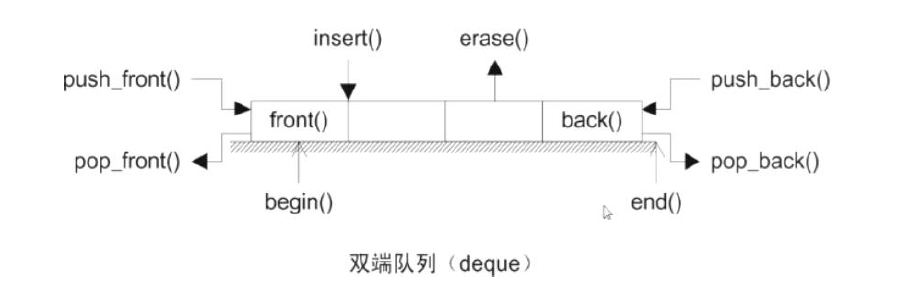
1.实现原理
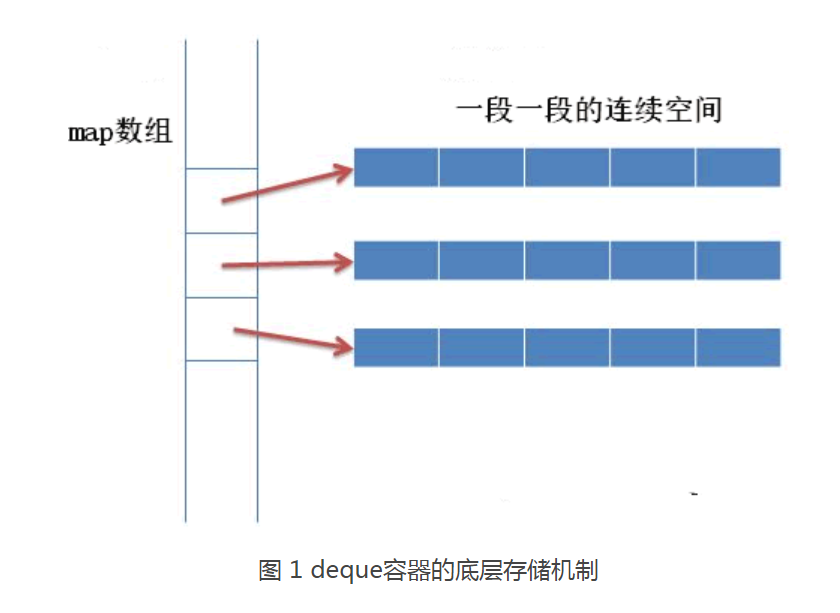
vector :
采用的是连续的线性空间
deque :
存储的空间是由一段一段等长的连续空间构成,各段空间之间并不一定是连续的,可以位于在内存的不同
为管理这些连续的空间,deque容器用数组存储着各个连续空间的地址,即数组中存储的都是指针,
由于 deque 容器底层将序列中的元素分别存储到了不同段的连续空间中,因此要想实现迭代器的功能,必须先解决如下 2 个问题:
(1)迭代器在遍历 deque 容器时,必须能够确认各个连续空间在 map 数组中的位置;
(2)迭代器在遍历某个具体的连续空间时,必须能够判断自己是否已经处于空间的边缘位置。如果是,则一旦前进或者后退,就需要跳跃到上一个或者下一个连续空间中。
2.使用方法
基本方法
#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<deque> using namespace std; int main() { deque<int> d; d.push_back(10); d.push_back(9); d.push_back(8); d.push_back(7); // 两种获取方式 printf(" "); for (auto i = d.begin(); i < d.end(); i++) { cout << *i << endl; } printf(" "); for (auto i = begin(d); i < end(d); i++) { cout << *i << endl; } // 访问方式 printf(" "); cout << d[1] << endl; cout << d.at(1) << endl; cout << d.front() << endl; cout << d.back() << endl; /* 1.没有提供data()成员,不能访问 cout << d.data() << endl; 2.deque存储元素时,无法保证其会将元素存储在连续的内存空间中,因为不能用指针访问 auto first = d.begin()+1; auto end = d.end()-1; while (first < end) { cout << *first << endl; ++first; } */ system("pause"); return 1; }
insert使用
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
#include<array>
using namespace std;
void ShowPrint(deque<int> d)
{
for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++) {
cout << d[i] << " ";
}
/* 这种显示不好
for (auto i = d.begin(); i < d.end(); i++) {
cout << *i << endl;
}
*/
printf("
");
}
int main()
{
deque<int> d{ 1,10 };
// 第一种
d.insert(d.begin() + 1, 33); // 1 33 10
ShowPrint(d);
// 第二种
d.insert(d.end(), 3, 6); // 1 33 10 6 6 6
ShowPrint(d);
// 第三种
array<int, 3>arr{ 11,21,31 };
d.insert(d.end(), arr.begin(), arr.end());
ShowPrint(d); // 1 33 10 6 6 6 11 21 31
// 第四种
d.insert(d.end(), { 41,51 });
ShowPrint(d);
system("pause");
return 1;
}