JAVA--IO流
(一) IO原理与概念
一、概念
流:流动 、流向 从一端移动到另一端 源头与目的地
程序 与 文件|数组|网络连接|数据库 ,以程序为中心
二、IO流分类
流向: 输入流与输出流
数据:字节流:二进制,可以一切文件 包括 纯文本 doc 音频、视频等等
字符流:文本文件,只能处理纯文本
3、功能:节点:包裹源头
处理:增强功能,提供性能
三、字符流与字节流 (重点) 与文件
1、字节流
输入流:InputStream read(byte[] b) 、read(byte[] b, int off, int len) +close()
FileInputStream()
输出流:OutputStream write(byte[] b) write(byte[] b, int off, int len) +flush() +close()
FileOutputStream
2、字符流
输入流:Reader read(char[] cbuf) read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) +close()
FileReader()
输出流:Writer write(char[] cbuf) write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) +flush() +close()
write(String str, int off, int len)
FileWriter()
四、操作
1、 举例:搬家 -->读取文件
1)、关联房子 --->建立与文件联系
2)、选择搬家 -->选择对应流
3)、搬家 -->读取|写出
a)、卡车大小 --->数组大小
b)、运输 -->读取、写出
4)、打发over -->释放资源
2、操作
1)建立联系
2)选择流
3)操作 数组大小+read 、write
4)释放资源
(二)字节流
字节流:可以处理一切文件,包括二进制 音频、视频 、doc等
节点流: InputStream FileInputStream
OutputStream FileOutputStream
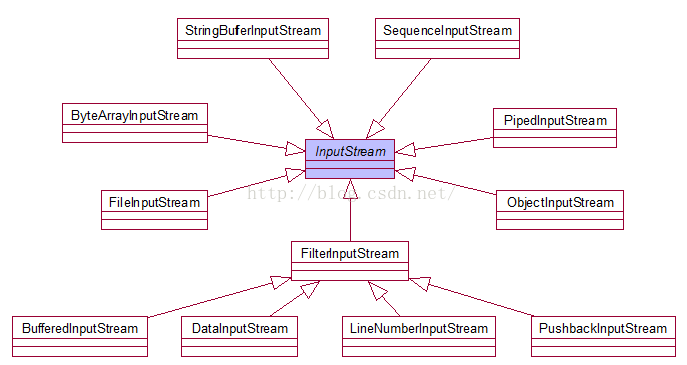
一、读取文件
1、建立联系 File对象 源头
2、选择流 文件输入流 InputStream FileInputStream
3、操作 : byte[] car =new byte[1024]; +read+读取大小
输出
4、释放资源 :关闭
5 类图

package com.bjsxt.io.byteIO; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; /** * 文件的读取 * 1、建立联系 File对象 2、选择流 文件输入流 InputStream FileInputStream 3、操作 : byte[] car =new byte[1024]; +read+读取大小 输出 4、释放资源 :关闭 * @author Administrator * */ public class Demo01 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { //1、建立联系 File对象 File src =new File("e:/xp/test/a.txt"); //2、选择流 InputStream is =null; //提升作用域 try { is =new FileInputStream(src); //3、操作 不断读取 缓冲数组 byte[] car =new byte[1024]; int len =0; //接收 实际读取大小 //循环读取 StringBuilder sb =new StringBuilder(); while(-1!=(len=is.read(car))){ //输出 字节数组转成字符串 String info =new String(car,0,len); sb.append(info); } System.out.println(sb.toString()); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("文件不存在"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("读取文件失败"); }finally{ try { //4、释放资源 if (null != is) { is.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { System.out.println("关闭文件输入流失败"); } } } }
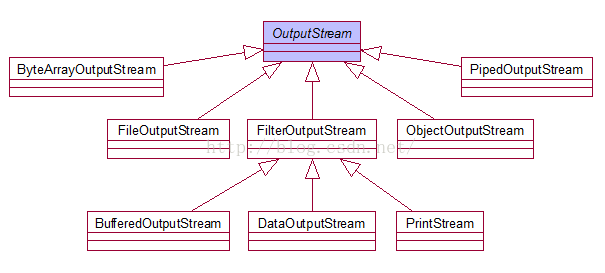
二、写出文件
1、建立联系 File对象 目的地
2、选择流 文件输出流 OutputStream FileOutputStream
3、操作 : write() +flush
4、释放资源 :关闭
5 类图

package com.bjsxt.io.byteIO; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; /** * 写出文件 1、建立联系 File对象 目的地 2、选择流 文件输出流 OutputStream FileOutputStream 3、操作 : write() +flush 4、释放资源 :关闭 * @author Administrator * */ public class Demo02 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { //1、建立联系 File对象 目的地 File dest =new File("e:/xp/test/test.txt"); //2、选择流 文件输出流 OutputStream FileOutputStream OutputStream os =null; //以追加形式 写出文件 必须为true 否则为覆盖 try { os =new FileOutputStream(dest,true); //3、操作 String str="bjsxt is very good "; //字符串转字节数组 byte[] data =str.getBytes(); os.write(data,0,data.length); os.flush(); //强制刷新出去 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("文件未找到"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("文件写出失败"); }finally{ //4、释放资源 :关闭 try { if (null != os) { os.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { System.out.println("关闭输出流失败"); } } } }
三、文件拷贝 程序为桥梁
1、建立联系 File对象 源头 目的地
2、选择流
文件输入流 InputStream FileInputStream
文件输出流 OutputStream FileOutputStream
3、操作 : 拷贝
byte[] flush =new byte[1024];
int len =0;
while(-1!=(len=输入流.read(flush))){
输出流.write(flush,0,len)
}
输出流.flush

package com.bjsxt.io.byteIO; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; /** 1、建立联系 File对象 源头 目的地 2、选择流 文件输入流 InputStream FileInputStream 文件输出流 OutputStream FileOutputStream 3、操作 : 拷贝 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len=输入流.read(flush))){ 输出流.write(flush,0,len) } 输出流.flush 4、释放资源 :关闭 两个流 * @author Administrator * */ public class CopyFileDemo { /** * @param args * @throws FileNotFoundException */ public static void main(String[] args) { String src ="E:/xp/test"; String dest="e:/xp/test/4.jpg"; try { copyFile(src,dest); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("文件不存在"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("拷贝文件失败|关闭流失败"); } } /** * 文件的拷贝 * @param 源文件路径 * @param 目录文件路径 * @throws FileNotFoundException,IOException * @return */ public static void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { //1、建立联系 源(存在且为文件) +目的地(文件可以不存在) File src =new File(srcPath); File dest =new File(destPath); if(! src.isFile()){ //不是文件或者为null System.out.println("只能拷贝文件"); throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件"); } //2、选择流 InputStream is =new FileInputStream(src); OutputStream os =new FileOutputStream(dest); //3、文件拷贝 循环+读取+写出 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; int len =0; //读取 while(-1!=(len=is.read(flush))){ //写出 os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); //强制刷出 //关闭流 os.close(); is.close(); } }
4、释放资源 :关闭 两个流
四、文件夹拷贝
1、递归查找子孙级文件|文件夹
2、文件 复制(IO流复制)
文件夹 创建
3、 A
/
as.txt b
|
b.txt
AA
|
A
/
a.txt b
|
b.txt
4、不能将父目录拷贝到子目录中
删除超长目录

package com.bjsxt.io.byteIO; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; /** * 文件夹的拷贝 * 1、文件 赋值 copyFile * 2、文件 创建 mkdirs() * 3、递归查找子孙级 * * @author Administrator * */ public class CopyDir { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { //源目录 String srcPath="E:/xp/test/a"; //目标目录 String destPath="E:/xp/test/a/b"; try { FileUtil.copyDir(srcPath,destPath); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 拷贝文件夹 * @param src 源路径 * @param dest 目标路径 */ public static void copyDir(String srcPath,String destPath){ File src=new File(srcPath); File dest =new File(destPath); copyDir(src,dest); } /** * 拷贝文件夹 * @param src 源File对象 * @param dest 目标File对象 */ public static void copyDir(File src,File dest){ if(src.isDirectory()){ //文件夹 dest =new File(dest,src.getName()); } copyDirDetail(src,dest); } /** * 拷贝文件夹细节 * @param src * @param dest */ public static void copyDirDetail(File src,File dest){ if(src.isFile()){ //文件 try { FileUtil.copyFile(src, dest); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }else if(src.isDirectory()){ //文件夹 //确保目标文件夹存在 dest.mkdirs(); //获取下一级目录|文件 for(File sub:src.listFiles()){ copyDirDetail(sub,new File(dest,sub.getName())); } } } }

package com.bjsxt.io.byteIO; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; /** * 文件操作 * 1、文件拷贝 * 2、文件夹拷贝 拒绝自己拷贝给自己 * @author Administrator * */ public class FileUtil { /** * 拷贝文件夹 * @param src 源路径 * @param dest 目标路径 * @throws IOException * @throws FileNotFoundException */ public static void copyDir(String srcPath,String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException{ //拒绝自己拷贝给自己 if(srcPath.equals(destPath)){ return ; } File src=new File(srcPath); File dest =new File(destPath); copyDir(src,dest); } /** * 拷贝文件夹 * @param src 源File对象 * @param dest 目标File对象 * @throws IOException * @throws FileNotFoundException */ public static void copyDir(File src,File dest) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException{ if(src.isDirectory()){ //文件夹 dest =new File(dest,src.getName()); if(dest.getAbsolutePath().contains(src.getAbsolutePath())){ System.out.println("父目录不能拷贝到子目录中"); return; } } copyDirDetail(src,dest); } /** * 拷贝文件夹细节 * @param src * @param dest */ public static void copyDirDetail(File src,File dest) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException{ if(src.isFile()){ //文件 try { FileUtil.copyFile(src, dest); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { //e.printStackTrace(); throw e; } catch (IOException e) { //e.printStackTrace(); throw e; } }else if(src.isDirectory()){ //文件夹 //确保目标文件夹存在 dest.mkdirs(); //获取下一级目录|文件 for(File sub:src.listFiles()){ copyDirDetail(sub,new File(dest,sub.getName())); } } } /** * 文件的拷贝 * @param 源文件路径 * @param 目录文件路径 * @throws FileNotFoundException,IOException * @return */ public static void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { //1、建立联系 源(存在且为文件) +目的地(文件可以不存在) copyFile(new File(srcPath),new File(destPath)); } /** * 文件的拷贝 * @param 源文件File对象 * @param 目录文件File对象 * @throws FileNotFoundException,IOException * @return */ public static void copyFile(File src,File dest) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { if(! src.isFile()){ //不是文件或者为null System.out.println("只能拷贝文件"); throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件"); } //dest为已经存在的文件夹,不能建立于文件夹同名的文件 if(dest.isDirectory()){ System.out.println(dest.getAbsolutePath()+"不能建立于文件夹同名的文件"); throw new IOException(dest.getAbsolutePath()+"不能建立于文件夹同名的文件"); } //2、选择流 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); OutputStream os =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest)); //3、文件拷贝 循环+读取+写出 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; int len =0; //读取 while(-1!=(len=is.read(flush))){ //写出 os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); //强制刷出 //关闭流 os.close(); is.close(); } }
(三) 字符流
字符流:只能处理 纯文本,全部为可见字符 .txt .html
节点流 Reader FileReader
Writer FileWriter
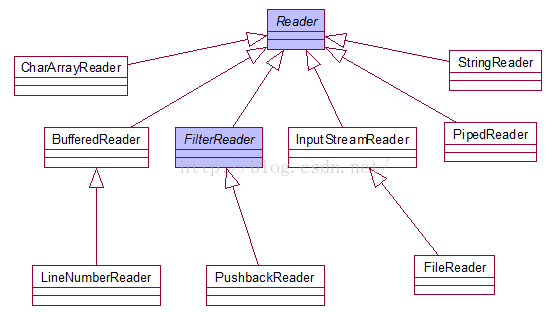
一、纯文本读取
1、建立联系
2、选择流 Reader FileReader
3、读取 char[] flush =new char[1024];
4、关闭
5 类图

package com.bjsxt.io.charIO; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; /** * 纯文本读取 * @author Administrator * */ public class Demo01 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { //创建源 File src =new File("E:/xp/test/a.txt"); //选择流 Reader reader =null; try { reader =new FileReader(src); //读取操作 char[] flush =new char[1024]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len=reader.read(flush))){ //字符数组转成 字符串 String str =new String(flush,0,len); System.out.println(str); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("源文件不存在"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("文件读取失败"); }finally{ try { if (null != reader) { reader.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { } } } }
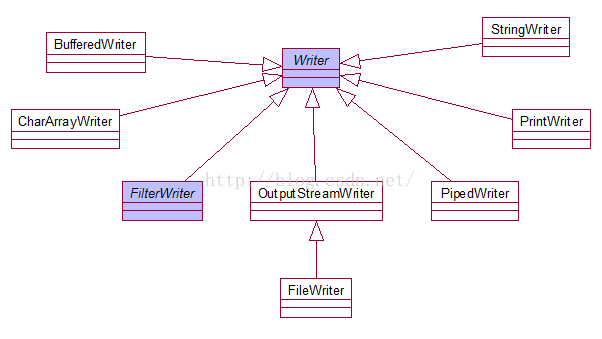
二、纯文本写出
1、建立联系
2、选择流 Writer FileWriter
3、读取 write(字符数组,0,长度)+flush
write(字符串)
append(字符|字符串)
4、关闭
5 类图

package com.bjsxt.io.charIO; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Writer; /** * 写出文件 * @author Administrator * */ public class Demo02 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { //创建源 File dest =new File("e:/xp/test/char.txt"); //选择流 Writer wr =null; try { //追加文件,而不是覆盖文件 wr =new FileWriter(dest); //写出 String msg ="追加.....锄禾日当午 码农真辛苦 一本小破书 一读一上午"; wr.write(msg); wr.append("倒萨发了看电视剧 "); wr.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { if (null != wr) { wr.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { } } } }

package com.bjsxt.io.charIO; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; import java.io.Writer; /** * 纯文本拷贝 * @author Administrator * */ public class CopyFileDemo { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { //创建源 仅限于 字符的纯文本 File src =new File("E:/xp/test/Demo03.java"); File dest =new File("e:/xp/test/char.txt"); //选择流 Reader reader =null; Writer wr =null; try { reader =new FileReader(src); wr =new FileWriter(dest); //读取操作 char[] flush =new char[1024]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len=reader.read(flush))){ wr.write(flush, 0, len); } wr.flush();//强制刷出 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("源文件不存在"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("文件读取失败"); }finally{ try { if (null != wr) { wr.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { } try { if (null != reader) { reader.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { } } } }
(四) 处理流
处理流:增强功能、提供性能,节点流之上
一、缓冲流
1)、字节缓冲流
BufferedInputStream
BufferedOutputStream

package com.bjsxt.io.buffered; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; /** * 字节流文件拷贝+缓冲流 ,提高性能 * 缓冲流(节点流) * @author Administrator * */ public class BufferedByteDemo { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { } /** * 文件的拷贝 * @param 源文件路径 * @param 目录文件路径 * @throws FileNotFoundException,IOException * @return */ public static void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { //1、建立联系 源(存在且为文件) +目的地(文件可以不存在) File src =new File(srcPath); File dest =new File(destPath); if(! src.isFile()){ //不是文件或者为null System.out.println("只能拷贝文件"); throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件"); } //2、选择流 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); OutputStream os =new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(dest)); //3、文件拷贝 循环+读取+写出 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; int len =0; //读取 while(-1!=(len=is.read(flush))){ //写出 os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); //强制刷出 //关闭流 os.close(); is.close(); } }
2)、字符缓冲流
BufferedReader readLine()
BufferedWriter newLine()

File src =new File("E:/xp/test/Demo03.java"); File dest =new File("e:/xp/test/char.txt"); //选择流 BufferedReader reader =null; BufferedWriter wr =null; try { reader =new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src)); wr =new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest)); //读取操作 /* char[] flush =new char[1024]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len=reader.read(flush))){ wr.write(flush, 0, len); }*/ //新增方法的操作 String line =null; while(null!=(line=reader.readLine())){ wr.write(line); //wr.append(" "); wr.newLine(); //换行符号 } wr.flush();//强制刷出 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace();
二、转换流: 字节流 转为字符流 处理乱码(编码集、解码集)
1、编码与解码概念
编码: 字符 ---编码字符集>二进制
解码 : 二进制 --解码字符集-> 字符
2、乱码:
1)编码与解码的字符集不统一
2)字节缺少,长度丢失
3、文件乱码
InputStreamReader(字节输入流,"解码集")
OutputStreamWriter(字符输出流,"编码集")

package com.bjsxt.io.convert; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; public class ConverDemo01 { /** * @param args * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { String str ="中国"; byte[] data =str.getBytes(); //字节数不完整 System.out.println(new String(data,0,3)); } /** * 编码与解码字符集必须相同,否则乱码 * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException */ public static void test1() throws UnsupportedEncodingException{ //解码 byte -->char String str ="中国"; //gbk //编码 char -->byte byte[] data =str.getBytes(); //编码与解码字符集同一 System.out.println(new String(data)); data =str.getBytes("utf-8"); //设定编码字符集 //不同一出现乱码 System.out.println(new String(data)); //编码 byte[] data2 = "中国".getBytes("utf-8"); //解码 str=new String(data2,"utf-8"); System.out.println(str); } }

package com.bjsxt.io.convert; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; /** * 转换流: 字节转为字符 * 1、输出流 OutputStreamWriter 编码 * 2、输入流 InputStreamReader 解码 * * 确保源不能为乱码 * @author Administrator * */ public class ConverDemo02 { /** * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //指定解码字符集 BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader( new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream( new File("E:/xp/test/Demo03.java"))),"UTF-8") ); //写出文件 编码 BufferedWriter bw =new BufferedWriter( new OutputStreamWriter( new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(new File("E:/xp/test/encode.java"))))); String info =null; while(null!=(info=br.readLine())){ //System.out.println(info); bw.write(info); bw.newLine(); } bw.flush(); bw.close(); br.close(); } }
(五) 处理流
一、节点流
1、字节数组 字节 节点流
输入流:ByteArrayInputStream read(byte[] b, int off, int len) + close()
输出流:ByteArrayOutputStream write(byte[] b, int off, int len) +toByteArray() 不要使用多态

package com.bjsxt.io.others; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; /** * 字节数组 节点流 * 数组的长度有限 ,数据量不会很大 * * 文件内容不用太大 * 1、文件 --程序->字节数组 * 2、字节数组 --程序->文件 * * * * @author Administrator * */ public class ByteArrayDemo01 { /** * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { read(write()); } /** * 输出流 操作与文件输出流 有些不同, 有新增方法,不能使用多态 * @throws IOException */ public static byte[] write() throws IOException{ //目的地 byte[] dest; //选择流 不同点 ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //操作 写出 String msg ="操作与 文件输入流操作一致"; byte[] info =msg.getBytes(); bos.write(info, 0, info.length); //获取数据 dest =bos.toByteArray(); //释放资源 bos.close(); return dest; } /** * 输入流 操作与 文件输入流操作一致 * 读取字节数组 * @throws IOException */ public static void read(byte[] src) throws IOException{ //数据源传入 //选择流 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream( new ByteArrayInputStream( src ) ); //操作 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len=is.read(flush))){ System.out.println(new String(flush,0,len)); } //释放资源 is.close(); } }

package com.bjsxt.io.others; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; /** *1、文件 --程序->字节数组 *1)、文件输入流 * 字节数组输出流 * * * 2、字节数组 --程序->文件 * 1)、字节数组输入流 * 文件输出流 * @author Administrator * */ public class ByteArrayDemo02 { /** * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { byte[] data =getBytesFromFile("e:/xp/test/1.jpg"); toFileFromByteArray(data,"e:/xp/test/arr.jpg"); } /** * 2、字节数组 --程序->文件 */ public static void toFileFromByteArray(byte[] src,String destPath) throws IOException{ //创建源 //目的地 File dest=new File(destPath); //选择流 //字节数组输入流 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(src)); //文件输出流 OutputStream os =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest)); //操作 不断读取字节数组 byte[] flush =new byte[1]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len =is.read(flush))){ //写出到文件中 os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); //释放资源 os.close(); is.close(); } /** * 1、文件 --程序->字节数组 * @return * @throws IOException */ public static byte[] getBytesFromFile(String srcPath) throws IOException{ //创建文件源 File src =new File(srcPath); //创建字节数组目的地 byte[] dest =null; //选择流 //文件输入流 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); //字节数组输出流 不能使用多态 ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //操作 不断读取文件 写出到字节数组流中 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len =is.read(flush))){ //写出到字节数组流中 bos.write(flush, 0, len); } bos.flush(); //获取数据 dest =bos.toByteArray(); bos.close(); is.close(); return dest; } }
二、处理流
1、基本类型+String 保留数据+类型
输入流:DataInputStream readXxx
输出流:DataOutputStream writeXxx

package com.bjsxt.io.others; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; /** * 数据类型(基本+String)处理流 * 1、输入流 DataInputStream readXxx() * 2、输出流 DataOutputStream writeXxx() * 新增方法不能使用多态 * * java.io.EOFException :没有读取到相关的内容 * @author Administrator * */ public class DataDemo01 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { try { //write("e:/xp/test/data.txt"); //read("e:/xp/test/arr.txt"); //非法内容 read("e:/xp/test/data.txt"); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 从文件读取数据+类型 * @throws IOException */ public static void read(String destPath) throws IOException{ //创建源 File src =new File(destPath); //选择流 DataInputStream dis =new DataInputStream( new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream(src) ) ); //操作 读取的顺序与写出一致 必须存在才能读取 //不一致,数据存在问题 long num2 =dis.readLong(); double num1 =dis.readDouble(); String str =dis.readUTF(); dis.close(); System.out.println(num2+"-->"+str); } /** * 数据+类型输出到文件 * @throws IOException */ public static void write(String destPath) throws IOException{ double point =2.5; long num=100L; String str ="数据类型"; //创建源 File dest =new File(destPath); //选择流 DataOutputStream DataOutputStream dos =new DataOutputStream( new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(dest) ) ); //操作 写出的顺序 为读取准备 dos.writeDouble(point); dos.writeLong(num); dos.writeUTF(str); dos.flush(); //释放资源 dos.close(); } }

package com.bjsxt.io.others; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; /** * 数据类型(基本+String)处理流 * 1、输入流 DataInputStream readXxx() * 2、输出流 DataOutputStream writeXxx() * 新增方法不能使用多态 * * java.io.EOFException :没有读取到相关的内容 * @author Administrator * */ public class DataDemo02 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { try { byte[] data=write(); read(data); System.out.println(data.length); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 从字节数组读取数据+类型 * @throws IOException */ public static void read(byte[] src) throws IOException{ //选择流 DataInputStream dis =new DataInputStream( new BufferedInputStream( new ByteArrayInputStream(src) ) ); //操作 读取的顺序与写出一致 必须存在才能读取 double num1 =dis.readDouble(); long num2 =dis.readLong(); String str =dis.readUTF(); dis.close(); System.out.println(num1+"-->"+num2+"-->"+str); } /** * 数据+类型输出到字节数组中 * @throws IOException */ public static byte[] write() throws IOException{ //目标数组 byte[] dest =null; double point =2.5; long num=100L; String str ="数据类型"; //选择流 ByteArrayOutputStream DataOutputStream ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); DataOutputStream dos =new DataOutputStream( new BufferedOutputStream( bos ) ); //操作 写出的顺序 为读取准备 dos.writeDouble(point); dos.writeLong(num); dos.writeUTF(str); dos.flush(); dest =bos.toByteArray(); //释放资源 dos.close(); return dest; } }
2、引用类型 (对象) 保留数据+类型
反序列化 输入流:ObjectInputStream readObject()
序列化 输出流:ObjectOutputStream writeObject()
注意:
1)、先序列化后反序列化;反序列化顺序必须与序列化一致
2)、不是所有的对象都可以序列化, java.io.Serializable
不是所有的属性都需要序列化,transient

package com.bjsxt.io.others; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; /** * 数据类型(基本+String)处理流 * 1、输入流 DataInputStream readXxx() * 2、输出流 DataOutputStream writeXxx() * 新增方法不能使用多态 * * java.io.EOFException :没有读取到相关的内容 * @author Administrator * */ public class DataDemo02 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { try { byte[] data=write(); read(data); System.out.println(data.length); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 从字节数组读取数据+类型 * @throws IOException */ public static void read(byte[] src) throws IOException{ //选择流 DataInputStream dis =new DataInputStream( new BufferedInputStream( new ByteArrayInputStream(src) ) ); //操作 读取的顺序与写出一致 必须存在才能读取 double num1 =dis.readDouble(); long num2 =dis.readLong(); String str =dis.readUTF(); dis.close(); System.out.println(num1+"-->"+num2+"-->"+str); } /** * 数据+类型输出到字节数组中 * @throws IOException */ public static byte[] write() throws IOException{ //目标数组 byte[] dest =null; double point =2.5; long num=100L; String str ="数据类型"; //选择流 ByteArrayOutputStream DataOutputStream ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); DataOutputStream dos =new DataOutputStream( new BufferedOutputStream( bos ) ); //操作 写出的顺序 为读取准备 dos.writeDouble(point); dos.writeLong(num); dos.writeUTF(str); dos.flush(); dest =bos.toByteArray(); //释放资源 dos.close(); return dest; } }

package com.bjsxt.io.others; /** * 空接口只是标识 * @author Administrator * */ public class Employee implements java.io.Serializable { //不需要序列化 private transient String name; private double salary; public Employee() { } public Employee(String name, double salary) { super(); this.name = name; this.salary = salary; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public void setSalary(double salary) { this.salary = salary; } }
3、打印流 PrintStream println() print()

package com.bjsxt.io.others; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.PrintStream; /** * PrintStream 打印流 -->处理流 * @author Administrator * */ public class PrintStreamDemo01 { /** * @param args * @throws FileNotFoundException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { System.out.println("test"); PrintStream ps =System.out; ps.println(false); //输出到文件 File src = new File("e:/xp/test/print.txt"); ps = new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(src))); ps.println("io is so easy...."); ps.close(); } }
4、三个常量 : System.in /out/err System.setIn() setOut() setErr()

package com.bjsxt.io.others; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.FileDescriptor; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.PrintStream; import java.util.Scanner; /** * 三个常量 * 1、System.in 输入流 键盘输入 * 2、System.out 输出流 控制台输出 * System.err * * ==>重定向 * setIn() * setOut() * setErr() * FileDescriptor.in * FileDescriptor.out * @author Administrator * */ public class SystemDemo01 { /** * @param args * @throws FileNotFoundException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { //test1(); //test2(); //重定向 System.setOut(new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("e:/xp/test/print.txt")),true)); System.out.println("a"); //控制台 -->文件 System.out.println("test"); //回控制台 System.setOut(new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.out)),true)); System.out.println("back...."); } public static void test2() throws FileNotFoundException{ InputStream is =System.in; //键盘输入 is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("e:/xp/test/print.txt")); Scanner sc = new Scanner(is); //System.out.println("请输入:"); System.out.println(sc.nextLine()); } public static void test1(){ System.out.println("test"); System.err.println("err"); } }

package com.bjsxt.io.others; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; /** * 封装输入 * @author Administrator * */ public class BuffereIn { /** * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { InputStream is =System.in; BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is)); System.out.println("请输入。。。。"); String msg =br.readLine(); System.out.println(msg); }
(六)文件分割与合并

package com.bjsxt.io.others; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import com.bjsxt.io.util.FileUtil; /** * 文件的分割思路 * 1、分割的块数 size n块 * 2、每一块的大小 blockSize * 最后:总的文件大小 -(n-1)*blockSize * * @author Administrator * */ public class RndDemo01 { /** * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { RandomAccessFile rnd =new RandomAccessFile(new File("E:/xp/20130502/test/test.java"),"r"); rnd.seek(40); //定义缓冲大小 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; //接收长度 int len =0; while(-1!=(len=rnd.read(flush))){ if(len>=20){ System.out.println(new String(flush,0,20)); break; }else{ System.out.println(new String(flush,0,len)); } } FileUtil.close(rnd); } }

package com.bjsxt.io.others; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.io.SequenceInputStream; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Vector; import com.bjsxt.io.util.FileUtil; public class SplitFile { //文件的路径 private String filePath; //文件名 private String fileName; //文件大小 private long length; //块数 private int size; //每块的大小 private long blockSize; //分割后的存放目录 private String destBlockPath; //每块的名称 private List<String> blockPath; public SplitFile(){ blockPath = new ArrayList<String>(); } public SplitFile(String filePath,String destBlockPath){ this(filePath,destBlockPath,1024); } public SplitFile(String filePath,String destBlockPath,long blockSize){ this(); this.filePath= filePath; this.destBlockPath =destBlockPath; this.blockSize=blockSize; init(); } /** * 初始化操作 计算 块数、确定文件名 */ public void init(){ File src =null; //健壮性 if(null==filePath ||!(((src=new File(filePath)).exists()))){ return; } if(src.isDirectory()){ return ; } //文件名 this.fileName =src.getName(); //计算块数 实际大小 与每块大小 this.length = src.length(); //修正 每块大小 if(this.blockSize>length){ this.blockSize =length; } //确定块数 size= (int)(Math.ceil(length*1.0/this.blockSize)); //确定文件的路径 initPathName(); } private void initPathName(){ for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ this.blockPath.add(destBlockPath+"/"+this.fileName+".part"+i); } } /** * 文件的分割 * 0)、第几块 * 1、起始位置 * 2、实际大小 * @param destPath 分割文件存放目录 */ public void split(){ long beginPos =0; //起始点 long actualBlockSize =blockSize; //实际大小 //计算所有块的大小、位置、索引 for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ if(i==size-1){ //最后一块 actualBlockSize =this.length-beginPos; } spiltDetail(i,beginPos,actualBlockSize); beginPos+=actualBlockSize; //本次的终点,下一次的起点 } } /** * 文件的分割 输入 输出 * 文件拷贝 * @param idx 第几块 * @param beginPos 起始点 * @param actualBlockSize 实际大小 */ private void spiltDetail(int idx,long beginPos,long actualBlockSize){ //1、创建源 File src = new File(this.filePath); //源文件 File dest = new File(this.blockPath.get(idx)); //目标文件 //2、选择流 RandomAccessFile raf = null; //输入流 BufferedOutputStream bos=null; //输出流 try { raf=new RandomAccessFile(src,"r"); bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest)); //读取文件 raf.seek(beginPos); //缓冲区 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; //接收长度 int len =0; while(-1!=(len=raf.read(flush))){ if(actualBlockSize-len>=0){ //查看是否足够 //写出 bos.write(flush, 0, len); actualBlockSize-=len; //剩余量 }else{ //写出最后一次的剩余量 bos.write(flush, 0, (int)actualBlockSize); break; } } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ FileUtil.close(bos,raf); } } /** * 文件的合并 */ public void merge(String destPath){ //创建源 File dest =new File(destPath); //选择流 BufferedOutputStream bos=null; //输出流 SequenceInputStream sis =null ;//输入流 //创建一个容器 Vector<InputStream> vi = new Vector<InputStream>(); try { for (int i = 0; i < this.blockPath.size(); i++) { vi.add(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(this.blockPath.get(i))))); } bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest,true)); //追加 sis=new SequenceInputStream(vi.elements()); //缓冲区 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; //接收长度 int len =0; while(-1!=(len=sis.read(flush))){ bos.write(flush, 0, len); } bos.flush(); FileUtil.close(sis); } catch (Exception e) { }finally{ FileUtil.close(bos); } } /** * 文件的合并 */ public void merge1(String destPath){ //创建源 File dest =new File(destPath); //选择流 BufferedOutputStream bos=null; //输出流 try { bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest,true)); //追加 BufferedInputStream bis = null; for (int i = 0; i < this.blockPath.size(); i++) { bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(this.blockPath.get(i)))); //缓冲区 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; //接收长度 int len =0; while(-1!=(len=bis.read(flush))){ bos.write(flush, 0, len); } bos.flush(); FileUtil.close(bis); } } catch (Exception e) { }finally{ FileUtil.close(bos); } } /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { SplitFile split = new SplitFile("E:/xp/20130502/test/学员设置(20130502).xls","E:/xp/20130502",51); //System.out.println(split.size); //split.split(); split.merge("E:/xp/20130502/test1.xls"); } }
