环境
Linux-4.14
Aarch64
正文
在前面的分析中调用print_symbol("PC is at %s
", instruction_pointer(regs))输出当前PC地址的时候,输出的的内容却是:PC is at demo_init+0xc/0x1000 [demo]
下面分析一下这个函数print_symbol。
1 static __printf(1, 2) 2 void __check_printsym_format(const char *fmt, ...) 3 { 4 } 5 6 static inline void print_symbol(const char *fmt, unsigned long addr) 7 { 8 __check_printsym_format(fmt, ""); 9 __print_symbol(fmt, (unsigned long) 10 __builtin_extract_return_addr((void *)addr)); 11 }
第8行,格式检查
第9行,__builtin_extract_return_addr((void *)addr)返回实际的addr,这里返回的还是addr,这个函数的说明可以参考GCC文档:

下面分析__print_symbol:
1 /* Look up a kernel symbol and print it to the kernel messages. */ 2 void __print_symbol(const char *fmt, unsigned long address) 3 { 4 char buffer[KSYM_SYMBOL_LEN]; 5 6 sprint_symbol(buffer, address); 7 8 printk(fmt, buffer); 9 }
第6行就是核心,这个函数完成了将address转换成对应的内核符号字符串,并将字符串存入buffer中
下面分析sprint_symbol:
1 /** 2 * sprint_symbol - Look up a kernel symbol and return it in a text buffer 3 * @buffer: buffer to be stored 4 * @address: address to lookup 5 * 6 * This function looks up a kernel symbol with @address and stores its name, 7 * offset, size and module name to @buffer if possible. If no symbol was found, 8 * just saves its @address as is. 9 * 10 * This function returns the number of bytes stored in @buffer. 11 */ 12 int sprint_symbol(char *buffer, unsigned long address) 13 { 14 return __sprint_symbol(buffer, address, 0, 1); 15 }
根据注释,这个函数用于查找一个地址为address的内核符号,然后将查找到的符号名字,偏移,大小以及模块名存放到buffer中,如果没有找到的话,只是将address按字符串的格式存入buffer。
这里说明一下:demo_init+0xc/0x1000 [demo]
符号名字:demo_init
偏移:0xc
大小:0x1000
模块名:demo
上面这行的意思是:传入的address处于函数demo_init中,距离demo_init起始地址的偏移为0xC,demo_init函数占用的代码空间是0x1000。所在的内核模块是demo
下面分析__sprint_symbol:
1 /* Look up a kernel symbol and return it in a text buffer. */ 2 static int __sprint_symbol(char *buffer, unsigned long address, 3 int symbol_offset, int add_offset) 4 { 5 char *modname; 6 const char *name; 7 unsigned long offset, size; 8 int len; 9 10 address += symbol_offset; 11 name = kallsyms_lookup(address, &size, &offset, &modname, buffer); 12 if (!name) 13 return sprintf(buffer, "0x%lx", address - symbol_offset); 14 15 if (name != buffer) 16 strcpy(buffer, name); 17 len = strlen(buffer); 18 offset -= symbol_offset; 19 20 if (add_offset) 21 len += sprintf(buffer + len, "+%#lx/%#lx", offset, size); 22 23 if (modname) 24 len += sprintf(buffer + len, " [%s]", modname); 25 26 return len; 27 }
上面的第11行的kallsyms_lookup就是根据address获取size,offset,modname
kallsyms_lookup:
1 /* 2 * Lookup an address 3 * - modname is set to NULL if it's in the kernel. 4 * - We guarantee that the returned name is valid until we reschedule even if. 5 * It resides in a module. 6 * - We also guarantee that modname will be valid until rescheduled. 7 */ 8 const char *kallsyms_lookup(unsigned long addr, 9 unsigned long *symbolsize, 10 unsigned long *offset, 11 char **modname, char *namebuf) 12 { 13 const char *ret; 14 15 namebuf[KSYM_NAME_LEN - 1] = 0; 16 namebuf[0] = 0; 17 18 if (is_ksym_addr(addr)) { 19 unsigned long pos; 20 21 pos = get_symbol_pos(addr, symbolsize, offset); 22 /* Grab name */ 23 kallsyms_expand_symbol(get_symbol_offset(pos), 24 namebuf, KSYM_NAME_LEN); 25 if (modname) 26 *modname = NULL; 27 28 ret = namebuf; 29 goto found; 30 } 31 32 /* See if it's in a module or a BPF JITed image. */ 33 ret = module_address_lookup(addr, symbolsize, offset, 34 modname, namebuf); 35 if (!ret) 36 ret = bpf_address_lookup(addr, symbolsize, 37 offset, modname, namebuf); 38 39 found: 40 cleanup_symbol_name(namebuf); 41 return ret; 42 }
上面会从三个地方去查找符号,首先是内核中,如果没有找到,就从内核模块中查找,如果还是没有找到的话,最后就从bpf中查找。
下面分析第18~30行,即从内核中查找,其他的以后再分析。
第18行,判断addr是否位于内核的代码段
第21行,要分析get_symbol_pos需要用到内核代码编译时生成的的.tmp_kallsyms2.S,其中存放了符号信息。
大致说明一下这个文件:
这个文件是动态生成的,使用的工具是scripts/kallsyms.c,下面说明一下.tmp_kallsyms2.S中的变量作用:
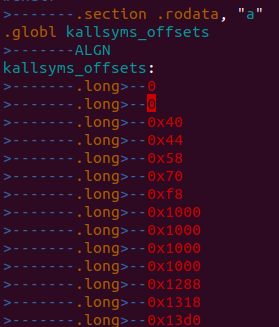
kallsyms_offsets数组中存放的是每个符号距离_text地址的偏移量,对于一下System.map:
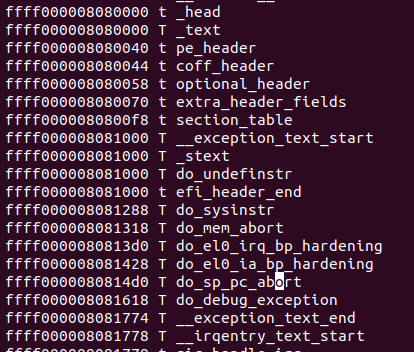
可以看到System.map中的符号地址减去_text的地址,就是kallsyms_offsets数组中的值。
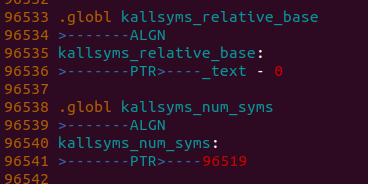
kallsyms_relative_base中存放的是符号的基地址,这个值加上kallsyms_offsets数组中的offset就是符号的实际地址
kallsyms_num_syms存放的是内核符号的个数
kallsyms_names中存放的是每个符号的名字,每一行对应一个,不过这里为了压缩字符串,第一列表示后面的字节数,第二列开始表示的都是索引,索引的是kallsyms_token_index数组中的元素,而kallsyms_token_index数组中存放的也是索引,它索引的是kallsyms_token_table

kallsyms_token_index:
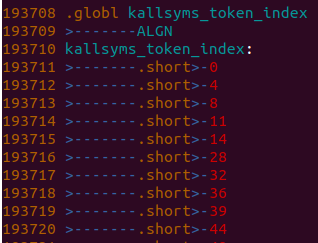
kallsyms_token_table:
在遍历kallsyms_names时为了加快索引速度,又引入了kallsyms_markers数组,这个数组每一个成员都是kallsyms_names中每256行的首地址,所以将来在根据address获得内核符号的索引下标后,将这个索引除以256,然后再在这个256行中找到对应的那行就快多了。
下面分析get_symbol_pos:
1 static unsigned long get_symbol_pos(unsigned long addr, 2 unsigned long *symbolsize, 3 unsigned long *offset) 4 { 5 unsigned long symbol_start = 0, symbol_end = 0; 6 unsigned long i, low, high, mid; 7 8 /* This kernel should never had been booted. */ 9 if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_KALLSYMS_BASE_RELATIVE)) 10 BUG_ON(!kallsyms_addresses); 11 else 12 BUG_ON(!kallsyms_offsets); 13 14 /* Do a binary search on the sorted kallsyms_addresses array. */ 15 low = 0; 16 high = kallsyms_num_syms; 17 18 while (high - low > 1) { 19 mid = low + (high - low) / 2; 20 if (kallsyms_sym_address(mid) <= addr) 21 low = mid; 22 else 23 high = mid; 24 } 25 26 /* 27 * Search for the first aliased symbol. Aliased 28 * symbols are symbols with the same address. 29 */ 30 while (low && kallsyms_sym_address(low-1) == kallsyms_sym_address(low)) 31 --low; 32 33 symbol_start = kallsyms_sym_address(low); 34 35 /* Search for next non-aliased symbol. */ 36 for (i = low + 1; i < kallsyms_num_syms; i++) { 37 if (kallsyms_sym_address(i) > symbol_start) { 38 symbol_end = kallsyms_sym_address(i); 39 break; 40 } 41 } 42 43 /* If we found no next symbol, we use the end of the section. */ 44 if (!symbol_end) { 45 if (is_kernel_inittext(addr)) 46 symbol_end = (unsigned long)_einittext; 47 else if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_KALLSYMS_ALL)) 48 symbol_end = (unsigned long)_end; 49 else 50 symbol_end = (unsigned long)_etext; 51 } 52 53 if (symbolsize) 54 *symbolsize = symbol_end - symbol_start; 55 if (offset) 56 *offset = addr - symbol_start; 57 58 return low; 59 }
第18~24,根据addr查找kallsyms_offsets,获取addr在哪两个符号之间。这里用到了二分法的查找方式,最后addr就位于索引为low和high的两个符号之间,其实就是位于索引为low的函数内部
第30,在kallsyms_offsets中可以看到有很多符号的地址是相同的,这行用于获取相同address的符号中的第一个对应的索引,即low
第33,获取索引为low的符号的地址symbol_start
第36~41,获取紧接着比symbol_start大的一个符号地址,symbol_end
第54行,获取地址为symbol_start内核函数的占用的空间的大小
第56行,获取address相对于symbol_start的偏移量
第58行,返回address所在的内核函数的首地址对应的索引号
接着分析kallsyms_lookup:
第21行,获取了address所在的内核函数的首地址对应的索引号
第23行,get_symbol_offset获取pos对应的内核符号字符串的地址相对于kallsyms_names的偏移量,可以结合之前对.tmp_kallsyms2.S的分析理解
1 /* 2 * Find the offset on the compressed stream given and index in the 3 * kallsyms array. 4 */ 5 static unsigned int get_symbol_offset(unsigned long pos) 6 { 7 const u8 *name; 8 int i; 9 10 /* 11 * Use the closest marker we have. We have markers every 256 positions, 12 * so that should be close enough. 13 */ 14 name = &kallsyms_names[kallsyms_markers[pos >> 8]]; 15 16 /* 17 * Sequentially scan all the symbols up to the point we're searching 18 * for. Every symbol is stored in a [<len>][<len> bytes of data] format, 19 * so we just need to add the len to the current pointer for every 20 * symbol we wish to skip. 21 */ 22 for (i = 0; i < (pos & 0xFF); i++) 23 name = name + (*name) + 1; 24 25 return name - kallsyms_names; 26 }
kallsyms_expand_symbol:
1 /* 2 * Expand a compressed symbol data into the resulting uncompressed string, 3 * if uncompressed string is too long (>= maxlen), it will be truncated, 4 * given the offset to where the symbol is in the compressed stream. 5 */ 6 static unsigned int kallsyms_expand_symbol(unsigned int off, 7 char *result, size_t maxlen) 8 { 9 int len, skipped_first = 0; 10 const u8 *tptr, *data; 11 12 /* Get the compressed symbol length from the first symbol byte. */ 13 data = &kallsyms_names[off]; 14 len = *data; 15 data++; 16 17 /* 18 * Update the offset to return the offset for the next symbol on 19 * the compressed stream. 20 */ 21 off += len + 1; 22 23 /* 24 * For every byte on the compressed symbol data, copy the table 25 * entry for that byte. 26 */ 27 while (len) { 28 tptr = &kallsyms_token_table[kallsyms_token_index[*data]]; 29 data++; 30 len--; 31 32 while (*tptr) { 33 if (skipped_first) { 34 if (maxlen <= 1) 35 goto tail; 36 *result = *tptr; 37 result++; 38 maxlen--; 39 } else 40 skipped_first = 1; 41 tptr++; 42 } 43 } 44 45 tail: 46 if (maxlen) 47 *result = '�'; 48 49 /* Return to offset to the next symbol. */ 50 return off; 51 }
最后会将转换得到的内核符号的字符串名字拷贝到namebuf中。
完。