为什么要使用数组: 因为不使用数组计算多个变量的时候太繁琐,不利于数据的处理。
-------- 数组也是一个变量,是存储一组相同类型的变量
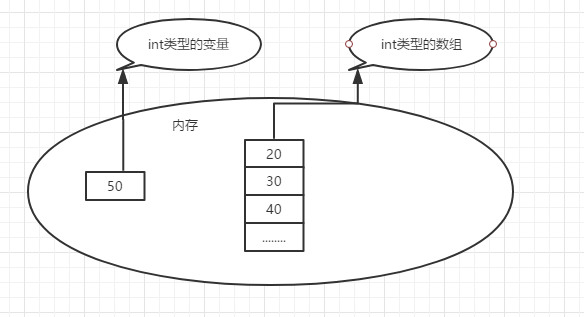
声明一个变量就是在内存中划出一块合适的空间
声明一个数组就是在内存中划出一块连续的空间
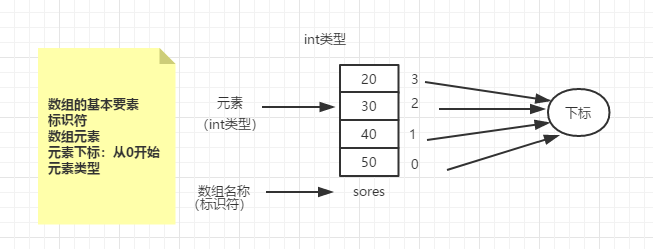
数组长度就是数组存放了多少个数,最大下标等于数组长度减一
数组中所有的元素必须属于相同的数据类型
----------- 如何使用数组


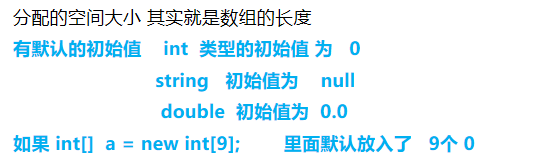



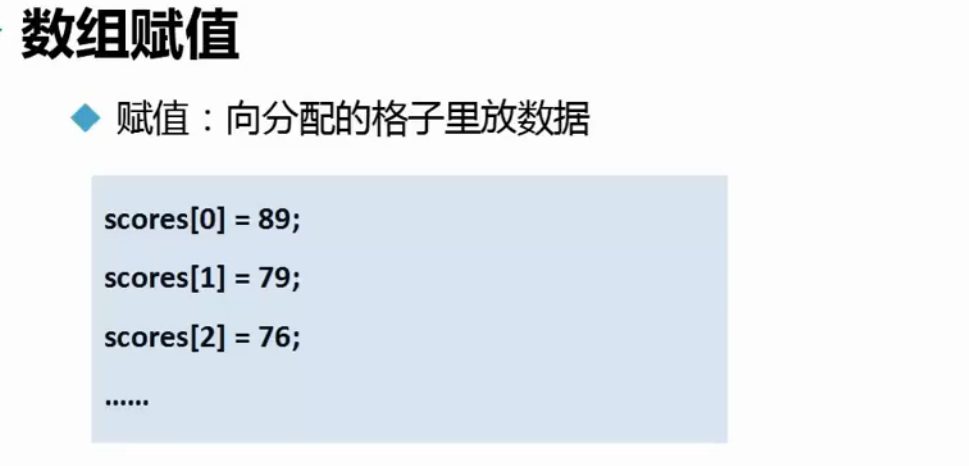

注意: 在边声明边赋值的时候不要再声明长度了 [] 中不要在写值了偶
边声明边赋值的时候数组的长度就被确定了,不能在往数组里面添加数字了
---- 练习
import java.util.Scanner; public class ArrayDemo { /** * 使用数组计算平均分 */ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] scores = new int[5]; //成绩数组 int sum = 0; //成绩总和 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入5位学员的成绩:"); for(int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++){ scores[i] = input.nextInt(); sum = sum + scores[i]; //成绩累加 } /*//使用foreach遍历 for(int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++){ scores[i] = input.nextInt(); } for(int score:scores){ sum+=score; }*/ //计算并输出平均分 System.out.println("学员的平均分是:" + (double)sum/scores.length); } }

----- 使用数组的常见错误
1、直接赋值的时候不需要写长度 但是不赋值的话要写长度, int[] scores = new int[];
2、数组下标越界异常 下标超过了数组长度减一的值

3、在进行创建数组并赋值的时候要放在同一条语句中
---- 猜数游戏
import java.util.*; public class GuessData { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] list = new int[] { 8, 4, 2, 1, 23, 344, 12 }; // 创建数组并赋值 int sum=0; //循环输出数列的值 //求数列中所有数值的和 for(int num:list){ System.out.println(num); sum+=num; } System.out.println("数组元素之和为:"+sum); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入一个整数: "); int guess = input.nextInt(); boolean isCorrect = false; for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { if (guess == list[i]) { isCorrect = true; break; } } if (isCorrect) { System.out.println("猜对了!"); } else { System.out.println("Sorry!"); } } }
----- 求最大值
import java.util.Scanner; public class MaxScore { /** * 求数组最大值 */ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] scores = new int[5]; int max = 0; //记录最大值 System.out.println("请输入5位学员的成绩:"); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); for(int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++){ scores[i] = input.nextInt(); } //计算最大值 //使用max存储擂主初始值:第一个元素为擂主 max = scores[0]; //循环打擂 for(int i = 1; i < scores.length; i++){ if(scores[i] > max){ max = scores[i]; } } System.out.println("考试成绩最高分为:" + max); } }
---------- 插入数值
有一个降序排列的数组,新增一个数字,也要保持降序排列
注要就是把插入的数值与数组中的值依次进行比较,找到第一个数值比他小的位置,就是他要插入的位置,然后在把他下标往后面的移动一位,
import java.util.*; public class Insert { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] list = new int[6]; // 长度为为6的数组 list[0] = 99; list[1] = 85; list[2] = 82; list[3] = 63; list[4] = 60; int index = list.length; // 保存新增成绩插入位置 System.out.println("请输入新增成绩: "); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int num = input.nextInt(); // 输入要插入的数据 // 找到新元素的插入位置 for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { if (num > list[i]) { index = i; break; } } // 元素后移 for (int j = list.length - 1; j > index; j--) { list[j] = list[j - 1]; // index下标开始的元素后移一个位置 } list[index] = num;// 插入数据 System.out.println("插入成绩的下标是:" + index); System.out.println("插入后的成绩信息是: "); for (int k = 0; k < list.length; k++) { // 循环输出目前数组中的数据 System.out.print(list[k] + " "); } } }
----- 统计数组中奇数和偶数的个数
package cn.jbit.lesson3; import java.util.Scanner; /** * 统计数组中的奇数和偶数的个数 * */ public class ArrayEx { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[8]; Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int count1 = 0; //记录奇数的个数 int count2 = 0; //记录偶数的个数 //从控制台接收8个整数,分别统计奇数和偶数的个数 for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){ System.out.print("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个整数:"); array[i] = input.nextInt(); if(array[i]%2==0){ count1++; }else{ count2++; } } System.out.println(); System.out.println("奇数的个数是:"+count2+"。"); System.out.println("偶数的个数是:"+count1+"。"); } }
---- 数组倒叙复制输出
1 package cn.jbit.lesson3; 2 /** 3 * 数组倒序复制输出 4 * @author boge 5 * 6 */ 7 public class ArrayEx2 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 int[] array = new int[10]; //源数组 10 int[] newArray = new int[10]; //目标数组 11 for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){ 12 array[i] = i; //元素的值等于其下标 13 } 14 System.out.println("原数组:"); 15 for(int num:array){ 16 System.out.print(num+" "); 17 } 18 19 System.out.println(); 20 21 int index = array.length-1; 22 23 for(int i=0;i<newArray.length;i++){ 24 newArray[i] = array[index--]; 25 } 26 27 System.out.println("新数组:"); 28 for(int num:newArray){ 29 System.out.print(num+" "); 30 } 31 } 32 }
------ 去除数组中的0
/** * 去除数组中的0 * */ public class ArrayEx3 { public static void main(String args[]){ int oldArr [] = {11,31,23,54,0,0,77,90,0,5,42,71,63,79,60,53} ; int count = 0 ; //记录数组中不为0的元素个数 for(int i = 0 ; i < oldArr.length; i++){ if(oldArr[i] != 0){ count ++ ; // 统计个数 } } int newArr [] = new int[count] ; // 新数组 //将原数组中不为0的元素保存到新数组中 int j = 0 ; // 控制新数组的下标 for(int i = 0 ; i < oldArr.length; i++){ if(oldArr[i] != 0){ newArr[j++] = oldArr[i] ; } } //输出新数组 for(int i = 0 ; i< newArr.length ; i++){ System.out.print(newArr[i] + " ") ; } } }
---- 合并数组
1 public class ArrayEx4 { 2 public static void main(String args[]){ 3 int arrayA [] = new int[] {1,7,9,11,13,17,19} ; 4 int arrayB [] = new int[] {2,4,6,8,10} ; 5 6 int len = arrayA.length + arrayB.length ; // 新数组的大小 7 int arrayC[] = new int[len] ; // 新数组 8 9 System.arraycopy(arrayA,0,arrayC,0,arrayA.length) ; // 拷贝第一个数组 10 System.arraycopy(arrayB,0,arrayC,arrayA.length,arrayB.length) ; // 拷贝第二个数组 11 java.util.Arrays.sort(arrayC) ; 12 13 14 for(int x = 0 ; x< arrayC.length ; x++){ 15 System.out.print(arrayC[x] + "、") ; 16 } 17 } 18 }