整数因子分解问题
http://acm.sdut.edu.cn/onlinejudge2.dev/index.php/Home/Index/problemdetail/pid/1722.html
Time Limit: 1000 ms Memory Limit: 65536 KiB
Problem Description
大于1的正整数n可以分解为:n=x1*x2*…*xm。例如,当n=12 时,共有8 种不同的分解式:
12=12;
12=6*2;
12=4*3;
12=3*4;
12=3*2*2;
12=2*6;
12=2*3*2;
12=2*2*3。
对于给定的正整数n,计算n共有多少种不同的分解式。
12=12;
12=6*2;
12=4*3;
12=3*4;
12=3*2*2;
12=2*6;
12=2*3*2;
12=2*2*3。
对于给定的正整数n,计算n共有多少种不同的分解式。
Input
输入数据只有一行,有1个正整数n (1≤n≤2000000000)。
Output
将计算出的不同的分解式数输出。
Sample Input
12
Sample Output
8
算法一(超时)
算法思路:
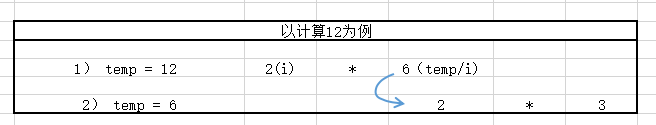
比如以 12为例,情况1)与 情况2)都应该计算在Count中,但情况2)是根据情况1)产生的。因此需要递归,每层函数对i进行遍历一遍,如果temp/i==0,说明该层的数可以被分解,再递归进入下一层。
代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int Count; 6 7 // 来计算整数因子分解问题 8 void func(int temp) { 9 10 for (int i = 2; i < temp; i++) { 11 if (temp%i == 0) { 12 Count++; 13 func(temp / i); 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 18 int main() { 19 20 Count = 0; 21 int temp; 22 cin >> temp; 23 func(temp); 24 cout << Count+1 << endl; 25 }
算法二(优化)
算法一存在的弊端:我们求(i,temp/i)中 temp/i 的因式分解个数时,会重复计算(如下图)
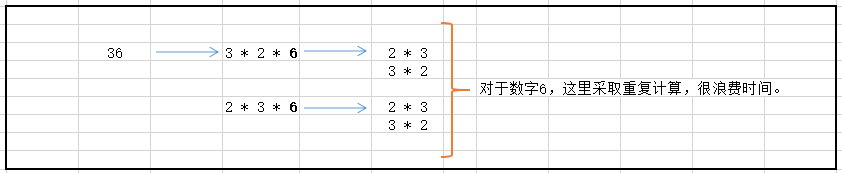
解决算法一的策略:我们采用一个数组直接存储数字6的因子,如果发现该arr[6]中存在数,则直接用避免重复计算。
算法思路:
依然采用递归,t = i * j,则 count(t) = count(i) + count(j);为避免重复计算 (t = i * j = j * i),应该限制 i < j,即 for(i;i<sqrt(t);i++)。

注意事项:
- 使用 map 时包含 <map>
- 使用 sqrt() 时包含 <math.h>
代码:
1 // 算法.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。 2 // 3 4 #include "pch.h" 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <math.h> 8 #include <algorithm> 9 using namespace std; 10 11 map<int, int> a; 12 13 int f(int n) { 14 15 if (a[n]) { 16 return a[n]; 17 } 18 19 int Count = 1; // x = x 20 for (int i = 2; i <= sqrt(n); i++) { 21 // 如果 x = j*k 可以分解,则先添加进 [j]。 22 if (n % i == 0) { 23 Count += f(i); 24 // 如果 j!=k,则再添加进k 25 if (i != n / i) { 26 Count += f(n / i); 27 } 28 } 29 30 } 31 32 a[n] = Count; // 记录在数组中,为之后的使用 33 return Count; 34 } 35 36 int main() { 37 int n; 38 cin >> n; 39 cout << f(n); 40 }