题目太长了!下载地址【传送门】
第1题
简述:识别图片上的数字。
1 import numpy as np 2 import scipy.io as scio 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 import scipy.optimize as op 5 6 #显示图片数据 7 def displayData(X): 8 m = np.size(X, 0) #X的行数,即样本数量 9 n = np.size(X, 1) #X的列数,即单个样本大小 10 example_width = int(np.round(np.sqrt(n))) #单张图片宽度 11 example_height = int(np.floor(n / example_width)) #单张图片高度 12 display_rows = int(np.floor(np.sqrt(m))) #显示图中,一行多少张图 13 display_cols = int(np.ceil(m / display_rows)) #显示图中,一列多少张图片 14 pad = 1 #图片间的间隔 15 display_array = - np.ones((pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad), 16 pad + display_cols * (example_width + pad))) #初始化图片矩阵 17 curr_ex = 0 #当前的图片计数 18 #将每张小图插入图片数组中 19 for j in range(0, display_rows): 20 for i in range(0, display_cols): 21 if curr_ex >= m: 22 break 23 max_val = np.max(abs(X[curr_ex, :])) 24 jstart = pad + j * (example_height + pad) 25 istart = pad + i * (example_width + pad) 26 display_array[jstart: (jstart + example_height), istart: (istart + example_width)] = 27 np.array(X[curr_ex, :]).reshape(example_height, example_width) / max_val 28 curr_ex = curr_ex + 1 29 if curr_ex >= m: 30 break 31 display_array = display_array.T 32 plt.imshow(display_array,cmap=plt.cm.gray) 33 plt.axis('off') 34 plt.show() 35 36 #计算hθ(z) 37 def sigmoid(z): 38 g = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z)) 39 return g 40 41 #计算cost 42 def lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lamb): 43 theta = np.array(theta).reshape((np.size(theta), 1)) 44 m = np.size(y) 45 h = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta)) 46 J = 1 / m * (-np.dot(y.T, np.log(h)) - np.dot((1 - y.T), np.log(1 - h))) 47 theta2 = theta[1:, 0] 48 Jadd = lamb / (2 * m) * np.sum(theta2 ** 2) 49 J = J + Jadd 50 return J.flatten() 51 52 #计算梯度 53 def gradient(theta, X, y, lamb): 54 theta = np.array(theta).reshape((np.size(theta), 1)) 55 m = np.size(y) 56 h = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta)) 57 grad = 1/m*np.dot(X.T, h - y) 58 theta[0,0] = 0 59 gradadd = lamb/m*theta 60 grad = grad + gradadd 61 return grad.flatten() 62 63 #θ计算 64 def oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lamb): 65 m = np.size(X, 0) 66 n = np.size(X, 1) 67 all_theta = np.zeros((num_labels, n+1)) 68 one = np.ones(m) 69 X = np.insert(X, 0, values=one, axis=1) 70 for c in range(0, num_labels): 71 initial_theta = np.zeros(n+1) 72 y_t = (y==c) 73 result = op.minimize(fun=lrCostFunction, x0=initial_theta, args=(X, y_t, lamb), method='TNC', jac=gradient) 74 all_theta[c, :] = result.x 75 return all_theta 76 77 #计算准确率 78 def predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X): 79 m = np.size(X, 0) 80 num_labels = np.size(all_theta, 0) 81 p = np.zeros((m, 1)) #用来保存每行的最大值 82 g = np.zeros((np.size(X, 0), num_labels)) #用来保存每次分类后的结果(一共分类了10次,每次保存到一列上) 83 one = np.ones(m) 84 X = np.insert(X, 0, values=one, axis=1) 85 for c in range(0, num_labels): 86 theta = all_theta[c, :] 87 g[:, c] = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta.T)) 88 p = g.argmax(axis=1) 89 # print(p) 90 return p.flatten() 91 92 #加载数据文件 93 data = scio.loadmat('ex3data1.mat') 94 X = data['X'] 95 y = data['y'] 96 y = y%10 #因为数据集是考虑了matlab从1开始,把0的结果保存为了10,这里进行取余,将10变回0 97 m = np.size(X, 0) 98 rand_indices = np.random.randint(0,m,100) 99 sel = X[rand_indices, :] 100 displayData(sel) 101 102 #计算θ 103 lamb = 0.1 104 num_labels = 10 105 all_theta = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lamb) 106 # print(all_theta) 107 108 #计算预测的准确性 109 pred = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X) 110 # np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf) 111 #在计算这个上遇到了一个坑: 112 #pred输出的是[[...]]的形式,需要flatten变成1维向量,y同样用flatten变成1维向量 113 acc = np.mean(pred == y.flatten())*100 114 print('Training Set Accuracy:',acc,'%')
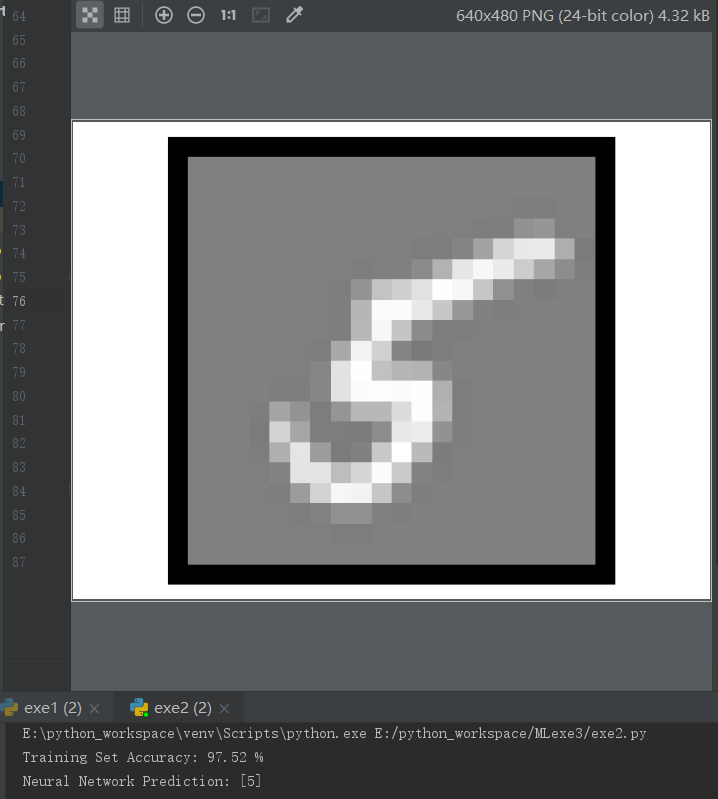
运行结果:
![]()
第2题
简介:使用神经网络实现数字识别(Θ已提供)
1 import numpy as np 2 import scipy.io as scio 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 import scipy.optimize as op 5 6 #显示图片数据 7 def displayData(X): 8 m = np.size(X, 0) #X的行数,即样本数量 9 n = np.size(X, 1) #X的列数,即单个样本大小 10 example_width = int(np.round(np.sqrt(n))) #单张图片宽度 11 example_height = int(np.floor(n / example_width)) #单张图片高度 12 display_rows = int(np.floor(np.sqrt(m))) #显示图中,一行多少张图 13 display_cols = int(np.ceil(m / display_rows)) #显示图中,一列多少张图片 14 pad = 1 #图片间的间隔 15 display_array = - np.ones((pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad), 16 pad + display_cols * (example_width + pad))) #初始化图片矩阵 17 curr_ex = 0 #当前的图片计数 18 #将每张小图插入图片数组中 19 for j in range(0, display_rows): 20 for i in range(0, display_cols): 21 if curr_ex >= m: 22 break 23 max_val = np.max(abs(X[curr_ex, :])) 24 jstart = pad + j * (example_height + pad) 25 istart = pad + i * (example_width + pad) 26 display_array[jstart: (jstart + example_height), istart: (istart + example_width)] = 27 np.array(X[curr_ex, :]).reshape(example_height, example_width) / max_val 28 curr_ex = curr_ex + 1 29 if curr_ex >= m: 30 break 31 display_array = display_array.T 32 plt.imshow(display_array,cmap=plt.cm.gray) 33 plt.axis('off') 34 plt.show() 35 36 #计算hθ(z) 37 def sigmoid(z): 38 g = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z)) 39 return g 40 41 #实现神经网络 42 def predict(theta1, theta2, X): 43 m = np.size(X,0) 44 p = np.zeros((np.size(X, 0), 1)) 45 #第二层计算 46 one = np.ones(m) 47 X = np.insert(X, 0, values=one, axis=1) 48 a2 = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta1.T)) 49 #第三层计算 50 one = np.ones(np.size(a2,0)) 51 a2 = np.insert(a2, 0, values=one, axis=1) 52 a3 = sigmoid(np.dot(a2, theta2.T)) 53 p = a3.argmax(axis=1) + 1 #y的值为1-10,所以此处0-9要加1 54 return p.flatten() 55 56 #读取数据文件 57 data = scio.loadmat('ex3data1.mat') 58 X = data['X'] 59 y = data['y'] 60 m = np.size(X, 0) 61 rand_indices = np.random.randint(0,m,100) 62 sel = X[rand_indices, :] 63 # displayData(sel) 64 65 theta = scio.loadmat('ex3weights.mat') 66 theta1 = theta['Theta1'] 67 theta2 = theta['Theta2'] 68 69 #预测准确率 70 pred = predict(theta1, theta2, X) 71 acc = np.mean(pred == y.flatten())*100 72 print('Training Set Accuracy:',acc,'%') 73 74 #识别单张图片 75 for i in range(0, m): 76 it = np.random.randint(0, m, 1) 77 it = it[0] 78 displayData(X[it:it+1, :]) 79 pred = predict(theta1, theta2, X[it:it+1, :]) 80 print('Neural Network Prediction:', pred) 81 print('input q to exit:') 82 cin = input() 83 if cin == 'q': 84 break
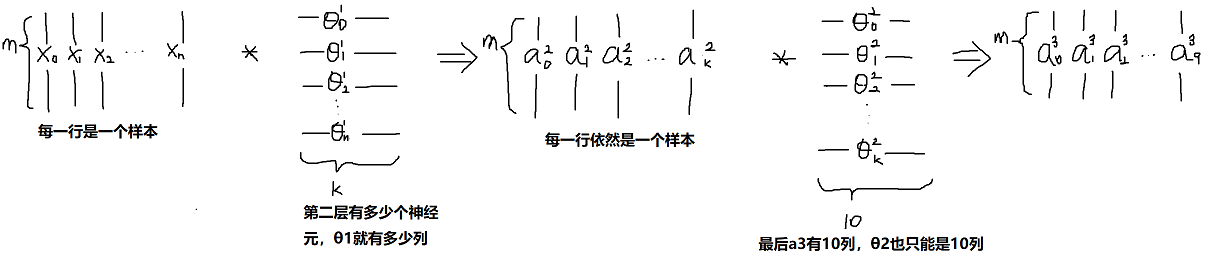
神经网络的矩阵表示分析:
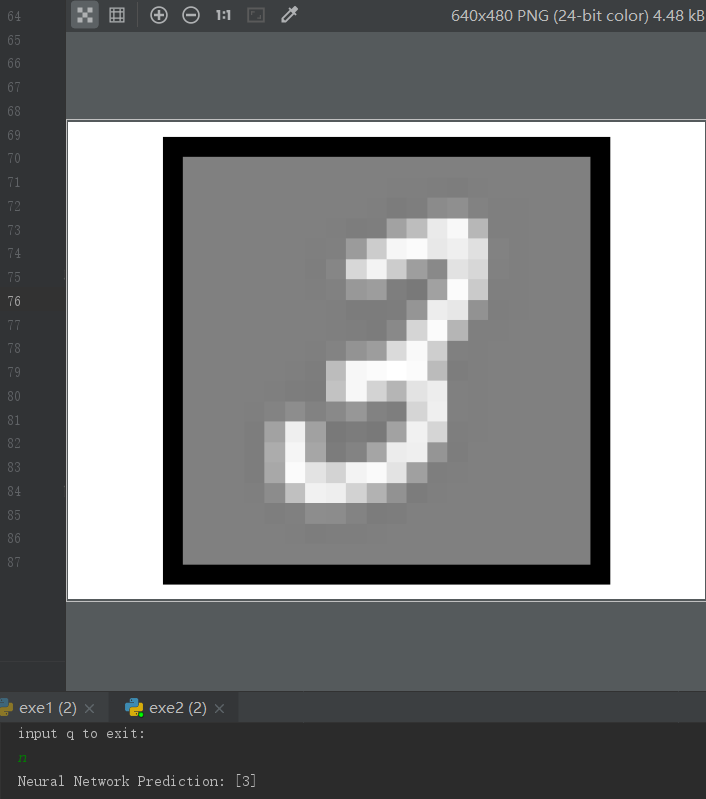
运行结果: