3. Java NIO系统的核心在于:通道(Channel)和缓冲区 (Buffer)。通道表示打开到 IO 设备(例如:文件、 套接字)的连接。若需要使用 NIO 系统,
需要获取 用于连接 IO 设备的通道以及用于容纳数据的缓冲 区。然后操作缓冲区,对数据进行处理。
4. 缓冲区(Buffer):一个用于特定基本数据类 型的容器。由 java.nio 包定义的,所有缓冲区 都是 Buffer 抽象类的子类。
Java NIO 中的 Buffer 主要用于与 NIO 通道进行 交互,数据是从通道读入缓冲区,从缓冲区写 入通道中的。
5 . Buffer 就像一个数组,可以保存多个相同类型的数据。根 据数据类型不同(boolean 除外) ,
有以下 Buffer 常用子类:
ByteBuffer
CharBuffer
ShortBuffer
IntBuffer
LongBuffer
FloatBuffer
DoubleBuffer
上述 Buffer 类 他们都采用相似的方法进行管理数据,只是各自管理的数据类型不同而已。都是通过如下方法获取一个 Buffer 对象:
static XxxBuffer allocate(int capacity) : 创建一个容量为 capacity 的 XxxBuffer 对象
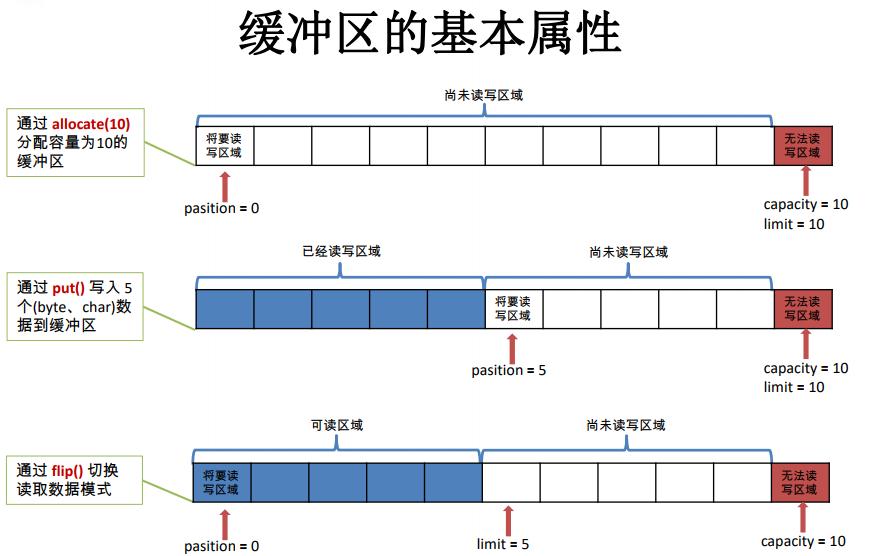
6. 缓冲区的基本属性
Buffer 中的重要概念:
容量 (capacity) :表示 Buffer 最大数据容量,缓冲区容量不能为负,并且创 建后不能更改。
限制 (limit):第一个不应该读取或写入的数据的索引,即位于 limit 后的数据 不可读写。缓冲区的限制不能为负,并且不能大于其容量。
位置 (position):下一个要读取或写入的数据的索引。缓冲区的位置不能为 负,并且不能大于其限制
标记 (mark)与重置 (reset):标记是一个索引,通过 Buffer 中的 mark() 方法 指定 Buffer 中一个特定的 position,之后可以通过调用 reset() 方法恢复到这 个 position.
标记、位置、限制、容量遵守以下不变式: 0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
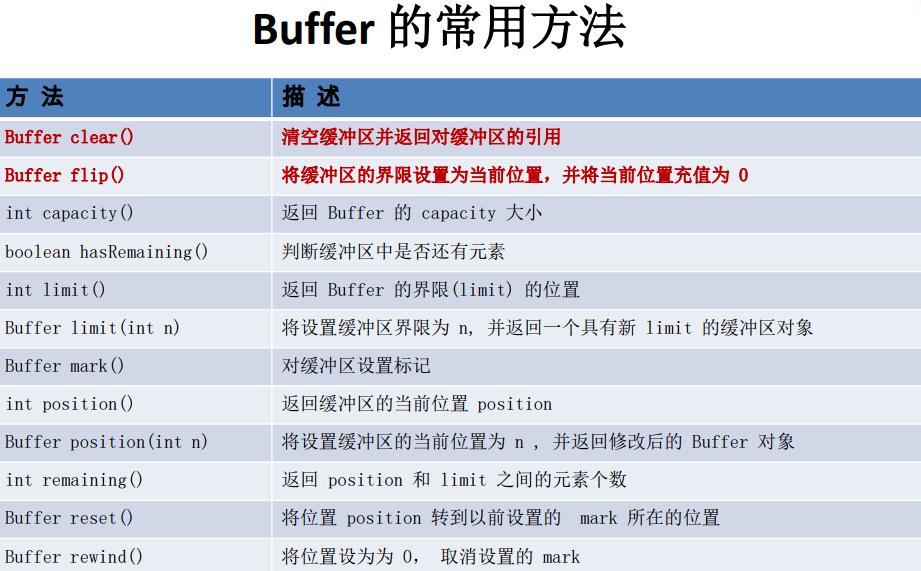
7. 缓冲区的数据操作
Buffer 所有子类提供了两个用于数据操作的方法:get() 与 put() 方法
获取 Buffer 中的数据 get() :读取单个字节 get(byte[] dst):批量读取多个字节到 dst 中 get(int index):读取指定索引位置的字节(不会移动 position)
放入数据到 Buffer 中 put(byte b):将给定单个字节写入缓冲区的当前位置 put(byte[] src):将 src 中的字节写入缓冲区的当前位置 put(int index, byte b):
将指定字节写入缓冲区的索引位置(不会移动 position)
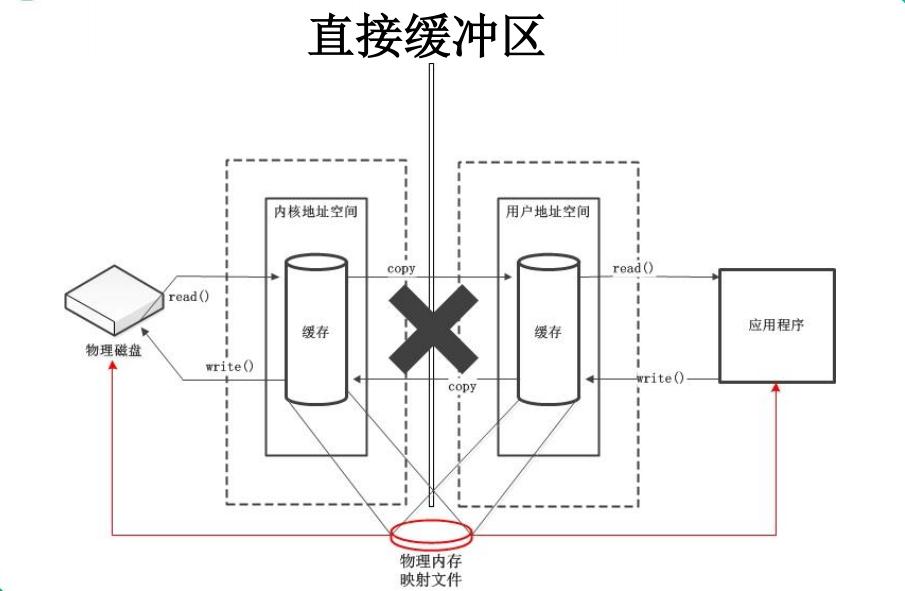
8. 直接与非直接缓冲区
字节缓冲区要么是直接的,要么是非直接的。如果为直接字节缓冲区,则 Java 虚拟机会尽最大努力直接在 此缓冲区上执行本机 I/O 操作。也就是说,在每次调用基础操作系统的一个本机 I/O 操作之前 (或 之后), 虚拟机都会尽量避免将缓冲区的内容复制到中间缓冲区中(或从中间缓冲区中复制内容)。
直接字节缓冲区可以通过调用此类的 allocateDirect() 工厂方法来创建。此方法返回的缓冲区进行分配和取消 分配所需成本通常高于非直接缓冲区。直接缓冲区的内容可以驻留在常规的垃圾回收堆之外,因 此,它们对 应用程序的内存需求量造成的影响可能并不明显。所以,建议将直接缓冲区主要分配给那些易受基础系统的 本机 I/O 操作影响的大型、持久的缓冲区。一般情况下,最好仅在直接缓冲区能在程 序性能方面带来明显好 处时分配它们。
直接字节缓冲区还可以通过 FileChannel 的 map() 方法 将文件区域直接映射到内存中来创建。该方法返回 MappedByteBuffer 。Java 平台的实现有助于通过 JNI 从本机代码创建直接字节缓冲区。如果以上 这些缓冲区 中的某个缓冲区实例指的是不可访问的内存区域,则试图访问该区域不会更改该缓冲区的内容,并且将会在 访问期间或稍后的某个时间导致抛出不确定的异常。
字节缓冲区是直接缓冲区还是非直接缓冲区可通过调用其 isDirect() 方法来确定。提供此方法是为了能够在 性能关键型代码中执行显式缓冲区管理。
9 通道(Channel):由 java.nio.channels 包定义 的。Channel 表示 IO 源与目标打开的连接。 Channel 类似于传统的“流”。只不过 Channel 本身不能直接访问数据,Channel 只能与 Buffer 进行交互。
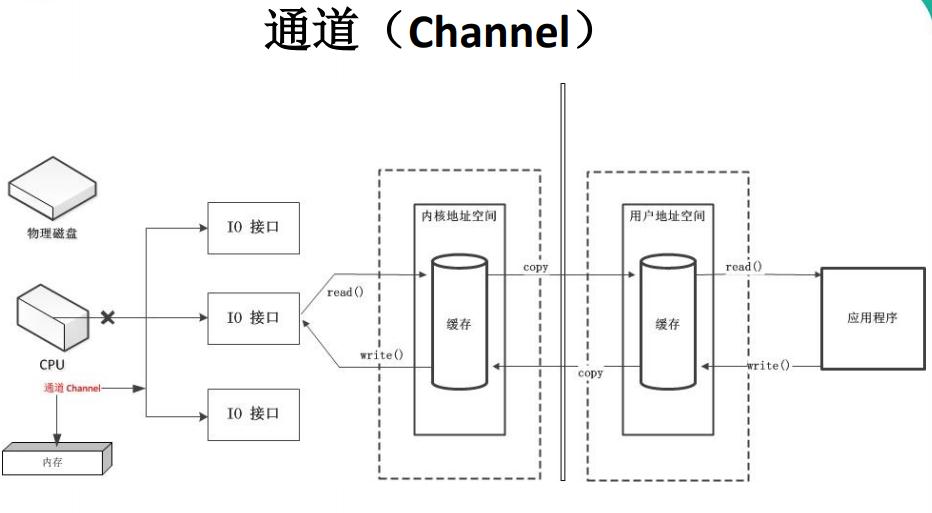
10. Java 为 Channel 接口提供的最主要实现类如下:
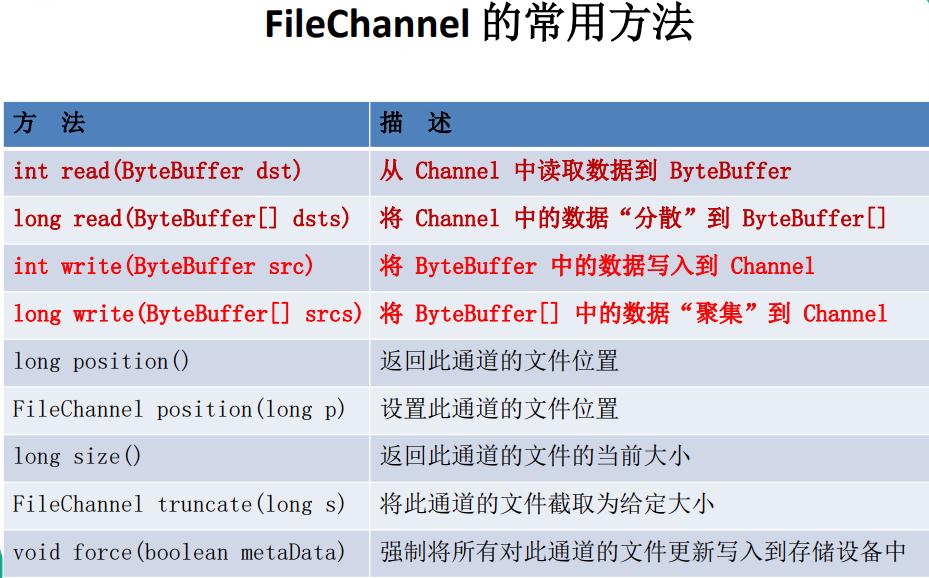
•FileChannel:用于读取、写入、映射和操作文件的通道。
•DatagramChannel:通过 UDP 读写网络中的数据通道。
•SocketChannel:通过 TCP 读写网络中的数据。
•ServerSocketChannel:可以监听新进来的 TCP 连接,对每一个新进来 的连接都会创建一个 SocketChannel。

package com.atguigu.nio; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import org.junit.Test; /* * 一、缓冲区(Buffer):在 Java NIO 中负责数据的存取。缓冲区就是数组。用于存储不同数据类型的数据 * * 根据数据类型不同(boolean 除外),提供了相应类型的缓冲区: * ByteBuffer * CharBuffer * ShortBuffer * IntBuffer * LongBuffer * FloatBuffer * DoubleBuffer * * 上述缓冲区的管理方式几乎一致,通过 allocate() 获取缓冲区 * * 二、缓冲区存取数据的两个核心方法: * put() : 存入数据到缓冲区中 * get() : 获取缓冲区中的数据 * * 三、缓冲区中的四个核心属性: * capacity : 容量,表示缓冲区中最大存储数据的容量。一旦声明不能改变。 * limit : 界限,表示缓冲区中可以操作数据的大小。(limit 后数据不能进行读写) * position : 位置,表示缓冲区中正在操作数据的位置。 * * mark : 标记,表示记录当前 position 的位置。可以通过 reset() 恢复到 mark 的位置 * * 0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity * * 四、直接缓冲区与非直接缓冲区: * 非直接缓冲区:通过 allocate() 方法分配缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在 JVM 的内存中 * 直接缓冲区:通过 allocateDirect() 方法分配直接缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在物理内存中。可以提高效率 */ public class TestBuffer { @Test public void test3(){ //分配直接缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024); System.out.println(buf.isDirect()); } @Test public void test2(){ String str = "abcde"; ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); buf.put(str.getBytes()); buf.flip(); byte[] dst = new byte[buf.limit()]; buf.get(dst, 0, 2); System.out.println(new String(dst, 0, 2)); System.out.println(buf.position()); //mark() : 标记 buf.mark(); buf.get(dst, 2, 2); System.out.println(new String(dst, 2, 2)); System.out.println(buf.position()); //reset() : 恢复到 mark 的位置 buf.reset(); System.out.println(buf.position()); //判断缓冲区中是否还有剩余数据 if(buf.hasRemaining()){ //获取缓冲区中可以操作的数量 System.out.println(buf.remaining()); } } /* ab 2 cd 4 2 3 */ @Test public void test1(){ String str = "abcde"; //1. 分配一个指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); System.out.println("-----------------allocate()----------------"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); //2. 利用 put() 存入数据到缓冲区中 buf.put(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("-----------------put()----------------"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); //3. 切换读取数据模式 buf.flip(); System.out.println("-----------------flip()----------------"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); //4. 利用 get() 读取缓冲区中的数据 byte[] dst = new byte[buf.limit()]; buf.get(dst); System.out.println(new String(dst, 0, dst.length)); System.out.println("-----------------get()----------------"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); //5. rewind() : 可重复读 buf.rewind(); System.out.println("-----------------rewind()----------------"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); //6. clear() : 清空缓冲区. 但是缓冲区中的数据依然存在,但是处于“被遗忘”状态 buf.clear(); System.out.println("-----------------clear()----------------"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); System.out.println((char)buf.get()); } /* -----------------allocate()---------------- 0 1024 1024 -----------------put()---------------- 5 1024 1024 -----------------flip()---------------- 0 5 1024 abcde -----------------get()---------------- 5 5 1024 -----------------rewind()---------------- 0 5 1024 -----------------clear()---------------- 0 1024 1024 a */ }

package com.atguigu.nio; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.CharBuffer; import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel.MapMode; import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder; import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Set; import org.junit.Test; /* * 一、通道(Channel):用于源节点与目标节点的连接。在 Java NIO 中负责缓冲区中数据的传输。Channel 本身不存储数据,因此需要配合缓冲区进行传输。 * * 二、通道的主要实现类 * java.nio.channels.Channel 接口: * |--FileChannel * |--SocketChannel * |--ServerSocketChannel * |--DatagramChannel * * 三、获取通道 * 1. Java 针对支持通道的类提供了 getChannel() 方法 * 本地 IO: * FileInputStream/FileOutputStream * RandomAccessFile * * 网络IO: * Socket * ServerSocket * DatagramSocket * * 2. 在 JDK 1.7 中的 NIO.2 针对各个通道提供了静态方法 open() * 3. 在 JDK 1.7 中的 NIO.2 的 Files 工具类的 newByteChannel() * * 四、通道之间的数据传输 * transferFrom() * transferTo() * * 五、分散(Scatter)与聚集(Gather) * 分散读取(Scattering Reads):将通道中的数据分散到多个缓冲区中 * 聚集写入(Gathering Writes):将多个缓冲区中的数据聚集到通道中 * * 六、字符集:Charset * 编码:字符串 -> 字节数组 * 解码:字节数组 -> 字符串 * */ public class TestChannel { //字符集 @Test public void test6() throws IOException{ Charset cs1 = Charset.forName("GBK"); //获取编码器 CharsetEncoder ce = cs1.newEncoder(); //获取解码器 CharsetDecoder cd = cs1.newDecoder(); CharBuffer cBuf = CharBuffer.allocate(1024); cBuf.put("尚硅谷威武!"); cBuf.flip(); //编码 ByteBuffer bBuf = ce.encode(cBuf); for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) { System.out.println(bBuf.get()); } //解码 bBuf.flip(); CharBuffer cBuf2 = cd.decode(bBuf); System.out.println(cBuf2.toString()); System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------"); Charset cs2 = Charset.forName("GBK"); bBuf.flip(); CharBuffer cBuf3 = cs2.decode(bBuf); System.out.println(cBuf3.toString()); } @Test public void test5(){ Map<String, Charset> map = Charset.availableCharsets(); Set<Entry<String, Charset>> set = map.entrySet(); for (Entry<String, Charset> entry : set) { System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue()); } } //分散和聚集 @Test public void test4() throws IOException{ RandomAccessFile raf1 = new RandomAccessFile("1.txt", "rw"); //1. 获取通道 FileChannel channel1 = raf1.getChannel(); //2. 分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(100); ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //3. 分散读取 ByteBuffer[] bufs = {buf1, buf2}; channel1.read(bufs); for (ByteBuffer byteBuffer : bufs) { byteBuffer.flip(); } System.out.println(new String(bufs[0].array(), 0, bufs[0].limit())); System.out.println("-----------------"); System.out.println(new String(bufs[1].array(), 0, bufs[1].limit())); //4. 聚集写入 RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile("2.txt", "rw"); FileChannel channel2 = raf2.getChannel(); channel2.write(bufs); } //通道之间的数据传输(直接缓冲区) @Test public void test3() throws IOException{ FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/1.mkv"), StandardOpenOption.READ); FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/2.mkv"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); // inChannel.transferTo(0, inChannel.size(), outChannel); outChannel.transferFrom(inChannel, 0, inChannel.size()); inChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); } //使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件) @Test public void test2() throws IOException{//2127-1902-1777 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/1.mkv"), StandardOpenOption.READ); FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/2.mkv"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); //内存映射文件 MappedByteBuffer inMappedBuf = inChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size()); MappedByteBuffer outMappedBuf = outChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size()); //直接对缓冲区进行数据的读写操作 byte[] dst = new byte[inMappedBuf.limit()]; inMappedBuf.get(dst); outMappedBuf.put(dst); inChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("耗费时间为:" + (end - start)); } //利用通道完成文件的复制(非直接缓冲区) @Test public void test1(){//10874-10953 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); FileInputStream fis = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; //①获取通道 FileChannel inChannel = null; FileChannel outChannel = null; try { fis = new FileInputStream("d:/1.mkv"); fos = new FileOutputStream("d:/2.mkv"); inChannel = fis.getChannel(); outChannel = fos.getChannel(); //②分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //③将通道中的数据存入缓冲区中 while(inChannel.read(buf) != -1){ buf.flip(); //切换读取数据的模式 //④将缓冲区中的数据写入通道中 outChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); //清空缓冲区 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(outChannel != null){ try { outChannel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(inChannel != null){ try { inChannel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(fos != null){ try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(fis != null){ try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("耗费时间为:" + (end - start)); } }
