https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
Easy
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
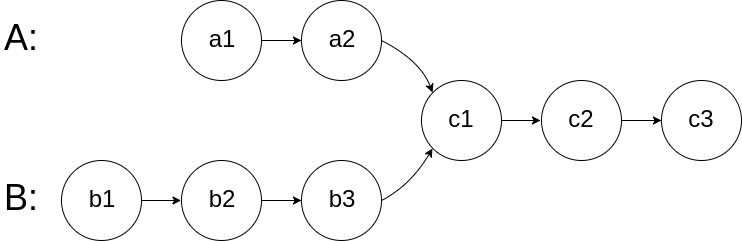
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
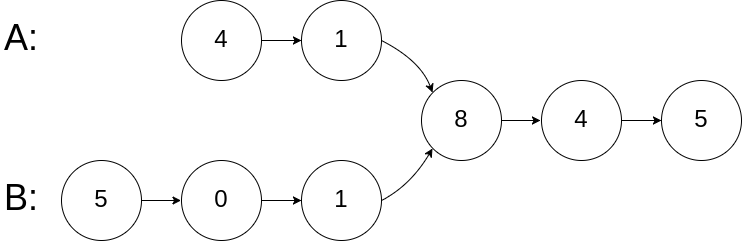
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output: Reference of the node with value = 8 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Example 2:
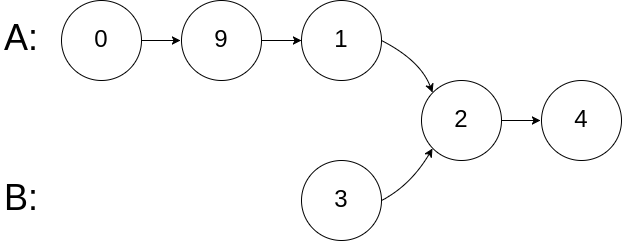
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Reference of the node with value = 2 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:
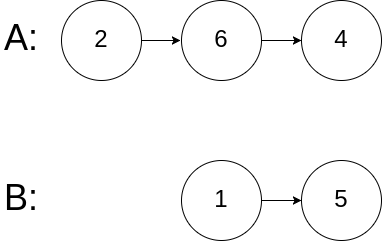
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: null Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values. Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
null. - The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
- 链表+双指针。两种解法:
- 一种是计算两个链表长度差,让长一点的链表的指针先走,到两个指针所在链表剩余长度一样时,再同时往后走。原理是若是两个链表再某一节点相遇,则相遇之后的剩余链表长度必然是一样的。
- 另一种是两个指针同时往后走,若是一个指针到达尾指针,则指向另一个链表的头指针,继续往后走。原理是通过交换头指针来抵消长度差,若是中途都没有相遇,则两个指针都再度到达尾指针,走的长度为len(linkA) + len(linkB) = len(linkB) + len(linkA)

1 # Definition for singly-linked list. 2 # class ListNode(object): 3 # def __init__(self, x): 4 # self.val = x 5 # self.next = None 6 7 class Solution(object): 8 def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB): 9 """ 10 :type head1, head1: ListNode 11 :rtype: ListNode 12 """ 13 14 if headA is None or headB is None: 15 return None 16 17 pA, pB = headA, headB 18 19 # if pA meets pB return the common node, 20 # otherwise both reach the tail and return None 21 while pA != pB: 22 # counteract the difference of length with switching head nodes 23 pA = headB if pA is None else pA.next 24 pB = headA if pB is None else pB.next 25 26 return pA
