在激活层中,对输入数据进行激活操作(实际上就是一种函数变换),是逐元素进行运算的。从bottom得到一个blob数据输入,运算后,从top输入一个blob数据。在运算过程中,没有改变数据的大小,即输入和输出的数据大小是相等的。
输入:n*c*h*w
输出:n*c*h*w
常用的激活函数有sigmoid, tanh,relu等,下面分别介绍。
1、Sigmoid
对每个输入数据,利用sigmoid函数执行操作。这种层设置比较简单,没有额外的参数。
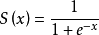
层类型:Sigmoid
示例:
layer { name: "encode1neuron" bottom: "encode1" top: "encode1neuron" type: "Sigmoid" }
2、ReLU / Rectified-Linear and Leaky-ReLU
ReLU是目前使用最多的激活函数,主要因为其收敛更快,并且能保持同样效果。
标准的ReLU函数为max(x, 0),当x>0时,输出x; 当x<=0时,输出0
f(x)=max(x,0)
层类型:ReLU
可选参数:
negative_slope:默认为0. 对标准的ReLU函数进行变化,如果设置了这个值,那么数据为负数时,就不再设置为0,而是用原始数据乘以negative_slope
1 layer { 2 name: "relu1" 3 type: "ReLU" 4 bottom: "pool1" 5 top: "pool1" 6 }
RELU层支持in-place计算,这意味着bottom的输出和输入相同以避免内存的消耗。
3、TanH / Hyperbolic Tangent
利用双曲正切函数对数据进行变换。
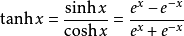
层类型:TanH
1 layer { 2 name: "layer" 3 bottom: "in" 4 top: "out" 5 type: "TanH" 6 }
4、Absolute Value
求每个输入数据的绝对值。
f(x)=Abs(x)
层类型:AbsVal
1 layer { 2 name: "layer" 3 bottom: "in" 4 top: "out" 5 type: "AbsVal" 6 }
5、Power
对每个输入数据进行幂运算
f(x)= (shift + scale * x) ^ power
层类型:Power
可选参数:
power: 默认为1
scale: 默认为1
shift: 默认为0
1 layer { 2 name: "layer" 3 bottom: "in" 4 top: "out" 5 type: "Power" 6 power_param { 7 power: 2 8 scale: 1 9 shift: 0 10 } 11 }
6、BNLL
binomial normal log likelihood的简称
f(x)=log(1 + exp(x))
层类型:BNLL
1 layer { 2 name: "layer" 3 bottom: "in" 4 top: "out" 5 type: “BNLL” 6 }