grpc使用记录(三)简单异步服务实例
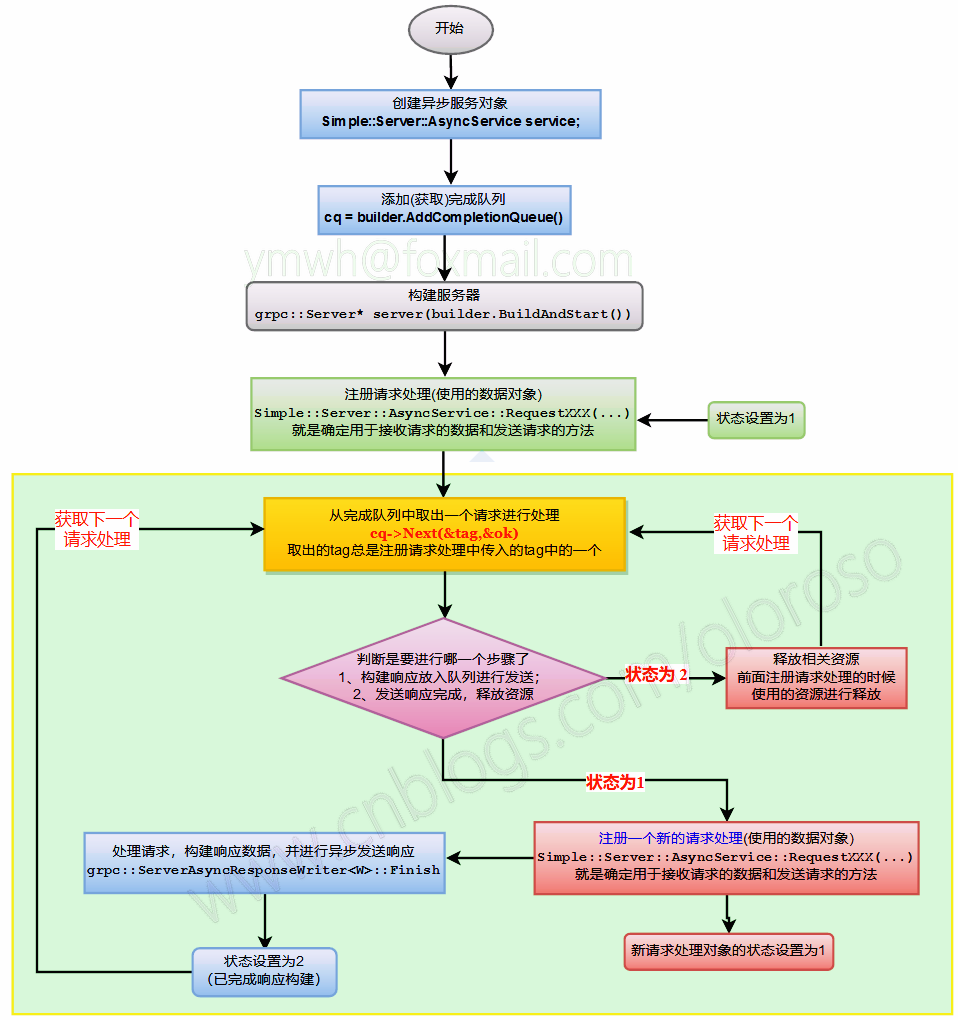
编写异步服务和编写同步服务的基本流程都差不多,稍有点区别。
同步服务你只需要实现相关服务接口的实现即可,不需要管理太多东西。异步服务GRPC运行时会把读取到的客户端请求放入CompletionQueue中,需要主动从中取出,然后进行相关的处理,可以多线程也可以单线程。
1、编写proto文件,定义服务
这里和grpc使用记录(二)简单同步服务实例中的一样,这里就不多说了。
2、编译proto文件,生成代码
这里也是和grpc使用记录(二)简单同步服务实例中的一样的。
3、编写服务端代码
这里可以复用前面同步服务的代码,只需要做简单的修改即可。
简单说一下创建一个GRPC异步服务的要点:
- 1、创建服务对象的时候要创建
AsyncService,而不是Service。 - 2、至少需要添加一个
grpc::ServerCompletionQueue用于异步任务操作。 - 3、必须要通过
AsyncService::RequestXXXX来注册XXXX接口的处理。 - 4、一个客户端请求的处理可简单的分为两个步骤:1、构建返回给客户端的响应数据;2、发送响应数据给客户端。
- 5、完成队列和注册请求处理都可以有多个,不一定非得是一个。
async_service.cpp
下面代码简单的创建了3个HandlerContext的结构体类型,用于保存三个接口请求处理过程中的数据,实际的请求处理还是和之前同步服务的一样,这里只是写成了Test1、Test2、Test3三个函数的形式。
// > g++ -o aservice async_service.cpp simple.grpc.pb.cc simple.pb.cc -std=c++11 -I. -lgrpc++ -lgrpc -lprotobuf -lgpr -lz -lcares -laddress_sorting -lpthread -Wno-deprecated
#include "simple.grpc.pb.h"
#include <grpcpp/grpcpp.h>
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
#include <strstream>
struct HandlerContext {
// 当前处理状态(处理分为两步:1处理请求构建响应数据;2发送响应)
// 这里记录一下完成到哪一步了,以便进行相关操作
int status_; // (1构建响应完成;2发送完成)
// rpc的上下文,允许通过它进行诸如压缩、身份验证,以及把元数据发回客户端等。
grpc::ServerContext ctx_;
};
struct HandlerTest1Context:public HandlerContext {
// 用于接收客户端发送的请求
Simple::TestRequest req_;
// 用于发送响应给客户端
Simple::TestNull rep_;
// 发送到客户端的方法对象
grpc::ServerAsyncResponseWriter<Simple::TestNull> responder_;
// 构造函数
HandlerTest1Context()
:responder_(&ctx_)
{}
};
struct HandlerTest2Context:public HandlerContext {
// 用于接收客户端发送的请求
Simple::TestNull req_;
// 用于发送响应给客户端
Simple::TestReply rep_;
// 发送到客户端的方法对象
grpc::ServerAsyncResponseWriter<Simple::TestReply> responder_;
// 构造函数
HandlerTest2Context()
:responder_(&ctx_)
{}
};
struct HandlerTest3Context:public HandlerContext {
// 用于接收客户端发送的请求
Simple::TestRequest req_;
// 用于发送响应给客户端
Simple::TestReply rep_;
// 发送到客户端的方法对象
grpc::ServerAsyncResponseWriter<Simple::TestReply> responder_;
// 构造函数
HandlerTest3Context()
:responder_(&ctx_)
{}
};
// Test1 实现都是差不都的,这里只是为了测试,就随便返回点数据了
grpc::Status Test1(grpc::ServerContext* context,
const Simple::TestRequest* request,
Simple::TestNull* response)
{
printf("%s %d
",__func__,__LINE__);
std::ostrstream os;
os << "Client Name = " << request->name() << '
';
os << "Clinet ID = " << request->id() << '
';
os << "Clinet Value= " << request->value()<< '
';
std::string message = os.str();
// grpc状态可以设置message,所以也可以用来返回一些信息
return grpc::Status(grpc::StatusCode::OK,message);
}
// Test2
grpc::Status Test2(grpc::ServerContext* context,
const Simple::TestNull* request,
Simple::TestReply* response)
{
printf("%s %d
",__func__,__LINE__);
response->set_tid(100);
response->set_svrname("Simple Server");
response->set_takeuptime(0.01);
return grpc::Status::OK;
}
// Test3
grpc::Status Test3(grpc::ServerContext* context,
const Simple::TestRequest* request,
Simple::TestReply* response)
{
printf("%s %d
",__func__,__LINE__);
std::ostrstream os;
os << "Client Name = " << request->name() << '
';
os << "Clinet ID = " << request->id() << '
';
os << "Clinet Value= " << request->value()<< '
';
std::string message = os.str();
response->set_tid(__LINE__);
response->set_svrname(__FILE__);
response->set_takeuptime(1.234);
// grpc状态可以设置message
return grpc::Status(grpc::StatusCode::OK,std::move(message));
}
int main()
{
// 服务构建器,用于构建同步或者异步服务
grpc::ServerBuilder builder;
// 添加监听的地址和端口,后一个参数用于设置认证方式,这里选择不认证
builder.AddListeningPort("0.0.0.0:33333",grpc::InsecureServerCredentials());
// 创建一个异步服务对象
Simple::Server::AsyncService service;
// 注册服务
builder.RegisterService(&service);
// 添加一个完成队列,用于与 gRPC 运行时异步通信
std::unique_ptr<grpc::ServerCompletionQueue> cq_ptr = builder.AddCompletionQueue();
// 构建服务器
std::unique_ptr<grpc::Server> server(builder.BuildAndStart());
std::cout<<"Server Runing"<<std::endl;
// 这里用一个map来记录一下下面要进行处理的请求
// 因为这里也是单线程的,所以不加锁了
std::map<HandlerContext*,int> handlerMap; // value用于记录是Test1还是2、3
{
// 先创建三个类型接口的请求处理上下文对象
HandlerTest1Context* htc1 = new HandlerTest1Context;
htc1->status_ = 1; // 设置状态为1(因为只需要区分是否已经发送响应完成)
HandlerTest2Context* htc2 = new HandlerTest2Context;
htc2->status_ = 1;
HandlerTest3Context* htc3 = new HandlerTest3Context;
htc3->status_ = 1;
// 将三个上下文对象存入map中
handlerMap[htc1] = 1; // 值用于区分是哪个类型
handlerMap[htc2] = 2;
handlerMap[htc3] = 3;
// 进入下面死循环前需要先注册一下请求
service.RequestTest1(
&htc1->ctx_ /*服务上下文对象*/,
&htc1->req_ /*用于接收请求的对象*/,
&htc1->responder_ /*异步写响应对象*/,
cq_ptr.get() /*新的调用使用的完成队列*/,
cq_ptr.get() /*通知使用的完成队列*/,
htc1 /*唯一标识tag*/);
service.RequestTest2(&htc2->ctx_,&htc2->req_,&htc2->responder_,cq_ptr.get(),cq_ptr.get(),htc2);
service.RequestTest3(&htc3->ctx_,&htc3->req_,&htc3->responder_,cq_ptr.get(),cq_ptr.get(),htc3);
}
// 异步服务这里不能使用 server.Wait() 来等待处理,因为是异步服务
// 服务器会把到达的请求放入队列,需要自己从完成队列取出请求进行处理
// 所以这里需要一个死循环来获取请求并进行处理
while(true){
// 前面已经注册了请求处理,这里阻塞从完成队列中取出一个请求进行处理
HandlerContext* htc = NULL;
bool ok = false;
GPR_ASSERT(cq_ptr->Next((void**)&htc, &ok));
GPR_ASSERT(ok);
// 根据tag判断是哪一个请求
// 因为前面注册请求处理的时候使用的就是对象地址
// 所以这里直接从map里面取出来判断即可
int type = handlerMap[htc];
// 判断状态,看是不是已经响应发送了
if(htc->status_ == 2) {
// 从map中移除
handlerMap.erase(htc);
// 因为这里并不是多态类,必须根据类型操作
switch(type) {
case 1:
{
// 释放对象(这里未对这个对象进行复用)
delete (HandlerTest1Context*)htc;
}
break;
case 2:
{
delete (HandlerTest2Context*)htc;
}
break;
case 3:
{
delete (HandlerTest3Context*)htc;
}
break;
}
continue; // 回到从完成队列获取下一个
}
// 根据type进行相应的处理
switch(type) {
case 1: /*Test1的处理*/
{
// 重新创建一个请求处理上下文对象(以便不影响下一个请求的处理)
HandlerTest1Context* htc1 = new HandlerTest1Context;
htc1->status_ = 1; // 设置状态为1
handlerMap[htc1] = 1; // 保存到handlerMap中
service.RequestTest1(&htc1->ctx_,&htc1->req_,&htc1->responder_,
cq_ptr.get(),cq_ptr.get(),htc1);
HandlerTest1Context* h = (HandlerTest1Context*)htc;
grpc::Status status = Test1(&h->ctx_,&h->req_,&h->rep_);
// 设置状态为发送响应
h->status_ = 2;
// 调用responder_进行响应发送(异步)
h->responder_.Finish(h->rep_/*发送的响应*/,status/*状态码*/,htc/*请求处理的唯一tag*/);
}
break;
case 2: /*Test2的处理*/
{
HandlerTest2Context* htc2 = new HandlerTest2Context;
htc2->status_ = 1; // 设置状态为1
handlerMap[htc2] = 2; // 保存到handlerMap中
service.RequestTest2(&htc2->ctx_,&htc2->req_,&htc2->responder_,
cq_ptr.get(),cq_ptr.get(),htc2);
HandlerTest2Context* h = (HandlerTest2Context*)htc;
grpc::Status status = Test2(&h->ctx_,&h->req_,&h->rep_);
// 设置状态为发送响应
h->status_ = 2;
// 调用responder_进行响应发送(异步)
h->responder_.Finish(h->rep_/*发送的响应*/,status/*状态码*/,htc/*请求处理的唯一tag*/);
}
break;
case 3: /*Test3的处理*/
{
HandlerTest3Context* htc3 = new HandlerTest3Context;
htc3->status_ = 1; // 设置状态为1
handlerMap[htc3] = 3; // 保存到handlerMap中
service.RequestTest3(&htc3->ctx_,&htc3->req_,&htc3->responder_,
cq_ptr.get(),cq_ptr.get(),htc3);
HandlerTest3Context* h = (HandlerTest3Context*)htc;
grpc::Status status = Test3(&h->ctx_,&h->req_,&h->rep_);
// 设置状态为发送响应
h->status_ = 2;
// 调用responder_进行响应发送(异步)
h->responder_.Finish(h->rep_/*发送的响应*/,status/*状态码*/,htc/*请求处理的唯一tag*/);
}
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
async_service2.cpp
上面虽然是使用到了grpc的异步服务机制,但是只是为了描述清楚异步服务的创建过程,是一个单线程的简陋实现。下面写一个使用线程池的实现。
// > g++ -o aservice2 async_service2.cpp simple.grpc.pb.cc simple.pb.cc -std=c++11 -I. -lgrpc++ -lgrpc -lprotobuf -lgpr -lz -lcares -laddress_sorting -lpthread -Wno-deprecated
// 线程池的代码可见 https://www.cnblogs.com/oloroso/p/5881863.html
#include "threadpool.h"
#include "simple.grpc.pb.h"
#include <grpcpp/grpcpp.h>
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
#include <strstream>
#include <chrono>
struct HandlerContextBase {
// 当前对象类型,用于确定是Test1/2/3哪一个请求的
int type_;
// 当前处理状态(处理分为两步:1处理请求构建响应数据;2发送响应)
// 这里记录一下完成到哪一步了,以便进行相关操作
int status_; // (1构建响应完成;2发送完成)
// rpc的上下文,允许通过它进行诸如压缩、身份验证,以及把元数据发回客户端等。
grpc::ServerContext ctx_;
};
template<typename RequestType,typename ReplyType>
struct HandlerContext:public HandlerContextBase {
// 用于接收客户端发送的请求
RequestType req_;
// 用于发送响应给客户端
ReplyType rep_;
// 发送到客户端的方法对象
grpc::ServerAsyncResponseWriter<ReplyType> responder_;
//================================================
// 构造函数
HandlerContext()
:responder_(&ctx_)
{}
};
typedef HandlerContext<Simple::TestRequest,Simple::TestNull> HandlerTest1Context;
typedef HandlerContext<Simple::TestNull,Simple::TestReply> HandlerTest2Context;
typedef HandlerContext<Simple::TestRequest,Simple::TestReply> HandlerTest3Context;
unsigned long get_tid()
{
std::thread::id tid = std::this_thread::get_id();
std::ostrstream os;
os << tid;
unsigned long tidx = std::stol(os.str());
return tidx;
}
// Test1 实现都是差不都的,这里只是为了测试,就随便返回点数据了
grpc::Status Test1(grpc::ServerContext* context,
const Simple::TestRequest* request,
Simple::TestNull* response)
{
printf("%s %d
",__func__,__LINE__);
std::ostrstream os;
os << "Client Name = " << request->name() << '
';
os << "Clinet ID = " << request->id() << '
';
os << "Clinet Value= " << request->value()<< '
';
std::string message = os.str();
// grpc状态可以设置message,所以也可以用来返回一些信息
return grpc::Status(grpc::StatusCode::OK,message);
}
// Test2
grpc::Status Test2(grpc::ServerContext* context,
const Simple::TestNull* request,
Simple::TestReply* response)
{
printf("%s %d
",__func__,__LINE__);
response->set_tid(100);
response->set_svrname("Simple Server");
response->set_takeuptime(0.01);
return grpc::Status::OK;
}
// Test3
grpc::Status Test3(grpc::ServerContext* context,
const Simple::TestRequest* request,
Simple::TestReply* response)
{
printf("%s %d
",__func__,__LINE__);
int tid = get_tid();
std::ostrstream os;
os << "Client Name = " << request->name() << '
';
os << "Clinet ID = " << request->id() << '
';
os << "Clinet Value= " << request->value()<< '
';
os << "Server TID = " << tid<<'
';
std::string message = os.str();
// 休眠0.5秒,以便观察异步执行的效果
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(500));
response->set_tid(tid);
response->set_svrname(__FILE__);
response->set_takeuptime(1.234);
// grpc状态可以设置message
return grpc::Status(grpc::StatusCode::OK,std::move(message));
}
int main()
{
// 服务构建器,用于构建同步或者异步服务
grpc::ServerBuilder builder;
// 添加监听的地址和端口,后一个参数用于设置认证方式,这里选择不认证
builder.AddListeningPort("0.0.0.0:33333",grpc::InsecureServerCredentials());
// 创建一个异步服务对象
Simple::Server::AsyncService service;
// 注册服务
builder.RegisterService(&service);
// 添加一个完成队列,用于与 gRPC 运行时异步通信
std::unique_ptr<grpc::ServerCompletionQueue> cq_ptr = builder.AddCompletionQueue();
// 构建服务器
std::unique_ptr<grpc::Server> server(builder.BuildAndStart());
std::cout<<"Server Runing"<<std::endl;
// 下面可以有几个工作线程就先注册几个,也可以仅注册一个(至少一个)
/*for(int i=0;i<4;++i)*/ {
// 先创建三个类型接口的请求处理上下文对象
HandlerTest1Context* htc1 = new HandlerTest1Context;
htc1->status_ = 1; // 设置状态为1(因为只需要区分是否已经发送响应完成)
htc1->type_ = 1; // 设置类型为1
HandlerTest2Context* htc2 = new HandlerTest2Context;
htc2->status_ = 1;
htc2->type_ = 2;
HandlerTest3Context* htc3 = new HandlerTest3Context;
htc3->status_ = 1;
htc3->type_ = 3;
// 进入下面死循环前需要先注册一下请求
service.RequestTest1(
&htc1->ctx_ /*服务上下文对象*/,
&htc1->req_ /*用于接收请求的对象*/,
&htc1->responder_ /*异步写响应对象*/,
cq_ptr.get() /*新的调用使用的完成队列*/,
cq_ptr.get() /*通知使用的完成队列*/,
htc1 /*唯一标识tag*/);
service.RequestTest2(&htc2->ctx_,&htc2->req_,&htc2->responder_,cq_ptr.get(),cq_ptr.get(),htc2);
service.RequestTest3(&htc3->ctx_,&htc3->req_,&htc3->responder_,cq_ptr.get(),cq_ptr.get(),htc3);
}
// 创建线程池,使用4个工作线程,用于构建请求的响应
ThreadPool pool(4);
// 异步服务这里不能使用 server->Wait() 来等待处理,因为是异步服务
// 服务器会把到达的请求放入队列,需要自己从完成队列取出请求进行处理
// 所以这里需要一个死循环来获取请求并进行处理
while(true){
// 前面已经注册了请求处理,这里阻塞从完成队列中取出一个请求进行处理
HandlerContextBase* htc = NULL;
bool ok = false;
GPR_ASSERT(cq_ptr->Next((void**)&htc, &ok));
GPR_ASSERT(ok);
// 根据tag判断是哪一个请求
// 因为前面注册请求处理的时候使用的就是对象地址
// 所以这里直接从map里面取出来判断即可
int type = htc->type_;
// 判断状态,看是不是已经响应发送了
if(htc->status_ == 2) {
// 因为这里并不是多态类,必须根据类型操作
switch(type) {
case 1:
{
// 释放对象(这里未对这个对象进行复用)
delete (HandlerTest1Context*)htc;
}
break;
case 2:
{
delete (HandlerTest2Context*)htc;
}
break;
case 3:
{
delete (HandlerTest3Context*)htc;
}
break;
}
continue; // 回到从完成队列获取下一个
}
// 重新创建一个请求处理上下文对象(以便能够接受下一个请求进行处理)
switch(type) {
case 1:
{
HandlerTest1Context* htc1 = new HandlerTest1Context;
htc1->status_ = 1; // 设置状态为1
htc1->type_ = 1; // 设置类型为1
service.RequestTest1(&htc1->ctx_,&htc1->req_,&htc1->responder_,
cq_ptr.get(),cq_ptr.get(),htc1);
}
break;
case 2:
{
HandlerTest2Context* htc2 = new HandlerTest2Context;
htc2->status_ = 1; // 设置状态为1
htc2->type_ = 1; // 设置类型为2
service.RequestTest2(&htc2->ctx_,&htc2->req_,&htc2->responder_,
cq_ptr.get(),cq_ptr.get(),htc2);
}
break;
case 3:
{
HandlerTest3Context* htc3 = new HandlerTest3Context;
htc3->status_ = 1; // 设置状态为1
htc3->type_ = 3; // 设置类型为3
service.RequestTest3(&htc3->ctx_,&htc3->req_,&htc3->responder_,
cq_ptr.get(),cq_ptr.get(),htc3);
}
break;
}
pool.enqueue([type,htc](){
// 根据type进行相应的处理
switch(type) {
case 1: /*Test1的处理*/
{
HandlerTest1Context* h = (HandlerTest1Context*)htc;
grpc::Status status = Test1(&h->ctx_,&h->req_,&h->rep_);
// 设置状态为发送响应
h->status_ = 2;
// 调用responder_进行响应发送(异步)
h->responder_.Finish(h->rep_/*发送的响应*/,status/*状态码*/,htc/*请求处理的唯一tag*/);
}
break;
case 2: /*Test2的处理*/
{
HandlerTest2Context* h = (HandlerTest2Context*)htc;
grpc::Status status = Test2(&h->ctx_,&h->req_,&h->rep_);
// 设置状态为发送响应
h->status_ = 2;
// 调用responder_进行响应发送(异步)
h->responder_.Finish(h->rep_/*发送的响应*/,status/*状态码*/,htc/*请求处理的唯一tag*/);
}
break;
case 3: /*Test3的处理*/
{
HandlerTest3Context* h = (HandlerTest3Context*)htc;
grpc::Status status = Test3(&h->ctx_,&h->req_,&h->rep_);
// 设置状态为发送响应
h->status_ = 2;
// 调用responder_进行响应发送(异步)
h->responder_.Finish(h->rep_/*发送的响应*/,status/*状态码*/,htc/*请求处理的唯一tag*/);
}
break;
}
});
}
return 0;
}