前言
上一章节,简单介绍了分布式配置中心
Spring Cloud Config的使用。同时,我们也遗漏了一些问题,比如如何配置实时生效,当服务端地址变更或者集群部署时,如何指定服务端地址?回想,在服务注册章节,服务提供者和服务消费者,同时往注册中心进行注册和获取服务地址,而本身注册中心又支持高可用配置。所以,对于配置中心,我们也可以将Server端和Client端往注册中心进行注册,借此实现配置中心的服务化,无需指定具体的ip地址,直接根据服务名称进行调用。
前言
关于高可用
将配置中心服务化,本身是为了实现高可用。而实现高可用的手段是很多的,最常用的就是负载均衡。客户端不直连服务端,而是访问负载均衡服务,由负载均衡来动态选择需要访问的服务端。只是Spring Cloud Config天然的就能进行服务化配置,所以,实际中可以根据实际的业务需求来进行合理化抉择的。
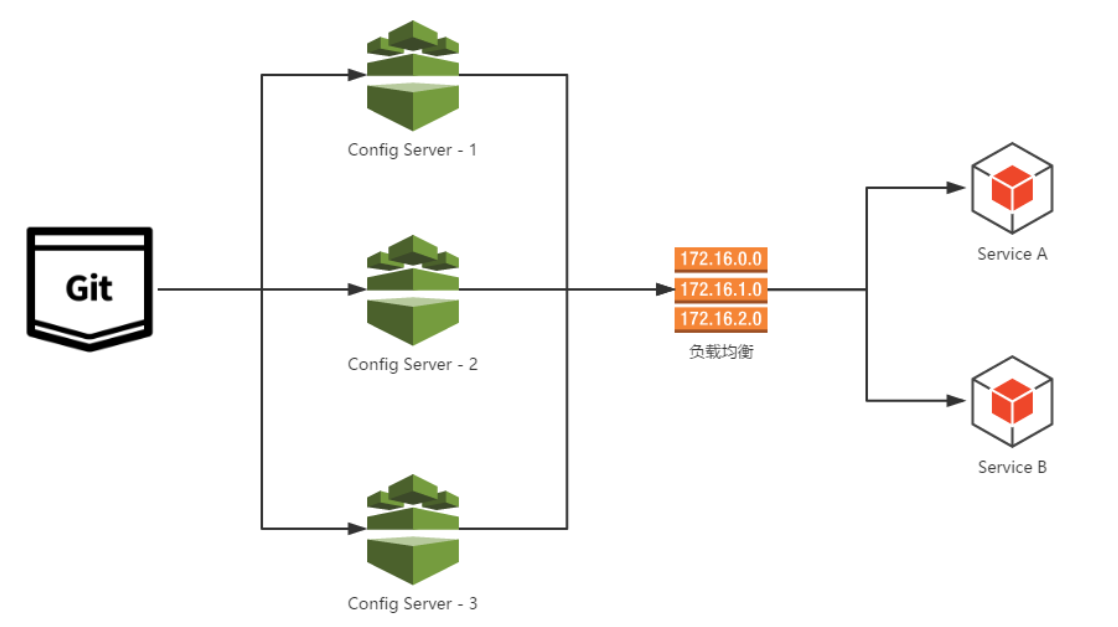
其次,对于使用了git或者svn作为存储方式时,本身配置仓库的高可用也是一个需要考虑的事项。本身如github或者码云这些第三方git仓库而言,已经实现了高可用了。但一般上部署的微服务都是内网服务,所以一般上是使用如gitlab开源的git仓库管理系统进行自建,此时就需要考虑本身仓库的高可用了。
注意:本身教程为了不混淆各知识点,所以都是独立项目进行实例,而不是在原工程上进行修改。
本章节教程采用了多模块工程进行构建实例。父类项目名为:spring-cloud-config-ha。同时创建服务化的配置文件:my-config-client-ha-dev.properties和my-config-client-ha-test.properties
my-config-client-ha-dev.properties
config=this is dev!
my-config-client-ha-dev.properties
config=this is test!
Server端
创建子工程:spring-cloud-confg-ha-server
0.加入pom依赖。
<!-- config server 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 客户端依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.配置文件加入注册中心相关配置。
spring.application.name=spring-cloud-config-ha-server
server.port=15678
#配置文件git配置
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri=https://github.com/xie19900123/spring-cloud-learning.git
# 搜索路径,即配置文件的目录,可配置多个,逗号分隔。默认为根目录。
spring.cloud.config.server.git.searchPaths=spring-cloud-config-repo
# git用户名和密码 针对私有仓库而言需要填写
spring.cloud.config.server.git.username=
spring.cloud.config.server.git.password=
#添加注册中心配置
# 注册中心地址 -此为单机模式
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://127.0.0.1:1000/eureka
# 启用ip配置 这样在注册中心列表中看见的是以ip+端口呈现的
eureka.instance.prefer-ip-address=true
# 实例名称 最后呈现地址:ip:15678
eureka.instance.instance-id=${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${server.port}
2.启动类加入@EnableDiscoveryClient和@EnableConfigServer,前者开启服务发现功能,后者声明一个config server。
/**
* config server 服务化
*
* @author oKong
*
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
//注意这里也可使用@EnableEurekaClient
//但由于springcloud是灵活的,注册中心支持eureka、consul、zookeeper等
//若写了具体的注册中心注解,则当替换成其他注册中心时,又需要替换成对应的注解了。
//所以 直接使用@EnableDiscoveryClient 启动发现。
//这样在替换注册中心时,只需要替换相关依赖即可。
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@Slf4j
public class ConfigServerHaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerHaApplication.class, args);
log.info("spring-cloud-config-ha-server启动!");
}
}
关于Eureka相关知识点,可以查看:《第二章:服务注册与发现(Eureka)-上》和《第三章:服务注册与发现(Eureka)-下》,这里就不加以阐述了。
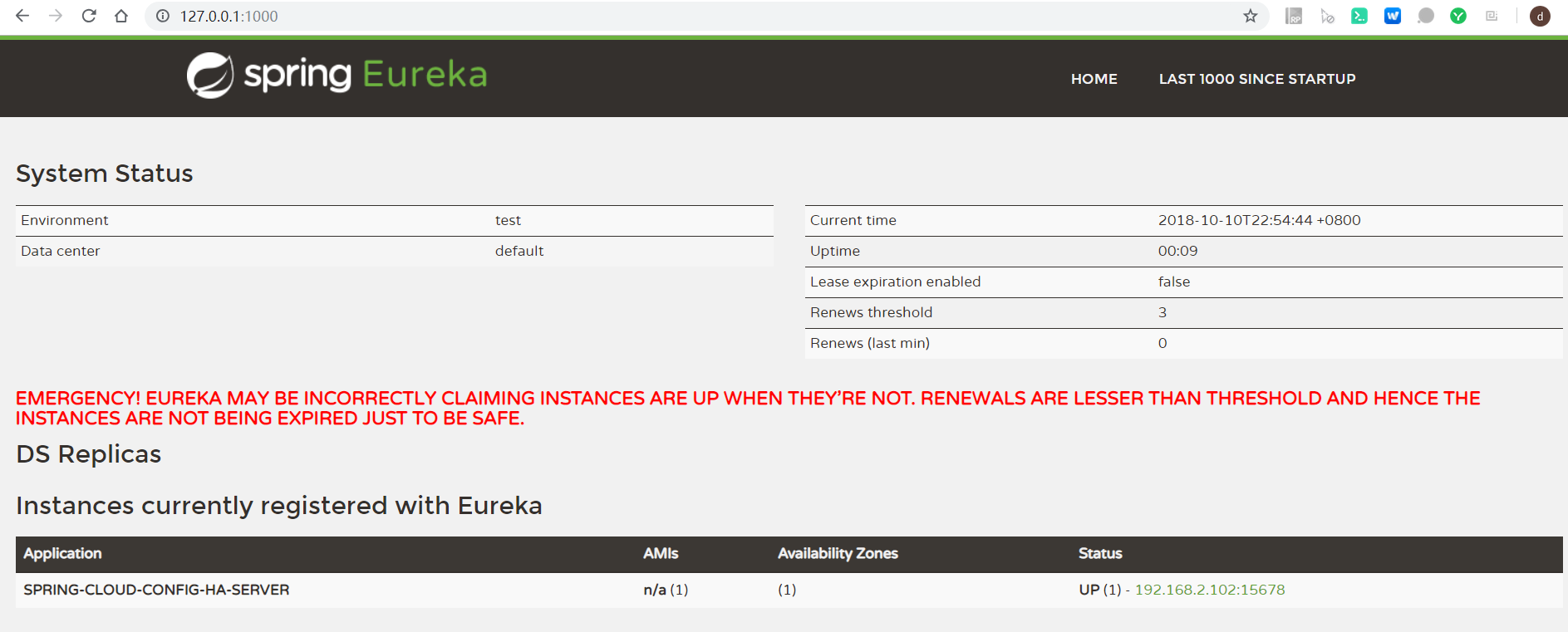
3.启动应用,同时启动Eureka服务端。访问下Eureka服务端地址:http://127.0.0.1:1000/ ,可以看见服务注册成功了。
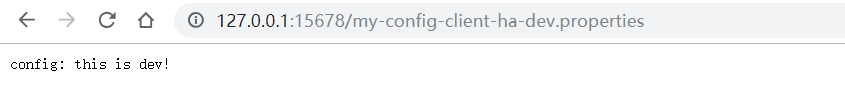
访问:http://127.0.0.1:15678/my-config-client-ha-dev.properties 可以看见配置信息了。
Client端
创建子工程:spring-cloud-confg-ha-client
0.加入pom依赖。
<!-- config client 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- eureka client 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.配置文件修改,bootstrap.properties添加注册中心配置。
bootstrap.properties
# 设置分支
spring.cloud.config.label=master
# 环境变量
spring.cloud.config.profile=dev
# 是否使用注册中心方式进行获取
spring.cloud.config.discovery.enabled=true
# 服务端地址
# 在不使用注册中心模式下 直接填写实际地址
#spring.cloud.config.uri=http://127.0.0.1:5678
# 注册中心应用id
spring.cloud.config.discovery.service-id=spring-cloud-config-ha-server
#添加注册中心配置
# 注册中心地址 -此为单机模式
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://127.0.0.1:1000/eureka
# 启用ip配置 这样在注册中心列表中看见的是以ip+端口呈现的
eureka.instance.prefer-ip-address=true
# 实例名称 最后呈现地址:ip:15678
eureka.instance.instance-id=${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${server.port}
application.properties
# 设置应用名称,需要和配置文件匹配
spring.application.name=my-config-client-ha
server.port=15666
注意:注册中心的相关配置需要放在bootstrap.properties中,这样才能利用注册中心进行服务端服务地址获取。
2.启动类,加入@EnableDiscoveryClient,开启服务发现功能。
/**
* 服务化方式调用config server
*
* @author oKong
*
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@Slf4j
public class ConfigClientHaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigClientHaApplication.class, args);
log.info("spring-cloud-config-ha-client启动!");
}
}
3.创建控制层,测试配置参数。
/**
* config client 简单示例
* @author oKong
*
*/
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@Value("${config}")
String config;
@GetMapping("/")
public String demo() {
return "返回的config参数值为:" + config;
}
}
4.启动应用。一般上应用能启动成功,就说明服务化已经成功了。
启动时,可以看见已经往注册中心去获取服务端地址了。
2018-10-10 23:15:15.302 INFO 26412 --- [ main] c.c.c.ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator : Fetching config from server at : http://192.168.2.102:15678/
2018-10-10 23:15:20.728 INFO 26412 --- [ main] c.c.c.ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator : Located environment: name=my-config-client-ha, profiles=[dev], label=master, version=f2645253a37db433d806914b1d04d6aba428831c, state=null
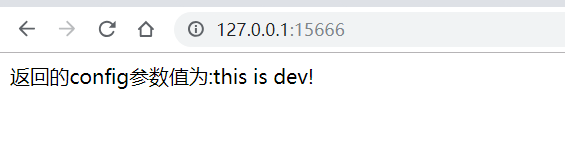
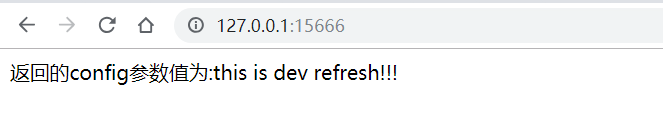
此时,我们访问:http://127.0.0.1:15666/ ,即可看见配置信息返回了。
refresh实现刷新
在默认情况下,客户端是不会自动感知配置的变化的。此时,我们可以使用/refresh端点来进行配置更新。
现在,我们改造下客户端。
0.加入端点依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.修改下变量使用类,加入@RefreshScope注解,标记在访问/refresh时,进行变量的更新操作。
/**
* config client 简单示例
* @author oKong
*
*/
@RestController
@RefreshScope//使用该注解的类,会在接到SpringCloud配置中心配置刷新的时候,自动将新的配置更新到该类对应的字段中。
public class DemoController {
@Value("${config}")
String config;
@GetMapping("/")
public String demo() {
return "返回的config参数值为:" + config;
}
}
重点就是注解@RefreshScope了。
2.配置文件开启端点refresh。这里需要注意,2.0之后,默认只开启了端点info、health。其他的需要通过management.endpoints.web.exposure.include进行额外配置。
#开启监控端点
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=refresh
3.启动应用,此时,动态修改下远程仓库的参数值为:config=this is dev refresh!!!,
使用Postman使用POST访问:http://127.0.0.1:15666/actuator/refresh。
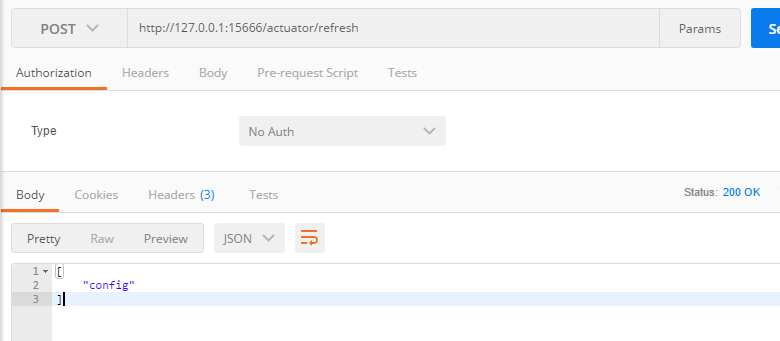
返回值即为有变动的参数值。
再次访问:http://127.0.0.1:15666/ 可以看见已经是最新的配置参数值了。
参考资料
总结
本章节主要讲解了如何将配置中心注册为一个服务,客户端像普通的服务消费者一样,根据服务名即可获取服务端地址,进而进行参数的获取。同时讲解了当属性参数有变时,客户端如何进行感知变化进行参数动态更新。大家应该可以想到,当我们客户端越来越多时,一个个去执行
refresh时不太现实的,虽然我们可以通过类似webhook功能当有提交记录时,主动去触发各客户端的refresh方法,在前期项目比较少的情况下,不失为一个好方法,只需要维护一份待更新的客户端地址列表即可。但当服务越来越多时,维护此列表也是令人头疼的。此时,我们可以使用Spring cloud bus消息总线进行通知。由于目前Spring cloud bus知识点尚未开始讲解,同时作者也比较少使用消息总线,所以待查阅相关之后介绍Spring Cloud bus章节时,再来进行讲解如何使用消息总线进行全自动的配置更新操作。
最后
目前互联网上大佬都有分享
SpringCloud系列教程,内容可能会类似,望多多包涵了。原创不易,码字不易,还希望大家多多支持。若文中有错误之处,还望提出,谢谢。
老生常谈
- 个人QQ:
499452441 - 微信公众号:
lqdevOps

个人博客:http://blog.lqdev.cn
源码示例:https://github.com/xie19900123/spring-cloud-learning
原文地址:http://blog.lqdev.cn/2018/10/11/SpringCloud/chapter-eight/