1、 (2.3.7) Describe a Θ(n lg n)-time algorithm that, given a set S of n integers and another integer x, determines whether or not there exist two elements in S whose sum is exactly x.给定含有n个整型数的集合S和整型数x,确定s中是否存在两个元素的和等于x。算法时间复杂度为c塔nlgn。



判断是否存在的函数的时间复杂度小于0(nlgn),归并排序的时间复杂度是0(nlgn)。

2 3 #include<stdio.h> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 void merge(int arr[],int low,int mid,int high){ 6 int i,k; 7 int *tmp=(int*)malloc((high-low+1)*sizeof(int)); 8 int left_low=low; 9 int left_high=mid; 10 int right_low=mid+1; 11 int right_high=high; 12 for(k=0;left_low<=left_high&&right_low<=right_high;k++) 13 { 14 if(arr[left_low]<=arr[right_low]){ 15 tmp[k]=arr[left_low++]; 16 } 17 else{ 18 tmp[k]=arr[right_low++]; 19 } 20 } 21 22 if(left_low<=left_high){ 23 for(i=left_low;i<=left_high;i++){ 24 tmp[k++]=arr[i]; 25 } 26 } 27 if(right_low<=right_high){ 28 for(i=right_low;i<=right_high;i++) 29 tmp[k++]=arr[i]; 30 } 31 for(i=0;i<high-low+1;i++) 32 arr[low+i]=tmp[i]; 33 34 } 35 36 void merge_sort(int a[],int p,int r){ 37 int q; 38 if(p<r){ 39 q=(p+r)/2; 40 merge_sort(a,p,q); 41 merge_sort(a,q+1,r); 42 merge(a,p,q,r); 43 } 44 } 45 int main(){ 46 int a[8]={3,5,8,6,4,1,1}; 47 int i,j; 48 int x=10; 49 merge_sort(a,0,6); 50 printf("after Merging-Sort: "); 51 for(i=0;i<7;i++){ 52 printf("%d",a[i]); 53 } 54 printf(" "); 55 i=0;j=6; 56 do{ 57 58 if(a[i]+a[j]==x){ 59 printf("exist"); 60 break; 61 } 62 if(a[i]+a[j]>x) 63 j--; 64 if(a[i]+a[j]<x) 65 i++; 66 }while(i<=j); 67 if(i>j) 68 printf("not exist"); 69 system("pause"); 70 return 0; 71 }
2、 Implement priority queue.
优先队列





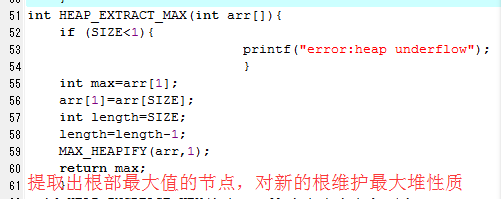



1 2 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<stdio.h> 5 #include<math.h> 6 #define SIZE 7 7 int PARENT(int i){ 8 return (int)floor(i/2); 9 } 10 int LEFT(int i){ 11 return 2*i; 12 } 13 int RIGHT(int i){ 14 return 2*i+1; 15 } 16 void MAX_HEAPIFY(int arr[],int i){ 17 int l=LEFT(i); 18 int r=RIGHT(i); 19 int largest; 20 if(l<=SIZE&&arr[l]>arr[i]){ 21 largest=l; 22 } 23 else largest=i; 24 if(r<SIZE&&arr[r]>arr[largest]){ 25 largest=r; 26 } 27 if(!largest==i){ 28 int t; 29 t=arr[i];arr[i]=arr[largest];arr[largest]=t; 30 MAX_HEAPIFY(arr,i); 31 } 32 } 33 void BULID_MAX_HEAP(int arr[]){ 34 //SIZE=arr[].length; 35 for(int i=(int)floor(SIZE/2);i>0;i--){ 36 MAX_HEAPIFY(arr,i); 37 } 38 } 39 void HEAPSORT(int arr[]){ 40 BULID_MAX_HEAP(arr); 41 int length=SIZE; 42 for(int i=length;i>1;i--){ 43 int t; 44 t=arr[1];arr[1]=arr[i];arr[i]=t; 45 length=length-1; 46 MAX_HEAPIFY(arr,1); 47 } 48 } 49 50 int HEAP_MAXIMUM(int arr[]){ 51 return arr[1]; 52 } 53 int HEAP_EXTRACT_MAX(int arr[]){ 54 if (SIZE<1){ 55 printf("error:heap underflow"); 56 } 57 int max=arr[1]; 58 arr[1]=arr[SIZE]; 59 int length=SIZE; 60 length=length-1; 61 MAX_HEAPIFY(arr,1); 62 return max; 63 } 64 void HEAP_INCREASE_KEY(int arr[],int i,int key){ 65 if(key<arr[i]){ 66 printf("error:new key is smaller than current key"); 67 } 68 arr[i]=key; 69 while (i>1&&arr[PARENT(i)]<arr[i]){ 70 int t; 71 t=arr[i];arr[i]=arr[PARENT(i)];arr[PARENT(i)]=t; 72 i=PARENT(i); 73 } 74 } 75 void MAX_HEAP_INSERT(int arr[],int key){ 76 int length=SIZE; 77 length=length+1; 78 arr[SIZE]=-10000; 79 HEAP_INCREASE_KEY(arr,SIZE,key); 80 } 81 /*int HEAP_MAXIMUM(int arr[]){ 82 BULID_MAX_HEAP(arr[]); 83 return arr[1]; 84 } 85 */ 86 int main(){ 87 int arr[7]={3,5,8,6,4,1,1}; 88 int key,i; 89 HEAPSORT(arr); 90 printf("堆排序后:"); 91 for(int i=0;i<7;i++){ 92 printf("%d ",arr[i]); 93 } 94 printf(" "); 95 printf("最大值是:%d ",HEAP_MAXIMUM(arr)); 96 HEAP_EXTRACT_MAX(arr); 97 printf("已经去掉最大值 "); 98 printf("请输入key的值"); 99 scanf("%d",&key); 100 printf("请输入i的值"); 101 scanf("%d",&i); 102 HEAP_INCREASE_KEY(arr,i,key); 103 printf("已经把下标为i的元素值增加到key"); 104 system("pause"); 105 return 0; 106 107 }
3、 Implement Quicksort and Randomized Quicksort. Answer the following questions. (1) How many comparisons will Quicksort do on a list of n elements that all have the same value? (2) What are the maximum and minimum number of comparisons will Quicksort do on a list of n elements, give an instance for maximum and minimum case respectively.
实现Quicksoet和Randomized。
实现普通快速排序的两个函数:

实现随机快速排序的两个函数:


请回答1、列表中n个元素的值都相同时,Quicksoet比较几次。
答: (n-1)+(n-2)+…+1=n(n-1)/2
2、列表中有n个元素,比较次数的最大值最小值是多少,分别给出对应情况。
答:最坏情况是枢纽元素把其余数字分的个数区别很大,O(n方)
最好情况是枢纽元素恰好是中位数,O(nlgn)

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<math.h> 4 int PARTITION(int a[],int p,int r){ 5 int x=a[r]; 6 int i=p-1; 7 int j; 8 for(j=p;j<r;j++){ 9 if(a[j]<=x){ 10 i=i+1; 11 int t=a[i];a[i]=a[j];a[j]=t; 12 } 13 } 14 int t=a[i+1];a[i+1]=a[r];a[r]=t; 15 return i+1; 16 } 17 18 void QUICKSORT(int a[],int p,int r){ 19 int q; 20 if(p<r){ 21 q=PARTITION(a,p,r); 22 QUICKSORT(a,p,q-1); 23 QUICKSORT(a,q+1,r); 24 } 25 } 26 27 int RAN_PAR(int a[],int p,int r){ 28 int i=p + rand()%(r-p+1); 29 int t=a[r];a[r]=a[i];a[i]=t; 30 return PARTITION(a,p,r); 31 } 32 void RAN_QUI(int a[],int p,int r){ 33 if(p<r){ 34 int q=RAN_PAR(a,p,r); 35 RAN_QUI(a,p,q-1); 36 RAN_QUI(a,q+1,r); 37 } 38 } 39 40 int main(){ 41 int a[8]={3,5,8,6,4,1,1}; 42 int i; 43 printf("输入1进行QUICKSORT,输入2进行RAN-QUI 请输入: "); 44 int k; 45 scanf("%d",&k); 46 47 if(k==1){ 48 printf("after QUICKSORT: "); 49 QUICKSORT(a,0,6); 50 for(i=0;i<7;i++){ 51 printf("%d",a[i]); 52 } 53 printf(" "); 54 } 55 56 if(k==2){ 57 printf("after RAN-QUI: "); 58 RAN_QUI(a,0,6); 59 for(i=0;i<7;i++){ 60 printf("%d",a[i]); 61 } 62 printf(" "); 63 } 64 system("pause"); 65 return 0; 66 }
4、(8.2) Sorting in place in linear time
Suppose that we have an array of n data records to sort and that the key of each record has the value 0 or 1. An algorithm for sorting such a set of records might possess some subset of the following three desirable characteristics:
1. The algorithm runs in O(n) time.
2. The algorithm is stable.
3. The algorithm sorts in place, using no more than a constant amount of storage space in addition to the original array.
a. Give an algorithm that satisfies criteria 1 and 2 above.
b. Give an algorithm that satisfies criteria 1 and 3 above.
c. Give an algorithm that satisfies criteria 2 and 3 above.
d. Can you use any of your sorting algorithms from parts (a)–(c) as the sorting method used in line 2 of RADIX-SORT, so that RADIX-SORT sorts n records with b-bit keys in O(bn) time? Explain how or why not.
e. Suppose that the n records have keys in the range from 1 to k. Show how to modify counting sort so that it sorts the records in place in O(n+k) time. You may use O(k) storage outside the input array. Is your algorithm stable? (Hint: How would you do it for k = 3?)
线性时间排序假设对一个有n个数据记录的数组进行排序,每个记录的key值是0或1,。设计给其排序的算法,该算法要包含以下3个要求:1、O(N);2、稳定;3、原址排序,使用的空间不能超过原数据的
A、满足1 2
B、满足1 3
C、满足2 3
D、能否将abc中的算法用于基数排序第二行,使其在排序有b个关键字的n个记录时的时间复杂度为o(bn)
E、假设有n条记录,关键字的范围是1-k。怎么修改基数排序使其为o(n+k)的原址排序。除了输入数组外,可以使用o(k)的额外存储。给出的算法稳定么(提示:当k=3时怎么做?)
4a计数排序满足o(n)和稳定
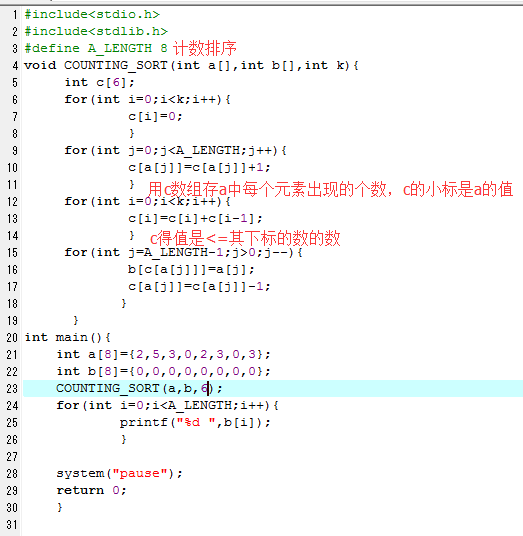

2 3 #include<stdio.h> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 #define A_LENGTH 8 6 void COUNTING_SORT(int a[],int b[],int k){ 7 int c[6]; 8 for(int i=0;i<k;i++){ 9 c[i]=0; 10 } 11 for(int j=0;j<A_LENGTH;j++){ 12 c[a[j]]=c[a[j]]+1; 13 } 14 for(int i=0;i<k;i++){ 15 c[i]=c[i]+c[i-1]; 16 } 17 for(int j=A_LENGTH-1;j>0;j--){ 18 b[c[a[j]]]=a[j]; 19 c[a[j]]=c[a[j]]-1; 20 } 21 } 22 int main(){ 23 int a[8]={2,5,3,0,2,3,0,3}; 24 int b[8]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}; 25 COUNTING_SORT(a,b,6); 26 for(int i=0;i<A_LENGTH;i++){ 27 printf("%d ",b[i]); 28 } 29 30 system("pause"); 31 return 0; 32 }
4b 冒泡排序满足o(n)和原址


1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 void bubble_sort(int a[],int n) 4 { 5 for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++) 6 { 7 for(int j=0; j<n-1-i; j++) 8 { 9 if(a[j] > a[j+1]) 10 { 11 int temp = a[j];a[j] = a[j+1];a[j+1]=temp; 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 int main(){ 17 int a[8]={4,5,6,3,2,1,8,7}; 18 bubble_sort(a,8); 19 printf("冒泡排序最好情况满足o(n)和原址 "); 20 for(int i=0;i<8;i++){ 21 printf("%d ",a[i]); 22 } 23 system("pause"); 24 return 0; 25 }
4c 插入排序满足稳定和原址
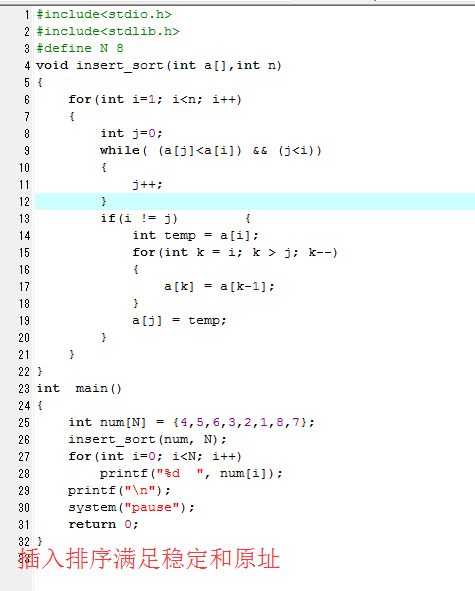

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #define N 8 4 void insert_sort(int a[],int n) 5 { 6 for(int i=1; i<n; i++) 7 { 8 int j=0; 9 while( (a[j]<a[i]) && (j<i)) 10 { 11 j++; 12 } 13 if(i != j) { 14 int temp = a[i]; 15 for(int k = i; k > j; k--) 16 { 17 a[k] = a[k-1]; 18 } 19 a[j] = temp; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 int main() 24 { 25 int num[N] = {4,5,6,3,2,1,8,7}; 26 insert_sort(num, N); 27 printf("插入排序满足稳定和原址 "); 28 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 29 printf("%d ", num[i]); 30 printf(" "); 31 system("pause"); 32 return 0; 33 }
4d
计数排序可以,因为其时间复杂度为o(n)且稳定。给定n
个b位数,其中每一个数位有k种可能取值,耗时为c塔n+k,则基数排序耗时c塔(b(n+k)),即o(bn)。
4e
当K=3时的示例图:

伪代码:
For i=k downto 1{
For(n=a.length;c[k]>0;c[k]--){
A[n]=I;
n--;
}
}
根据c数组记录a中元素出现的次数,在a数组中直接替换,不引入b数组。