安装:
npm install vuex --save
npm install es6-promise --save //依赖promise
绑定:
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) import 'es6-promise/auto'
Vuex是啥?
Vuex是Vue应用程序开发的状态管理模式,即用于存储大量Vue组件都是使用的共享的数据,并且都可以对数据进行相关的操作,实现响应式数据。(就好像是类的原型,所有的实例对象都可以操作)
为啥要使用Vuex进行状态的管理呢?
当很多个组件都要使用同一个数据对象的时候,使用原来的父向子传递数据的方式,需要一级一级的实现数据的调用,如果使用vuex可以实现直接使用。
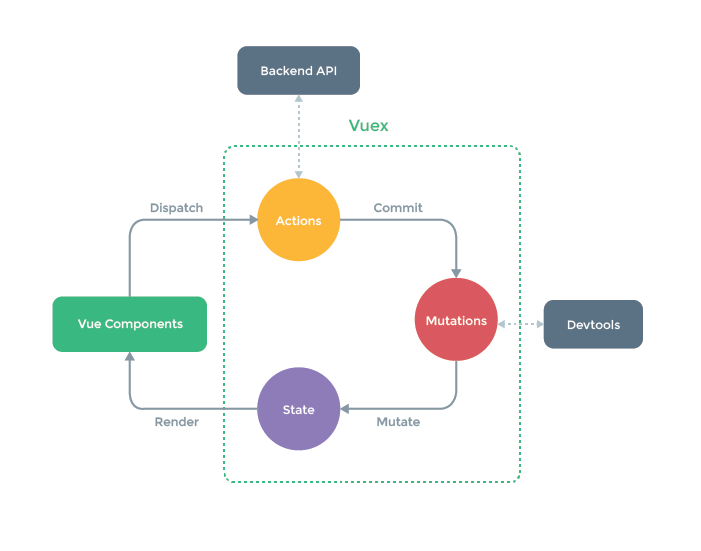
Vuex 是单一状态树:
也就是说整个应用程序中只是使用一个store实例对象,所有的数据都保存在该store对象上(类似于单例模式)
Vuex的特点:
1.Vuex的状态储存是响应式的,也就是说,当在某个组件中使得数据改变了,则其他的组件中的该数据也会更新。
2.你不能直接改变 store 中的状态,只能使用commit体骄傲mutation实现数据改变
Vuex目录结构:
Store的创建:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0 //组件中的获取方式 this.$store.state.count
},
mutations: {
increment (state) { //调用方式:this.$store.commit('increment')
state.count++
}
}
,
actions,getters,moudles
})
state :
保存着多个组件中共享的状态或是数据
this.$store.state.count //this.$store 就是生成的store对象 获取一个状态时
//获取多个组件的时候
computed:mapState({ count:state=>state.counter, //可以直接使用state不需要再通过$store来使用 countAlias:'counter', //这里调用的是state中的counter数据 countPlusLocalState(state){ //可将store中的 数据和当前组件中的数据一起使用 return state.counter+ this.counter } })
//简写形式
//mapState和局部计算属性的混用
computed: {
localComputed () { /* ... */ },
// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState({
// ...
})
}
Getter:
类似于store 的计算属性,当他的依赖值发生变化的时候被重新计算
//通过属性访问
const getters = { //store中设置 doneTodos:state=>{ return state.info.filter(item=>item.age>8) //对state进行公共的处理的数据 }, donTodosCount:()=>{ // state.info.filter(item=>item.age>8).length 是2 有问题 return getters.doneTodos.length //这样写的数据是1 } }
{{this.$store.getters.doneTodos}} //组件中的调用方式
{{ this.$store.getters.donTodosCount}} //这里有问题
//通过方法访问 geTAgeById:(state) => (id) => { return state.info.find(item =>item.id == id); }
{{this.$store.getters.geTAgeById(1)}} //通过方法调用getters
//组件中调用多个getter计算属性 computed:{ ...mapState({ count:state=>state.counter, //可以直接使用state不需要再通过$store来使用 countAlias:'counter', //这里调用的是state中的counter数据 countPlusLocalState(state){ return state.counter+this.coutner },
//简写 ,也可使用{} ...mapGetters([ "doneTodos", "donTodosCount", "geTAgeById", //计算方法也可以直接这样使用 ]) }) }
{{doneTodos}}
{{donTodosCount}}
{{geTAgeById(1)}} //计算方法调用
Mutation:
提交commit是更新Vuex中state的唯一方法。只能执行同步方法。如果执行异步方法,vue开发工具就无法跟踪数据。
注意:1.只有修改store中state一些的数据有效,对于新生产的state数据或是属性,并不影响。
2.当需要在对象上添加新的属性时,
Vue.set(obj,'newProp',124);
或是
satte.obj = {...state.obj,newProp:123} //以旧换新
3.可以使用常量来替换Mutation事件的类型
const INCREMENT = ‘increment’;
使用
[ INCREMENT] (state){
//code
}
const mutations = { increment:(state)=>{ state.counter++; }, increment1:function(state,payload){ //payload也可是对象 state.counter +=payload; } }
methods:{
increment:function(){ //注意this指向问题
this.$store.commit("increment")
} ,
increment1:function(){
//参数也可以是对象
this.$store.commit("increment1",5);
//或是 this.$store.commit({
// type:"increment1"
amount:10
})
}
},
//多个mutation被使用时
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
})
}Action:
Action和mutation基本相同,但是iaction提交的是mutation 不是直接变更状态 ,可以执行异步操作。
const actions = { increment:function(context){ //context 和 store实例对象有相同的方法和属性,但不是同一个 context.commit("increment") } }
//传递参数
store.dispatch('incrementAsync', {
amount: 10
})
// 以对象形式分发
store.dispatch({
type: 'incrementAsync',
amount: 10
})
asyncIncrement:function(){
this.$store.dispatch("increment"); //使用dispath调用 actions方法
}
//多个异步actions methods: { ...mapActions([ 'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')` // `mapActions` 也支持载荷: 'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)` ]), ...mapActions({ add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')` }) } //组合action :通过Promise或是 async语法糖
Module:
由于store是单一树的情况,可能出现大量数据都保存在state中的情况,于是可以将其分成多个模块onst moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... }, //这里 mutations中写的函数的state参数的是模块局部的状态
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态 调用的时候和之前的基本相同。
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
{{this.$store.state.moduleQ.msg}}
const moduleA = { // ... actions: { incrementIfOddOnRootSum ({ state, commit, rootState }) {
//rootState 表示根节点中的state状态 if ((state.count + rootState.count) % 2 === 1) { commit('increment') } } } }
{{this.$store.getters.add}}
//对于子modules中的getters mutations actions都是直接这样调用
开启严格模式:
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state, mutations, actions, getters, modules, strict: true//开启严格模式 });
Vuex 的Moldle的命名空间,插件