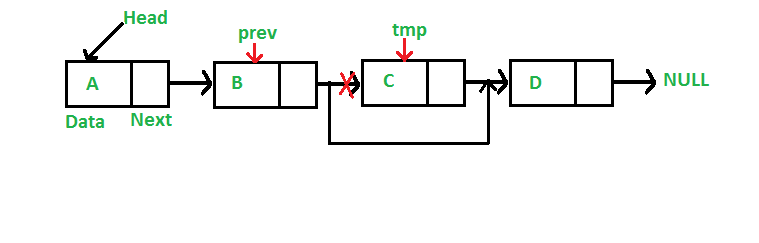
删除节点(3步操作)
删除步骤
1) 找到待删除节点的前驱
2) 修改前驱节点的指针域指向待删除节点的后继节点
3)释放待删除的节点的内存空间
//todo:没有c#的代码添加上去。修改结构,添加一个尾部节点地址的指针
c语言实现:
因为链表中的每个节点都是使用malloc()动态创建的,所以需要调用free()释放待删除节点占用的内存空间。
// A complete working C program to demonstrate deletion in singly
// linked list
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// A linked list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
/* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list
and an int, inserts a new node on the front of the list. */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list
and a key, deletes the first occurrence of key in linked list */
void deleteNode(struct Node **head_ref, int key)
{
// Store head node
struct Node* temp = *head_ref, *prev;
// If head node itself holds the key to be deleted
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key)
{
*head_ref = temp->next; // Changed head
free(temp); // free old head
return;
}
// Search for the key to be deleted, keep track of the
// previous node as we need to change 'prev->next'
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key)
{
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// If key was not present in linked list
if (temp == NULL) return;
// Unlink the node from linked list
prev->next = temp->next;
free(temp); // Free memory
}
// This function prints contents of linked list starting from
// the given node
void printList(struct Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf(" %d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Drier program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
puts("Created Linked List: ");
printList(head);
deleteNode(&head, 1);
puts("
Linked List after Deletion of 1: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
因为涉及到遍历,时间复杂度O(n)
输出
Created Linked List:
2 3 1 7
Linked List after Deletion of 1:
2 3 7
java:
// A complete working Java program to demonstrate deletion in singly
// linked list
class LinkedList
{
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Given a key, deletes the first occurrence of key in linked list */
void deleteNode(int key)
{
// Store head node
Node temp = head, prev = null;
// If head node itself holds the key to be deleted
if (temp != null && temp.data == key)
{
head = temp.next; // Changed head
return;
}
// Search for the key to be deleted, keep track of the
// previous node as we need to change temp.next
while (temp != null && temp.data != key)
{
prev = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// If key was not present in linked list
if (temp == null) return;
// Unlink the node from linked list
prev.next = temp.next;
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
/* This function prints contents of linked list starting from
the given node */
public void printList()
{
Node tnode = head;
while (tnode != null)
{
System.out.print(tnode.data+" ");
tnode = tnode.next;
}
}
/* Drier program to test above functions. Ideally this function
should be in a separate user class. It is kept here to keep
code compact */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(7);
llist.push(1);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
System.out.println("
Created Linked list is:");
llist.printList();
llist.deleteNode(1); // Delete node at position 4
System.out.println("
Linked List after Deletion at position 4:");
llist.printList();
}
}
文章来源:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/linked-list-set-3-deleting-node/