前言
上几节讲了利用
Mybatis-Plus这个第三方的ORM框架进行数据库访问,在实际工作中,在存储一些非结构化或者缓存一些临时数据及热点数据时,一般上都会用上mongodb和redis进行这方面的需求。所以这一章节准备讲下缓存数据库Redis的集成,同时会介绍下基于Redis和注解驱动的Spring Cache的简单使用。
- [Redis 介绍](#Redis 介绍)
- SpringBoot的Redis集成
- SpringCache和redis使用
- [关于SpringCache注解的简单介绍](#关于SpringCache 注解的简单介绍)
- SpEL上下文数据
- 总结
- 最后
- 老生常谈
Redis 介绍
大家应该对
Redis应该比较熟悉了。这几年也是大行其道的缓存数据库,目前的memcached由于使用场景及其存储数据结构的单一(不知道现在是否有改善,现在基本没有接触了),在工作中也使用的少了。引用官网的简介,Redis是一个开源的使用ANSI C语言编写、遵守BSD协议、支持网络、可基于内存亦可持久化的日志型、Key-Value数据库,并提供多种语言的API。
推荐redis中国社区:http://www.redis.cn/
SpringBoot的Redis集成
0.本章节以上一章节的示例基础上进行集成。所以大家可下载第十章节示例或者在章节末尾直接下载本章节示例。
1.pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
直接引入,相关依赖会自动加载的,这就是springboot让人愉悦之处呀。
2.application.properties配置加入redis相关配置
配置自动加载类为:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisProperties,可在属性文件中点击某属性快捷跳转。注意到其启动类为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration。这里就不介绍了,后面会写一篇关于Springboot自动加载配置的文章。
# REDIS (RedisProperties)
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-active=8
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=8
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=0
3.一般上通过以上两步就可使用了,但工作中一般上是通过StringRedisTemplate(默认采用string的序列化,保存key和值时都是通过此序列化策略)接口进行操作,所以这里直接配置了StringRedisTemplatebean类。
RedisConfig.java
/**
*
* @author oKong
*
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
/**
* 定义 StringRedisTemplate ,指定序列化和反序列化的处理类
* @param factory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(factory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(
Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
//序列化 值时使用此序列化方法
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}
4.编写控制类,测试集成是否生效。
RedisController.java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/redis")
@Api(tags = "redis 测试API")
public class RedisController {
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("set/{key}/{value}")
@ApiOperation(value="设置缓存")
public String set(@PathVariable("key")String key,@PathVariable("value") String value) {
//注意这里的 key不能为null spring 内部有检验
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
return key + "," + value;
}
@GetMapping("get/{key}")
@ApiOperation(value="根据key获取缓存")
public String get(@PathVariable("key") String key) {
return "key=" + key + ",value=" + redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
}
}
5.访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/swagger-ui.html。 也可直接浏览器输入:
set值
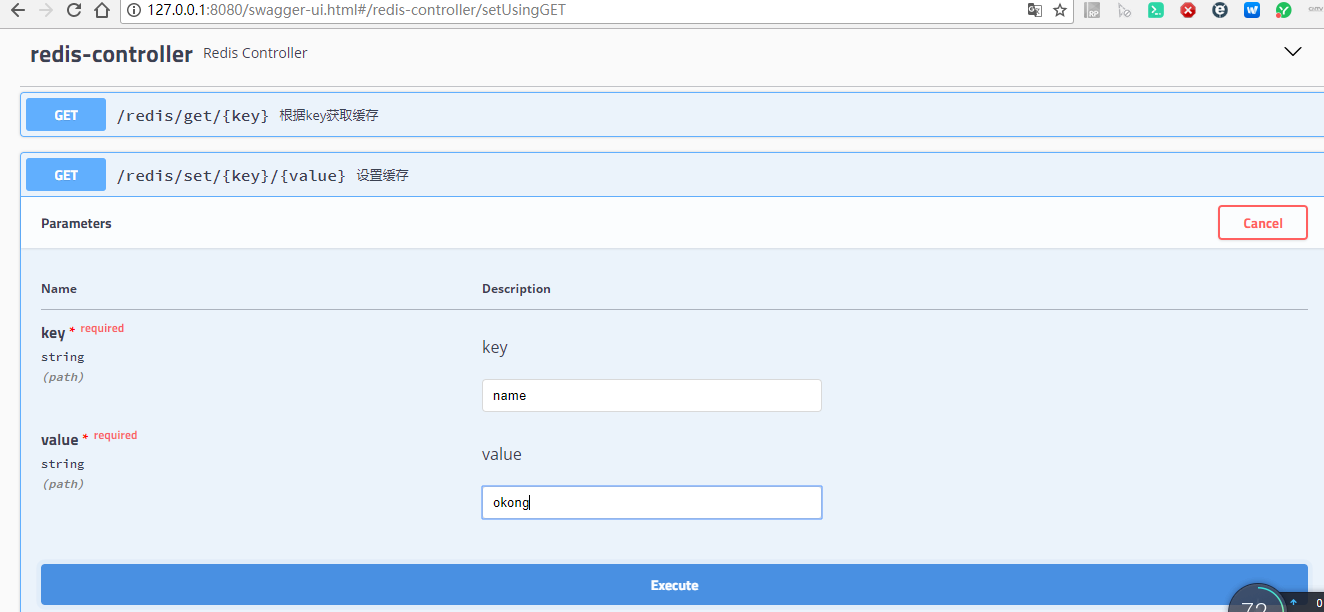
get值
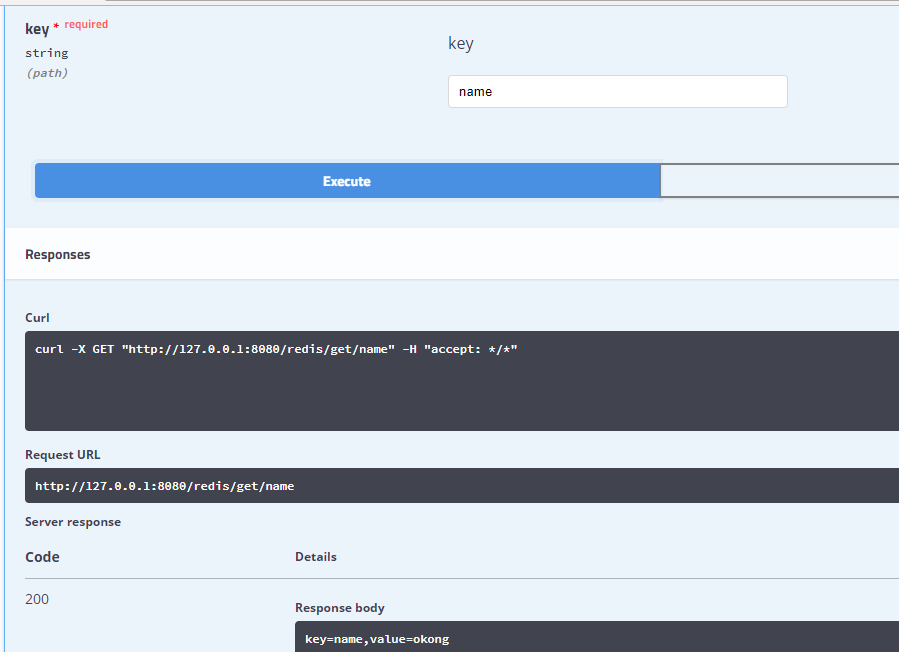
浏览器访问
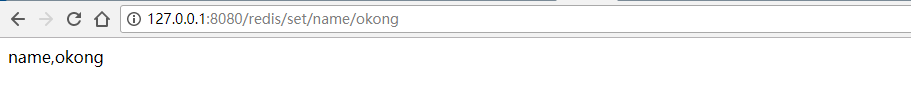
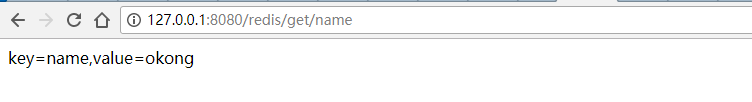
查看redis记录:
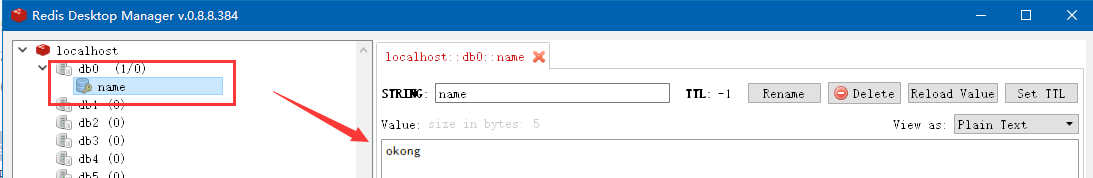
至此,redis就集成好了。实际中可根据业务需要进行相关操作,比如缓存session记录,缓存菜单列表等。
SpringCache和redis使用。
Spring Cache是Spring框架提供的对缓存使用的抽象类,支持多种缓存,比如Redis、EHCache等,集成很方便。同时提供了多种注解来简化缓存的使用,可对方法进行缓存。
0.修改RedisConfig配置类,加入注解@EnableCaching,同时设置CacheManager缓存管理类,这里使用RedisCacheManager,其他的管理类还有:SimpleCacheManager、ConcurrentMapCacheManager等,默认提供的在类org.springframework.cache.support下,可自行查阅。
/**
*
* @author oKong
*
*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
/**
* 定义 StringRedisTemplate ,指定序列号和反序列化的处理类
* @param factory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(factory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(
Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
//序列化 值时使用此序列化方法
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate) {
RedisCacheManager rcm = new RedisCacheManager(redisTemplate);
//使用前缀
rcm.setUsePrefix(true);
//缓存分割符 默认为 ":"
// rcm.setCachePrefix(new DefaultRedisCachePrefix(":"));
//设置缓存过期时间
//rcm.setDefaultExpiration(60);//秒
return rcm;
}
}
1.改造UserController控制层,引入@Cacheable等注解。
/**
* 用户控制层 简单演示增删改查及分页
* 新增了swagger文档内容 2018-07-21
* 新增了@caching使用 2018-07-23
* @author oKong
*
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Api(tags="用户API")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
IUserService userService;
@PostMapping("add")
@ApiOperation(value="用户新增")
//正常业务时, 需要在user类里面进行事务控制,控制层一般不进行业务控制的。
//@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public Map<String,String> addUser(@Valid @RequestBody UserReq userReq){
User user = new User();
user.setCode(userReq.getCode());
user.setName(userReq.getName());
//由于设置了主键策略 id可不用赋值 会自动生成
//user.setId(0L);
userService.insert(user);
Map<String,String> result = new HashMap<String,String>();
result.put("respCode", "01");
result.put("respMsg", "新增成功");
//事务测试
//System.out.println(1/0);
return result;
}
@PostMapping("update")
@ApiOperation(value="用户修改")
//更新时 直接删除缓存 以保证下次获取时先从数据库中获取最新数据
@CacheEvict(value="OKONG", key="#userReq.id")
public Map<String,String> updateUser(@Valid @RequestBody UserReq userReq){
if(userReq.getId() == null || "".equals(userReq.getId())) {
throw new CommonException("0000", "更新时ID不能为空");
}
User user = new User();
user.setCode(userReq.getCode());
user.setName(userReq.getName());
user.setId(Long.parseLong(userReq.getId()));
userService.updateById(user);
Map<String,String> result = new HashMap<String,String>();
result.put("respCode", "01");
result.put("respMsg", "更新成功");
return result;
}
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
@ApiOperation(value="用户查询(ID)")
@ApiImplicitParam(name="id",value="查询ID",required=true)
@Cacheable(value="OKONG",key="#id")
public Map<String,Object> getUser(@PathVariable("id") String id){
//查询
User user = userService.selectById(id);
if(user == null) {
throw new CommonException("0001", "用户ID:" + id + ",未找到");
}
UserResp resp = UserResp.builder()
.id(user.getId().toString())
.code(user.getCode())
.name(user.getName())
.status(user.getStatus())
.build();
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<String,Object>();
result.put("respCode", "01");
result.put("respMsg", "成功");
result.put("data", resp);
return result;
}
@GetMapping("/page")
@ApiOperation(value="用户查询(分页)")
public Map<String,Object> pageUser(int current, int size){
//分页
Page<User> page = new Page<>(current, size);
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<String,Object>();
result.put("respCode", "01");
result.put("respMsg", "成功");
result.put("data", userService.selectPage(page));
return result;
}
}
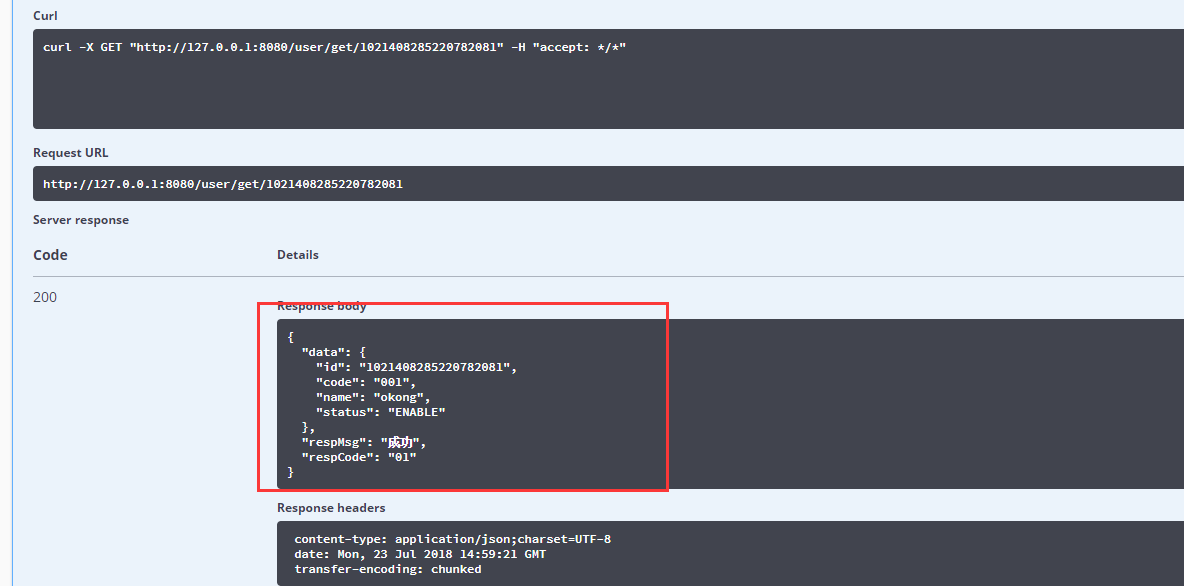
2.利用Swagger控制页面,新增一个用户,然后获取用户,会发现缓存里已经有此id的用户数据了。
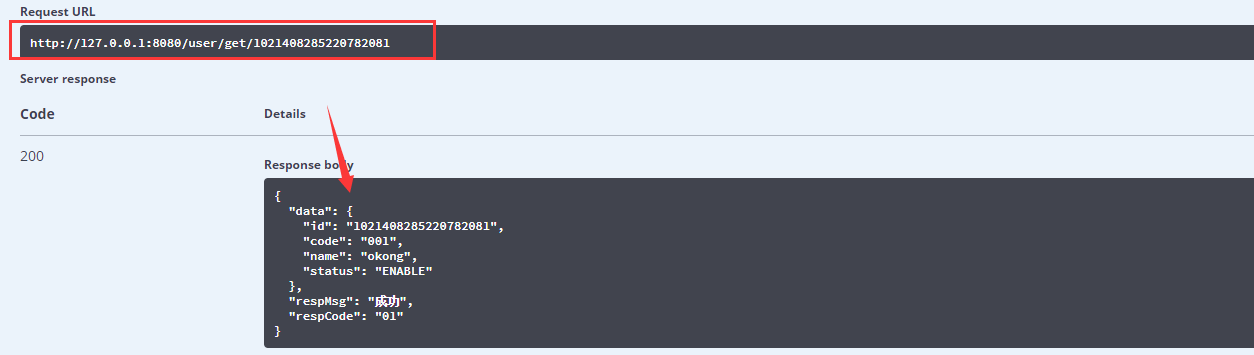
redis查看:
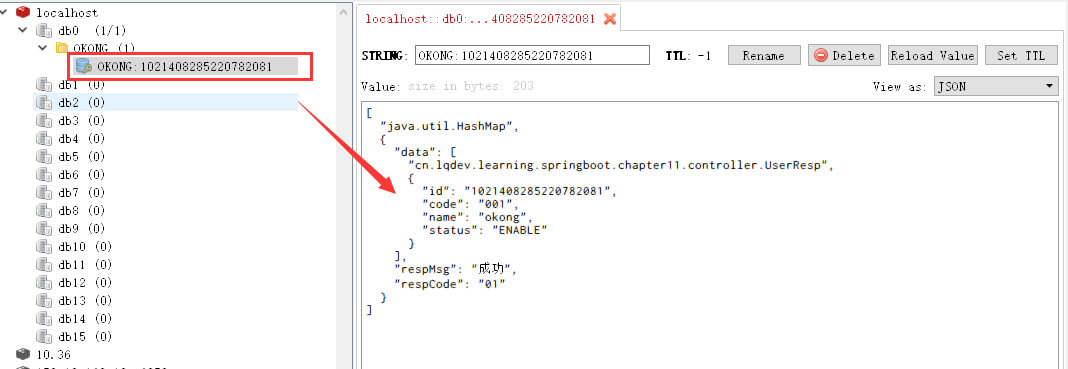
再次获取,会发现这次没有直接访问数据库了,而是直接从缓存读取。大家可在观察下控制台的输出情况(可先清空控制台,然后在请求)。
此时控制台无任何输出,但前端已经获取到值了。
关于SpringCache 注解的简单介绍
- @Cacheable:标记在一个方法上,也可以标记在一个类上。主要是缓存标注对象的返回结果,标注在方法上缓存该方法的返回值,标注在类上,缓存该类所有的方法返回值。
参数: value缓存名、 key缓存键值、 condition满足缓存条件、unless否决缓存条件

- @CacheEvict:从缓存中移除相应数据。

- @CachePut:方法支持缓存功能。与@Cacheable不同的是使用@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。

- @Caching:多个Cache注解使用,比如新增用户时,删除用户属性等需要删除或者更新多个缓存时,集合以上三个注解。
常用的就以上几个,对于@CacheConfig没使用过,这里就不说明了。
对于对几个注解类的简单使用就结束了,相关的详细用法,比如自定义条件缓存,自定义注解等,这里就不阐述了,请读者自行
SpEL上下文数据
Spring Cache提供了一些供我们使用的SpEL上下文数据,下表直接摘自互联网:
| 名称 | 位置 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| methodName | root对象 | 当前被调用的方法名 | root.methodName |
| method | root对象 | 当前被调用的方法 | root.method.name |
| target | root对象 | 当前被调用的目标对象 | root.target |
| targetClass | root对象 | 当前被调用的目标对象类 | root.targetClass |
| args | root对象 | 当前被调用的方法的参数列表 | root.args[0] |
| caches | root对象 | 当前方法调用使用的缓存列表(如@Cacheable(value={“cache1”, “cache2”})),则有两个cache | root.caches[0].name |
| argument name | 执行上下文 | 当前被调用的方法的参数,如findById(Long id),我们可以通过#id拿到参数 | user.id |
| result | 执行上下文 | 方法执行后的返回值(仅当方法执行之后的判断有效,如‘unless’,’cache evict’的beforeInvocation=false) | result |
@CacheEvict(value = "user", key = "#user.id", condition = "#root.target.canCache() and #root.caches[0].get(#user.id).get().username ne #user.username", beforeInvocation = true) public void conditionUpdate(User user)
总结
本章节主要是对
redis结合Spring Cache的集成和简单使用进行了说明,详细的用法,可自行搜索相关资料下,这里就不阐述了。因为对于百分之八十之上的缓存要求基本能满足了。使用缓存时,一定要注意缓存生命周期的控制,不然容易出现数据不一致的情况,谨记!
最后
目前互联网上很多大佬都有
SpringBoot系列教程,如有雷同,请多多包涵了。本文是作者在电脑前一字一句敲的,每一步都是实践的。若文中有所错误之处,还望提出,谢谢。
老生常谈
- 个人QQ:
499452441 - 微信公众号:
lqdevOps

完整示例:chapter-11