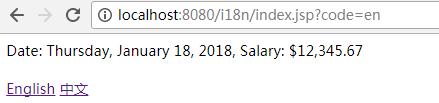
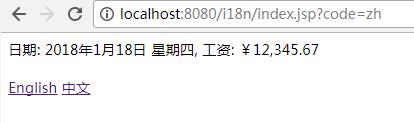
1. 什么是国际化和本地化:
I. 本地化:一个软件在某个国家或地区使用时,采用该国家或地区的语言,数字,货币,日期等习惯。
II. 国际化:软件开发时,让它能支持多个国家和地区的本地化应用。使得应用软件能够适应多个地区的语言和文化风俗习惯
III. 本地敏感数据: 随用户区域信息而变化的数据称为本地信息敏感数据。例如数字,货币, 日期,时间等数据
2. 相关的 API:
I. DateFormat 和 SimpleDateFormat √.
II. NumberFormat
III. MessageFormat
IV. ResourceBundle
V. Locale
3. 关于国际化资源文件:
I. properties 文件格式
II. 必须提供 基名.properties 文件和 基名_语言代码_国家代码.properties 文件
III. 相同的 基名 的资源文件必须有相同的 key.
IV. 可能需要使用 native2ascii 工具把非 asc 码转为 asc 码.
4. WEB 的国际化
I. 可以使用 request.getLocale() 获取 Locale 对象
II. 可以使用 JSTL 的 fmt 标签完成的国际化. 后面使用框架提供的标签完成.
III. 实现 "中文" "英文" 的切换:
> 提供两个超简洁. 携带不同的变量值
> 根据变量值确定对应的 Locale 对象
> 把 Locale 对象放入到 session 中
> 绑定 Locale 对应的资源文件.
IV. 其他 fmt 标签可以参考 standard-examples.war 中的例子.
5.代码区

package com.atguigu.i18n; import java.text.DateFormat; import java.text.MessageFormat; import java.text.NumberFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.ResourceBundle; import org.junit.Test; public class I18nTest { /* @Test public void testMessageFormat2(){ String str = "Date: {0}, Salary: {1}"; Locale locale = Locale.CHINA; Date date = new Date(); double sal = 12345.12; StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer(); FieldPosition fieldPosition = new FieldPosition(0); MessageFormat messageFormat = new MessageFormat(str, locale); messageFormat.format(date, result, fieldPosition); System.out.println(result); } */ /** * ResourceBundle: 资源包类. * * 1. 在类路径下需要有对应的资源文件: baseName.properties. 其中 baseName 是基名. * 2. 可以使用 基名_语言代码_国家代码.properties 来添加不同国家或地区的资源文件. i18n_zh_CN.properties * 3. 要求所有基名相同的资源文件的 key 必须完全一致. * 4. 可以使用 native2ascii 命令来得到 汉字 对一个的 asc 码. Eclipse 内置了工具 * 5. 可以调用 ResourceBundle 的 getBundle(基名, Locale 实例) 获取获取 ResourceBundle 对象 * 6. 可以调用 ResourceBundle 的 getString(key) 来获取资源文件的 value 字符串的值. * 7. 结合 DateFormat, NumberFormat, MessageFormat 即可实现国际化. * */ @Test public void testResourceBundle(){ Locale locale = Locale.CHINA; ResourceBundle resourceBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("i18n", locale); //日期 工资 System.out.println(resourceBundle.getString("date")); System.out.println(resourceBundle.getString("salary")); String dateLabel = resourceBundle.getString("date"); String salLabel = resourceBundle.getString("salary"); String str = "{0}:{1}, {2}:{3}"; Date date = new Date(); double sal = 12345.12; DateFormat dateFormat = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM, locale); String dateStr = dateFormat.format(date); NumberFormat numberFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(locale); String salStr = numberFormat.format(sal); String result = MessageFormat.format(str, dateLabel, dateStr, salLabel, salStr); //日期:2018-1-18, 工资:¥12,345.12 System.out.println(result); } /** * MessageFormat: 可以格式化模式字符串 * 模式字符串: 带占位符的字符串: "Date: {0}, Salary: {1}" * 可以通过 format 方法会模式字符串进行格式化 */ @Test public void testMessageFormat(){ String str = "Date: {0}, Salary: {1}"; Locale locale = Locale.CHINA; Date date = new Date(); double sal = 12345.12; DateFormat dateFormat = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM, locale); String dateStr = dateFormat.format(date); NumberFormat numberFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(locale); String salStr = numberFormat.format(sal); String result = MessageFormat.format(str, dateStr, salStr); //Date: 2018-1-18, Salary: ¥12,345.12 定义信息格式 System.out.println(result); } /** * NumberFormat: 格式化数字到数字字符串, 或货币字符串的工具类 * 1. 通过工厂方法获取 NumberFormat 对象 * NumberFormat.getNumberInstance(locale); //仅格式化为数字的字符串 * NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(locale); //格式为货币的字符串 * * 2. 通过 format 方法来进行格式化 * 3. 通过 parse 方法把一个字符串解析为一个 Number 类型. */ @Test public void testNumberFormat() throws ParseException{ double d = 123456789.123d; Locale locale = Locale.FRANCE; NumberFormat numberFormat = NumberFormat.getNumberInstance(locale); String str = numberFormat.format(d); //123 456 789,123 System.out.println(str); NumberFormat numberFormat2 = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(locale); str = numberFormat2.format(d); //123 456 789,12 € System.out.println(str); str = "123 456 789,123"; d = (Double) numberFormat.parse(str); //1.23456789123E8 System.out.println(d); str = "123 456 789,12 €"; d = (Double) numberFormat2.parse(str); //1.2345678912E8 System.out.println(d); } @Test public void testDateFormat2() throws ParseException{ String str = "1990-12-12 12:12:12"; DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"); //Wed Dec 12 00:12:12 CST 1990 Date date = dateFormat.parse(str); System.out.println(date); } /** * DateFormat: 格式化日期的工具类. * DateFormate 本身是一个抽象类. * * 1. 若只希望通过 DateFormat 把一个 Date 对象转为一个字符串, 则可以通过 DateFormat 的工厂方法来获取 DateFormat 对象 * 2. 可以获取只格式化 Date 的 DateFormat 对象: getDateInstance(int style, Locale aLocale) * 3. 可以获取只格式化 Time 的 DateFormat 对象: getTimeInstance(int style, Locale aLocale) * 4. 可以获取既格式化 Date, 也格式化 Time 的 DateFormat 对象: * getDateTimeInstance(int dateStyle, int timeStyle, Locale aLocale) * 5. 其中 style 可以取值为: DateFormat 的常量: SHORT, MEDIUM, LONG, FULL. Locale 则为代表国家地区的 Locale 对象 * 6. 通过 DateFormat 的 format 方法来格式化个 Date 对象到字符串. * * 7. 若有一个字符串, 如何解析为一个 Date 对象呢 ? * I. 先创建 DateFormat 对象: 创建 DateFormat 的子类 SimpleDateFormat 对象 * SimpleDateFormat(String pattern). * 其中 pattern 为日期, 时间的格式, 例如: yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss * II. 调用 DateFormat 的 parse 方法来解析字符串到 Date 对象. * */ @Test public void testDateFormat(){ Locale locale = Locale.CHINA; Date date = new Date(); //Thu Jan 18 14:29:48 CST 2018 System.out.println(date); //获取 DateFormat 对象 2018年1月18日 14:30:29 DateFormat dateFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.LONG, DateFormat.MEDIUM, locale); String str = dateFormat.format(date); System.out.println(str); } /** * Locale: Java 中表示国家或地区的类. JDK 中提供了很多常量. * 也可以通过 Locale(languageCode, countryCode) 的方式来创建 * 在 WEB 应用中可以通过 request.getLocale() 方法来获取. */ @Test public void testLocale(){ Locale locale = Locale.CHINA; // 中国 zh System.out.println(locale.getDisplayCountry()); System.out.println(locale.getLanguage()); // 美国 en locale = new Locale("en", "US"); System.out.println(locale.getDisplayCountry()); System.out.println(locale.getLanguage()); } }

date=Date
salary=Salary

date=u65E5u671F
salary=u5DE5u8D44

date=Date
salary=Salary

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5">
<display-name>i18n</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>

<%@page import="java.util.Locale"%> <%@page import="java.util.Date"%> <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %> <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <% Date date = new Date(); request.setAttribute("date", date); request.setAttribute("salary", 12345.67); %> <%-- <fmt:bundle basename="i18n"> <fmt:message key="date"></fmt:message>: <fmt:formatDate value="${date }"/>, <fmt:message key="salary"></fmt:message>: <fmt:formatNumber value="${salary }"></fmt:formatNumber> </fmt:bundle> <br><br> --%> <% String code = request.getParameter("code"); if(code != null){ if("en".equals(code)){ session.setAttribute("locale", Locale.US); }else if("zh".equals(code)){ session.setAttribute("locale", Locale.CHINA); } } %> <c:if test="${sessionScope.locale != null }"> <fmt:setLocale value="${sessionScope.locale }"/> </c:if> <fmt:setBundle basename="i18n"/> <fmt:message key="date"></fmt:message>: <fmt:formatDate value="${date }" dateStyle="FULL"/>, <fmt:message key="salary"></fmt:message>: <fmt:formatNumber value="${salary }" type="currency"></fmt:formatNumber> <br><br> <a href="index.jsp?code=en">English</a> <a href="index.jsp?code=zh">中文</a> </body> </html>