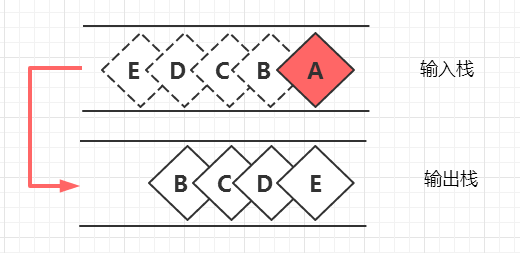
步骤2
对输出栈栈顶进行出栈操作,即可完成出队列功能
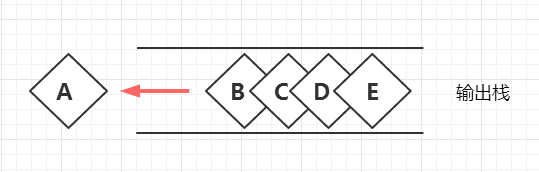
步骤3
具体代码
import java.util.Stack; class MyQueue { private Stack<Integer> stack1; private Stack<Integer> stack2; private boolean isPushState = true; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public MyQueue() { // 输入栈 stack1 = new Stack<Integer>(); // 输出栈 stack2 = new Stack<Integer>(); } /** Push element x to the back of queue. */ public void push(int x) { stack1.push(x); } public void transformStack () { if (stack2.empty()) { while (!stack1.empty()) { int t = stack1.pop(); stack2.push(t); } } } /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */ public int pop() { transformStack(); return stack2.pop(); } /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */ public boolean empty() { return stack1.empty() && stack2.empty(); } }
用队列实现栈
这里同样有两个功能需要我们实现,分别是入栈功能和出栈功能
入栈功能
我们可以用入栈操作模拟实现
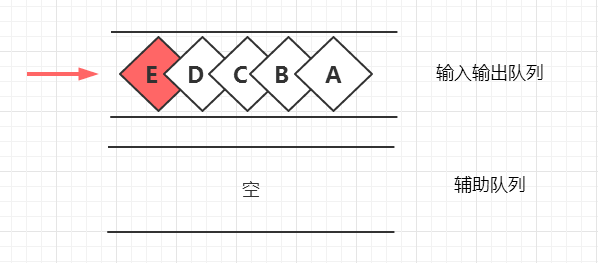
出栈功能
我们又来到了关键功能,这时候你能猜到,我们又需要用到两个队列去实现这个出栈功能了
但问题在于,我们还能否通过讲数据从一个队列“倒”到另一个队列的方式逆转数据方向呢? 这是不行的,因为队列先入先出的特性,导致分割后队列的出入方向仍然是不变的。所以我们要换个思路:
一个元素入队列了,我们接下来希望这个队列像栈一样通过pop把它直接弹出来,但是前面还有很多个元素排着队呢,这时我们想,只要把前面排队的所有元素先出列到另外一个辅助队列里面去,接下来不就可以直接把这个元素踢出队列从而模拟出栈了吗?
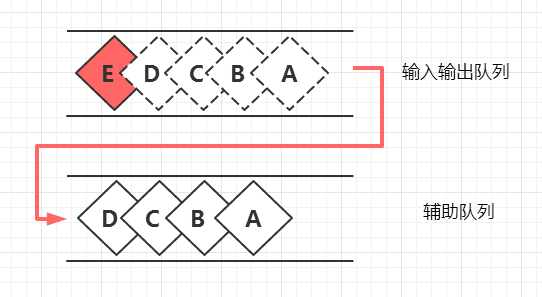
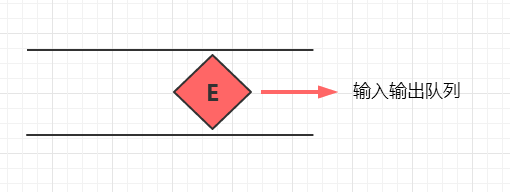
当然完成pop操作后我们还要做一件事情,就是辅助队列和主队列互换,以让未来还能按同样的流程再来一次。
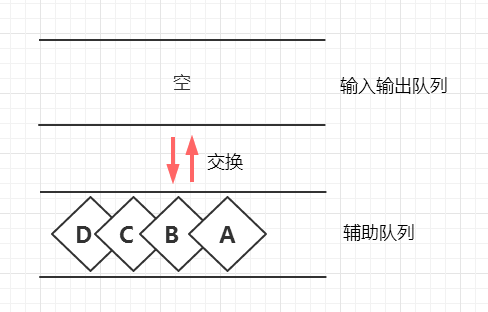
具体代码
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; class MyStack { private Queue queue1; private Queue queue2; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public MyStack() { queue1 = new LinkedList<Integer>(); queue2 = new LinkedList<Integer>(); } /** Push element x onto stack. */ public void push(int x) { queue1.offer(x); } /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ public int pop() { while (queue1.size()>1) { queue2.offer(queue1.poll()); } int result = (Integer) queue1.poll(); Queue temp =queue1; queue1 = queue2; queue2 = temp; return result; } /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ public boolean empty() { return queue1.isEmpty(); } }
循环队列的实现
设计循环队列的原因
对于普通的单向队列,在入队列和出队列的时候可能会遇到一种“队列假满”的现象,导致空间的浪费如下图所示
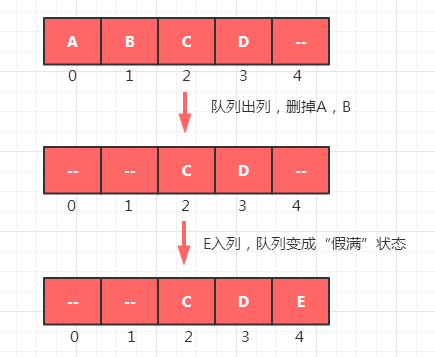
所以我们要做的,就是通过设置头部(front)和尾部(rear)两个指针来区分队列的“满的部分”和“空的部分”,并且允许在填充到数组末尾的时候,能通过回到数组的头部这种循环的方式继续填充数组,从而提高数组空间的利用率。
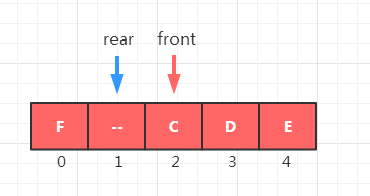
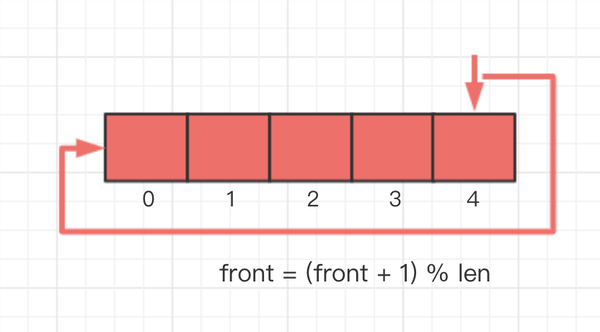
怎么实现从尾部到头部的循环呢? 我们可以通过取余运算符实现,因为当 i = 数组长度- 1的时候,(i + 1) % 数组长度 = 0,也就是说这个时候指针又从尾部回到了数组的头部
具体代码
class MyCircularQueue { private int [] queue; private int front; private int rear; private int len; /** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */ public MyCircularQueue(int k) { queue = new int[k+1]; // 包含 front = 0; // 不包含 rear = 0; len = k+1; } /** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */ public boolean enQueue(int value) { if (isFull()) return false; queue[rear] = value; rear =(rear+1) % len; return true; } /** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */ public boolean deQueue() { if (isEmpty()) return false; queue[front] = -1; front = (front + 1) % len; return true; } /** Get the front item from the queue. */ public int Front() { if (isEmpty()) return -1; return queue[front]; } /** Get the last item from the queue. */ public int Rear() { if (isEmpty()) return -1; if (rear>0) return queue[rear-1]; else return queue[len - 1]; } /** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */ public boolean isEmpty() { if (rear == front) return true; else return false; } /** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */ public boolean isFull() { if ((rear + 1)%len== front) return true; else return false; } }