本文转自http://www.cnblogs.com/gaopeng527/p/4448105.html 感谢作者
分页查询
通过JDBC实现分页查询的方法有很多种,而且不同的数据库机制也提供了不同的分页方式,在这里介绍两种非常典型的分页方法。
- 通过ResultSet的光标实现分页
通过ResultSet的光标实现分页,优点是在各种数据库上通用,缺点是占用大量资源,不适合数据量大的情况。
2. 通过数据库机制进行分页
很多数据库自身都提供了分页机制,如SQL Server中提供的top关键字,MySQL数据库中提供的limit关键字,它们都可以设置数据返回的记录数。
通过各种数据库的分页机制实现分页查询,其优点是减少数据库资源的开销,提高程序的性能;缺点是只针对某一种数据库通用。
说明:由于通过ResultSet的光标实现数据分页存在性能方面的缺陷,所以,在实际开发中,很多情况下都是采用数据库提供的分页机制来实现分页查询功能。
例1.1 通过MySQL数据库提供的分页机制,实现商品信息的分页查询功能,将分页数据显示在JSP页面中。
(1)创建名称为Product的类,用于封装商品信息,该类是商品信息的JavaBean。关键代码如下:
package com.cn.gao;
public class Product {
public static final int PAGE_SIZE=2; //每页记录数
private int id; //编号
private String name; //名称
private double price; //价格
private int num; //数量
private String unit; //单位
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String getUnit() {
return unit;
}
public void setUnit(String unit) {
this.unit = unit;
}
}
技巧:在Java语言中,如果定义了静态的final类型变量,通常情况下将这个变量大写。该种编写方式是一种规范,能够很容易地与其它类型的变量进行区分。
(2) 创建名称为ProductDao的类,主要用于封装商品对象的数据库相关操作。在ProduceDao类中,首先编写getConnection()方法,用于创建数据库连接Connnection对象,其关键代码如下:
/**
* 获取数据库连接
* @return Connection 对象
*/
public Connection getConnection(){
Connection conn=null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
String user = "root";
String password = "1234";
conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
然后创建商品信息的分页查询方法find(),该方法包含一个page参数,用于传递要查询的页码。关键代码如下:
/**
* 分页查询所有商品信息
* @param page 页数
* @return List<Product>
*/
public List<Product> find(int page){
List<Product> list = new ArrayList<Product>();
Connection conn = getConnection();
String sql = "select* from tb_product order by id desc limit ?,?";
try {
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setInt(1, (page-1)*Product.PAGE_SIZE);
ps.setInt(2, Product.PAGE_SIZE);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
Product p=new Product();
p.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
p.setName(rs.getString("name"));
p.setNum(rs.getInt("num"));
p.setPrice(rs.getDouble("price"));
p.setUnit(rs.getString("unit"));
list.add(p);
}
ps.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
find()方法用于实现分页查询功能,该方法根据入口参数page传递的页码,查询指定页码中的记录,主要通过limit关键字实现。
说明:MySQL数据库提供的limit关键字能够控制查询数据结果集起始位置及返回记录的数量,它的使用方式如下:
limit arg1,arg2 参数说明: arg1:用于指定查询记录的起始位置。 arg2:用于指定查询数据所返回的记录数。
在分页查询过程中,还需要获取商品信息的总记录数,用于计算商品信息的总页数,该操作编写在findCount()方法中。关键代码如下:
/**
* 查询总记录数
* @return 总记录数
*/
public int findCount(){
int count=0;
Connection conn = getConnection();
String sql = "select count(*) from tb_product";
try {
Statement sta = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = sta.executeQuery(sql);
if(rs.next()){
count = rs.getInt(1); //对总记录数赋值
}
rs.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return count; //返回总记录数
}
(3)创建名称为FindServlet1的类,该类是分页查询商品信息的Servlet对象。在FindServlet1类中重写doGet()方法,对分页请求进行处理,其关键代码如下:
package com.cn.gao;
import java.awt.print.Pageable;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class FindServlet1 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
int currPage=1;
if(request.getParameter("page")!=null){
currPage=Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("page"));
}
ProductDao dao = new ProductDao();
List<Product> list = dao.find(currPage);
request.setAttribute("list", list);
int pages; //总页数
int count=dao.findCount(); //查询总记录数
if(count%Product.PAGE_SIZE==0){
pages=count/Product.PAGE_SIZE;
}else{
pages=count/Product.PAGE_SIZE+1;
}
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
//通过循环构建分页条
for(int i=1;i<=pages;i++){
if(i==currPage){ //判断是否为当前页
sb.append("『"+i+"』"); //构建分页条
}else{
sb.append("<a href='FindServlet1?page="+i+"'>"+i+"</a>"); //构建分页条
}
sb.append(" ");
}
request.setAttribute("bar", sb.toString());;
request.getRequestDispatcher("product_list.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
}
技巧:分页条在JSP页面中是动态内容,每次查看新页面都要重新构造,所以,实例中将分页的构造放置到Servlet中,以简化JSP页面的代码。
在获取查询结果集List与分页条后,FindServlet1分别将这两个对象放置到request中,将请求转发到product_list.jsp页面做出显示。
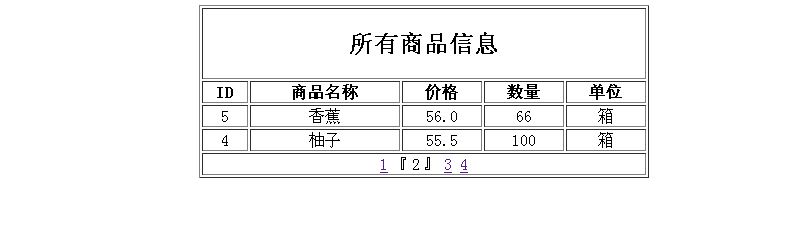
(4)创建product_list.jsp页面,该页面通过获取查询结果集List与分页条来分页显示商品信息数据。关键代码如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=GB18030"
pageEncoding="GB18030"%>
<%@ page import="java.util.*" %>
<%@ page import="com.cn.gao.*" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=GB18030">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<table align="center" width="450" border="1">
<tr>
<td align="center" colspan="5">
<h2>所有商品信息</h2>
</td>
</tr>
<tr align="center">
<td><b>ID</b></td>
<td><b>商品名称</b></td>
<td><b>价格</b></td>
<td><b>数量</b></td>
<td><b>单位</b></td>
</tr>
<%
List<Product> list=(List<Product>)request.getAttribute("list");
for(Product p:list){
%>
<tr align="center">
<td><%=p.getId() %></td>
<td><%=p.getName() %></td>
<td><%=p.getPrice() %></td>
<td><%=p.getNum() %></td>
<td><%=p.getUnit() %></td>
</tr>
<%
}
%>
<tr>
<td align="center" colspan="5">
<%=request.getAttribute("bar") %>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
(5)编写程序中的主页面showproduct.jsp,在该页面中编写分页查询商品信息的超链接,指向FindServlet1。关键代码如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=GB18030"
pageEncoding="GB18030"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=GB18030">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="FindServlet1">查看所有商品信息</a>
</body>
</html>
编写完成该页面后,部署运行项目,此时打开showproduct.jsp页面,其效果如下图所示: