一.IntentService的基本概念
IntentService是继承于Service并处理异步请求的一个类,在IntentService内有一个工作线程来处理耗时操作,启动IntentService的方式和启动传统Service一样,同时,当任务执行完后,IntentService会自动停止,而不需要我们去手动控制。另外,可以启动IntentService多次,而每一个耗时操作会以工作队列的方式在IntentService的onHandleIntent回调方法中执行,并且,每次只会执行一个工作线程,执行完第一个再执行第二个,以此类推。所有请求都在一个单线程中,不会阻塞应用程序的主线程(UI Thread),同一时间只处理一个请求。那么,用IntentService有什么好处呢?首先,我们省去了在Service中手动开线程的麻烦,第二,当操作完成时,我们不用手动停止Service,第三,it's so easy to use!
二.开启代码之旅
OK!接下看看如何去使用,新建工程,新建一个继承IntentService的类,代码如下:
package com.nyl.intentservicesummarize; import android.app.IntentService; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.IBinder; import android.util.Log; /** * Created by Administrator on 2017/3/4 0004. */ public class ServiceTest extends IntentService{ private static final String TAG = ServiceTest.class.getSimpleName(); //必须实现父类的构造方法 public ServiceTest() { super("aa"); } /** * 必须重写的核心方法 * @param intent */ @Override protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) { //Intent是从Activity发过来的,携带识别参数,根据参数不同执行不同的任务 String action = intent.getExtras().getString("param"); if (action.equals("s1")) { Log.i(TAG,"启动第一个service"); }else if (action.equals("s2")){ Log.i(TAG,"启动第二个service"); }else if (action.equals("s3")){ Log.i(TAG,"启动第三个service"); try { //让服务休眠2秒 Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 重写其他方法,用于查看方法的调用顺序 * @param intent * @return */ @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { Log.i(TAG,"onBind"); return super.onBind(intent); } @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { Log.i(TAG,"onStartCommand"); return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); } @Override public void setIntentRedelivery(boolean enabled) { super.setIntentRedelivery(enabled); Log.i(TAG,"setIntentRedelivery"); } @Override public void onDestroy() { Log.i(TAG,"onDestroy"); super.onDestroy(); } }
AndroidManifest.xml注册下Service
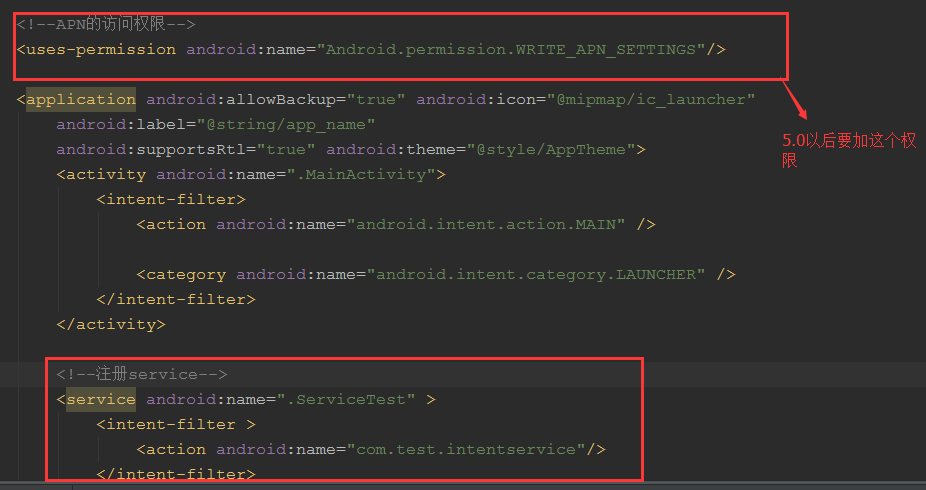
在MainActivity启动三次服务,代码如下:
package com.nyl.intentservicesummarize; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener { private Button btnStartIntentService; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); btnStartIntentService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStartIntentService); btnStartIntentService.setOnClickListener(this); } @Override public void onClick(View view) { if (view.getId() == R.id.btnStartIntentService){ /** * 有些时候我们使用Service的时需要采用隐私启动的方式, * 但是Android 5.0一出来后,其中有个特性就是Service Intent must be explitict, * 也就是说从Lollipop开始,service服务必须采用显示方式启动。 * 解决方法: 设置Intent的Action和packageName */ Intent it1 = new Intent(); it1.setAction("com.test.intentservice"); it1.setPackage(getPackageName()); Bundle b1 = new Bundle(); b1.putString("param", "s1"); it1.putExtras(b1); Intent it2 = new Intent("com.test.intentservice"); it2.setPackage(getPackageName()); Bundle b2 = new Bundle(); b2.putString("param", "s2"); it2.putExtras(b2); Intent it3 = new Intent("com.test.intentservice"); it3.setPackage(getPackageName()); Bundle b3 = new Bundle(); b3.putString("param", "s3"); it3.putExtras(b3); //接着启动多次IntentService,每次启动,都会新建一个工作线程 //但始终只有一个IntentService实例 startService(it1); startService(it2); startService(it3); } } }
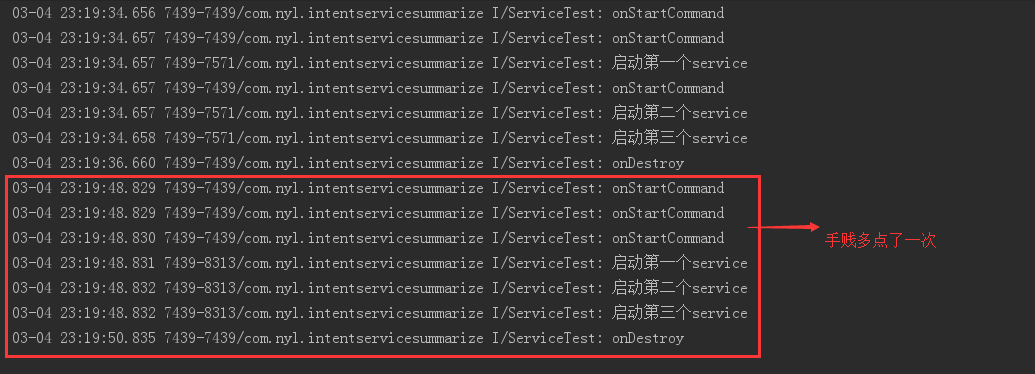
代码之路已经完成了,我们来看看打印的结果吧,如下图:
关于IntentService的内容总结暂时就这么多,文章如果有写得不对的地方,欢迎广大园友指正!