基于ajax的加法运算
前端代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" id="i1"> + <input type="text" id="i2"> = <input type="text" id="i3">
<button id="b1">求和</button>
<script>
$('#b1').on('click', function () {
{#alert('123')#}
$.ajax({
url:'', // 控制发送给谁,不写就是朝当前地址提交
type: 'post', // 发送方式post请求
data: {'i1': $('#i1').val(),'i2': $('#i2').val()}, //发送数据, 取第一个匹配元素的当前值
success:function (data) {
{#alert(data) // 将后端计算好的结果 通过dom操作 ,渲染到第三个input框中#}
$('#i3').val(data)
}
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
后端代码:
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
if request.is_ajax():
print(request.is_ajax())
if request.method == 'POST':
i1 = request.POST.get('i1')
i2 = request.POST.get('i2')
res = int(i1) + int(i2)
print(res)
return HttpResponse(res)
return render(request, 'index.html')
路由层:
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib import admin
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
url(r'^index/', views.index)
]
基于ajax的文件传输
前端代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="file" id="d1">
<button id="b1">提交</button>
<script>
$('#b1').on('click',function () { // 绑定一个事件
var formDate = new FormData(); // new 一个对象 ,既可以传输文件,也可以传输普通键值对
// 先找出文件标签, 再生成一个原生的js,利用原生js对象的方法 .files[0]获取到标签内部存储的文件对象
formDate.append('myfile', $('#d1')[0].files[0]);
$.ajax({
url: '',
type: 'post',
data: formDate,
processData:false, // 告诉后端不要对数据进行任何处理
contentType: false, // 告诉后端不要进行编码, Django自带有编码机制
success: function () {
$('#i3').val()
}
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html
后端代码;
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
print(request.POST)
print(request.FILES)
return render(request, 'index.html')
路由层:
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
url(r'^;index/', views.index)
]
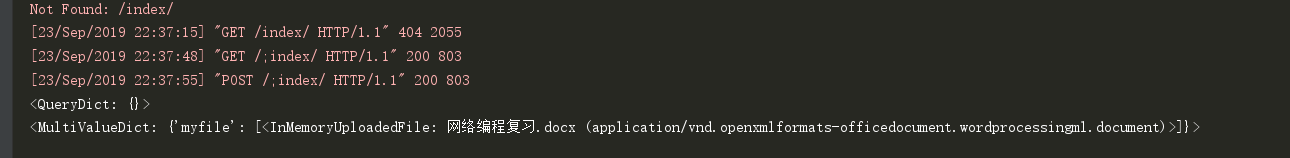
传输文件的结果:
序列化组件
后端代码:
from django.core import serializers # django自带的一个小型的序列化工具
def reg(request):
user_list = models.User.objects.all()
res = serializers.serialize('json',user_list)
return render(request,'index.html',locals())
前端代码:
{% for user in user_l %}
<p>{{ res }}</p>
{% endfor %}
自定义分页器:
前端代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
{% load static %}
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css' %}">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'dist/sweetalert.css' %}">
<script src="{% static 'bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/js/bootstrap.min.js' %}"></script>
<script src="{% static 'dist/sweetalert.min.js' %}"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2">
{% for book in page_queryset %}
<p>{{ book.title }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{{ page_obj.page_html|safe }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
后端代码:
from app01.utils.mypage import Pagination
def book(request):
# 使用封装好的自定义分页器
book_list = models.Book.objects.all()
current_page = request.GET.get("page",1)
all_count = book_list.count()
page_obj = Pagination(current_page=current_page,all_count=all_count,per_page_num=10)
page_queryset = book_list[page_obj.start:page_obj.end]
return render(request,'booklist.html',locals())