一、框架体系结构
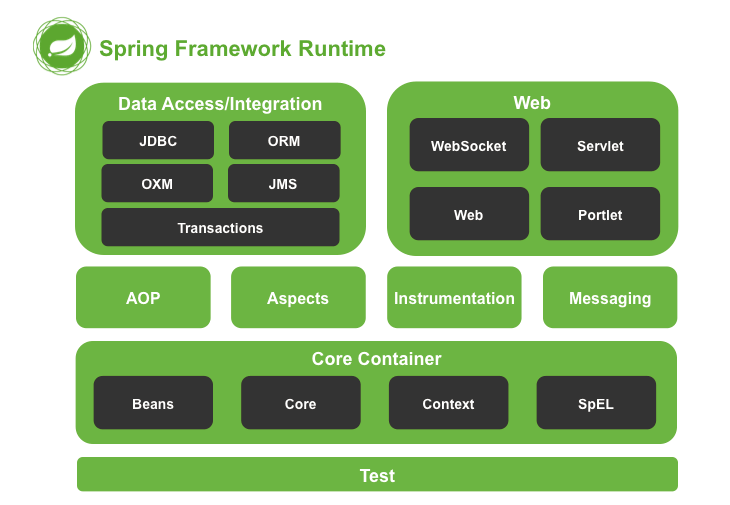
简单介绍
1. Data Access/Integration(数据访问/集成)
数据访问/集成层包括 JDBC、ORM、OXM、JMS 和 Transactions 模块,具体介绍如下。
- JDBC 模块:提供了一个 JDBC 的抽象层,大幅度减少了在开发过程中对数据库操作的编码。
- ORM 模块:对流行的对象关系映射 API,包括 JPA、JDO、Hibernate 和 iBatis 提供了的集成层。
- OXM 模块:提供了一个支持对象/XML 映射的抽象层实现,如 JAXB、Castor、XMLBeans、JiBX 和 XStream。
- JMS 模块:指 Java 消息服务,包含的功能为生产和消费的信息。
- Transactions 事务模块:支持编程和声明式事务管理实现特殊接口类,并为所有的 POJO。
2. Web 模块
Spring 的 Web 层包括 Web、Servlet、Struts 和 Portlet 组件,具体介绍如下。
- Web 模块:提供了基本的 Web 开发集成特性,例如多文件上传功能、使用的 Servlet 监听器的 IoC 容器初始化以及 Web 应用上下文。
- Servlet模块:包括 Spring 模型—视图—控制器(MVC)实现 Web 应用程序。
- Struts 模块:包含支持类内的 Spring 应用程序,集成了经典的 Struts Web 层。
- Portlet 模块:提供了在 Portlet 环境中使用 MV C实现,类似 Web-Servlet 模块的功能。
3. Core Container(核心容器)
Spring 的核心容器是其他模块建立的基础,由 Beans 模块、Core 核心模块、Context 上下文模块和 Expression Language 表达式语言模块组成,具体介绍如下。
- Beans 模块:提供了 BeanFactory,是工厂模式的经典实现,Spring 将管理对象称为 Bean。
- Core 核心模块:提供了 Spring 框架的基本组成部分,包括 IoC 和 DI 功能。
- Context 上下文模块:建立在核心和 Beans 模块的基础之上,它是访问定义和配置任何对象的媒介。ApplicationContext 接口是上下文模块的焦点。
- Expression Language 模块:是运行时查询和操作对象图的强大的表达式语言。
4. 其他模块
Spring的其他模块还有 AOP、Aspects、Instrumentation 以及 Test 模块,具体介绍如下。
- AOP 模块:提供了面向切面编程实现,允许定义方法拦截器和切入点,将代码按照功能进行分离,以降低耦合性。
- Aspects 模块:提供与 AspectJ 的集成,是一个功能强大且成熟的面向切面编程(AOP)框架。
- Instrumentation 模块:提供了类工具的支持和类加载器的实现,可以在特定的应用服务器中使用。
- Test 模块:支持 Spring 组件,使用 JUnit 或 TestNG 框架的测试。
二、下载
https://repo.spring.io/simple/libs-release-local/org/springframework/spring/
各个版本
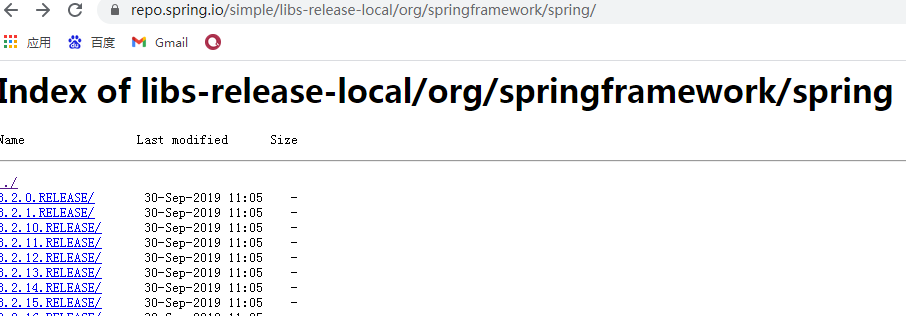
下载第一个
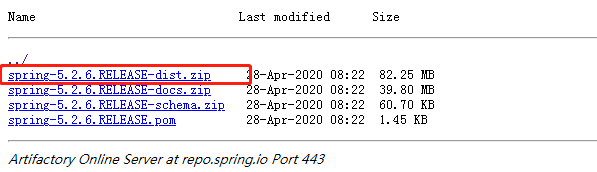
下载后
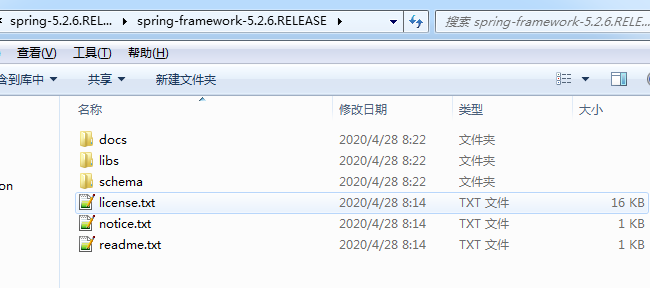
其中
docs 包含 Spring 的 API 文档和开发规范
libs 包含开发需要的 JAR 包和源码包
schema 包含开发所需要的 schema 文件,在这些文件中定义了 Spring 相关配置文件的约束
在lib 中
spring-core.jar 包含 Spring 框架基本的核心工具类,Spring 其他组件都要用到这个包中的类,是其他组件的基本核心。 spring-beans.jar 所有应用都要用到的,它包含访问配置文件、创建和管理 bean 以及进行 Inversion of Control(IoC)或者 Dependency Injection(DI)操作相关的所有类。 spring-context.jar Spring 提供在基础 IoC 功能上的扩展服务,此外还提供许多企业级服务的支持,如邮件服务、任务调度、JNDI 定位、EJB 集成、远程访问、缓存以及各种视图层框架的封装等 spring-expression.jar 定义了 Spring 的表达式语言。 需要注意的是,在使用 Spring 开发时,除了 Spring 自带的 JAR 包以外,还需要一个第三方 JAR 包 commons.logging 处理日志信息
日志jar地址
http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-logging/download_logging.cgi
三、IOC 容器 和spring bean
IoC 是指在程序开发中,实例的创建不再由调用者管理,而是由 Spring 容器创建。Spring 容器会负责控制程序之间的关系,而不是由程序代码直接控制,因此,控制权由程序代码转移到了 Spring 容器中,控制权发生了反转,这就是 Spring 的 IoC 思想,两种 IoC 容器,分别为 BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext
1、BeanFactory
BeanFactory 是基础类型的 IoC 容器,它由 org.springframework.beans.facytory.BeanFactory 接口定义,并提供了完整的 IoC 服务支持。简单来说,BeanFactory 就是一个管理 Bean 的工厂,它主要负责初始化各种 Bean,并调用它们的生命周期方法。
2、ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext 是 BeanFactory 的子接口,也被称为应用上下文。该接口的全路径为 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext,它不仅提供了 BeanFactory 的所有功能,还添加了对 i18n(国际化)、资源访问、事件传播等方面的良好支持。
两个常用的实现类:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 和 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类从类路径 ClassPath 中寻找指定的 XML 配置文件,找到并装载完成 ApplicationContext 的实例化工作
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext类从指定的文件系统路径中寻找指定的 XML 配置文件,找到并装载完成 ApplicationContext 的实例化工作
3、spring bean 常用属性

四、实践
简单的项目结构

1、两个实体 class 和 student
注意:需要测试在student 获取 calss ,故私有化一个

2、applicationContext.xml 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
bean 对象
<bean name="class" class="com.obge.model.Class">
<!-- 初始化 -->
<property name="name" value="一班" />
</bean>
依赖
<bean name="student" class="com.obge.model.Student">
<property name="name" value="小明" />
<!-- 使用ref来注入另一个bean -->
<property name="classStu" ref="class" />
</bean>
3、测试
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
//import com.obge.model.Class;
import com.obge.model.Student;
public class SpringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取 ApplicationContext.xml 中的内容
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"applicationContext.xml"});
Student stu = (Student)context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(stu.getName());
//从学生获取 班级
System.out.println(stu.getClassStu().getName());
}
}