Hashtable 是 JDK 中较早的数据结构了,目前已不再推荐使用了。但抱着学习的目的,还是看了下它的实现。
简介
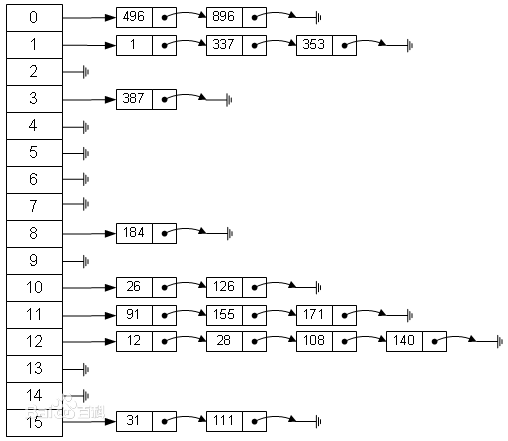
Hashtable,顾名思义即哈希表,是一种经典的数据结构。其基本结构是一个数组,而数组中的每个元素都是一个单向链表。哈希表的内部结构如下图:
先解释下 Hashtable 类中几个变量属性的含义:
/**
* The hash table data.
*/
private transient Entry<?,?>[] table;
/**
* The total number of entries in the hash table.
*/
private transient int count;
/**
* The table is rehashed when its size exceeds this threshold. (The
* value of this field is (int)(capacity * loadFactor).)
*
* @serial
*/
private int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hashtable.
*
* @serial
*/
private float loadFactor;
- table 即存放单向链表的数组;
- count 表示哈希表的元素总数;
- capacity 表示哈希表数组的总长度;
- loadFactor 表示负载因子,用于平衡时间和空间,默认值为:0.75
- threshold 表示哈希表自动扩容的阈值,其值即为:capacity * loadFactor
Hashtable 类为了提高查询速度,防止每个元素的单向链表过长,使用了自动扩容机制,下面就详细说说 Hashtable 的自动扩容机制。
自动扩容机制
学习自动扩容机制当然是从新增元素的 put 方法看起了:
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
添加一个元素实际上是调用了 addEntry 方法:
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
可以看到,在这个方法里判断了条件 count >= threshold ,也就是说当哈希表中的元素总数超过自动扩容阈值时就进行自动扩容。而实际的扩容方法则是 rehash:
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table;
// overflow-conscious code
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity];
modCount++;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap;
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry<K,V> e = old;
old = old.next;
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
}
扩容的主要逻辑就是:
- 将当前容量值乘以 2 之后再加 1,计算得到新的容量值;
- 若新容量值超过了哈希表允许的最大容量值,则取最大容量值;
- 以新容量值新生成一个数组;
- 遍历旧数组中的每个单向链表,遍历单向链表上的每个元素,然后重新计算哈希值,并放入新数组中;