单表查询
数据库中包含大量的数据,根据特殊要求,可能只需要查询表中的指定数据,即对数据进行过滤在 select 语句中,通过 where 子句可以对数据进行过滤。
select [all | distinct] * | column_name from table_name where <条件表达式>;
下面总结:
开始建表
创建部门表(dept)
create table dept( `deptno` int(2) not null comment '部门编号', `dname` varchar(14) comment '部门名称', `loc` varchar(13) comment '部门所在地' );
插入表数据
insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc) values (10, 'ACCOUNTING', 'NEW YORK'), (20, 'RESEARCH', 'DALLAS'), (30, 'SALES', 'CHICAGO'), (40, 'OPERATIONS', 'BOSTON');
创建员工表(emp)
create table emp ( `empno` int(4) not null comment '员工编号', `ename` varchar(10) comment '员工姓名', `job` varchar(9) comment '员工职位', `mgr` int(4) comment '上级编号', `hiredate` date comment '入职日期', `sal` int(7) comment '员工工资', `comm` int(7) comment '员工奖金', `deptno` int(2) comment '部门编号' );
插入表数据
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7369, 'SMITH', 'CLERK', 7902, str_to_date('17-12-1980', '%d-%m-%Y'), 800,null,20), (7499, 'ALLEN', 'SALESMAN', 7698, str_to_date('20-02-1981', '%d-%m-%Y'),1600, 300, 30), (7521, 'WARD', 'SALESMAN', 7698, str_to_date('22-02-1981', '%d-%m-%Y'),1250, 500, 30), (7566, 'JONES', 'MANAGER', 7839, str_to_date('02-04-1981', '%d-%m-%Y'),2975, null, 20), (7654, 'MARTIN', 'SALESMAN', 7698, str_to_date('28-09-1981', '%d-%m-%Y'),1250, 1400, 30), (7698, 'BLAKE', 'MANAGER', 7839, str_to_date('01-05-1981', '%d-%m-%Y'),2850, null, 30), (7782, 'CLARK', 'MANAGER', 7839, str_to_date('09-06-1981', '%d-%m-%Y'),2450, null, 10), (7788, 'SCOTT', 'ANALYST', 7566, str_to_date('19-04-1987', '%d-%m-%Y'),3000,null, 20), (7839, 'KING', 'PRESIDENT', null, str_to_date('17-11-1981', '%d-%m-%Y'),5000,null, 10), (7844, 'TURNER', 'SALESMAN', 7698, str_to_date('08-09-1981', '%d-%m-%Y'),1500, 0, 30), (7876, 'ADAMS', 'CLERK', 7788, str_to_date('23-05-1987', '%d-%m-%Y'),1100,null, 20), (7900, 'JAMES', 'CLERK', 7698, str_to_date('03-12-1981', '%d-%m-%Y'),950,null, 30), (7902, 'FORD', 'ANALYST', 7566, str_to_date('03-12-1981', '%d-%m-%Y'),3000,null, 20), (7934, 'MILLER', 'CLERK', 7782, str_to_date('23-01-1982', '%d-%m-%Y'),1300,null, 10);
创建工资等级表(salgrade)
create table salgrade ( `grade` numeric primary key comment '工资等级', `losal` numeric comment '最低工资', `hisal` numeric comment '最高工资' );
插入表数据
insert into salgrade values (1, 700, 1200), (2, 1201, 1400), (3, 1401, 2000), (4, 2001, 3000), (5, 3001, 9999);
添加外键
alter table EMP add constraint PK_EMP primary key (EMPNO); alter table EMP add constraint FK_DEPTNO foreign key (DEPTNO) references DEPT (DEPTNO);
表建完了!
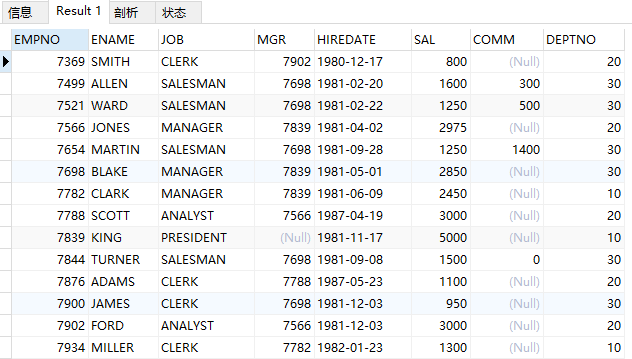
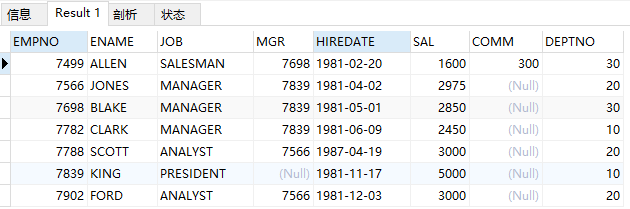
查询emp全部信息
select * from emp;
结果:
查询dept全部信息
select * from dept;
结果:

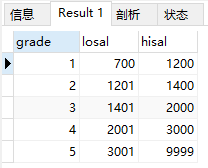
查询salgrade全部信息
select * from salgrade;
结果:
1.查询指定记录
例题:
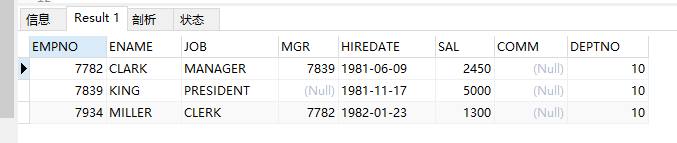
(1)查询编号为10的员工信息;
select * from emp where dpetno = 10;
结果:
(2)查询奖金为null的人员姓名与工资
select ename, sal from emp where comm is null;
结果:
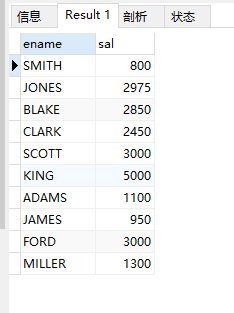
(3)查询年薪大于3万的人员的姓名与部门编号
select ename, deptno, sal*12+ifnull(comm,0) '年薪' from emp where sal*12+ifnull(comm,0) > 30000;
ifnull(n1, n2) 函数 作用为当 n1 为 null 时,函数返回 n2,反之,当 n1 不为 null 时,返回 n1 本身。
结果:
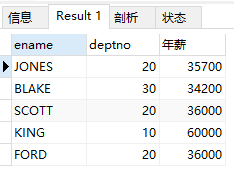
(4)查询工资大于1500
select * from emp where sal >1500;
结果:
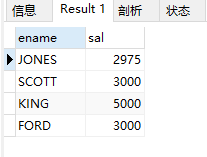
(5)查询emp表显示工资超过2850的员工姓名和工资
select ename, sal from emp where sal > 2850;
结果:
(6)查询emp表员工编号为7566的员工及所在部门编号
select ename,deptno from emp where empno = 7566;
结果:

2.带 in 关键字的查询
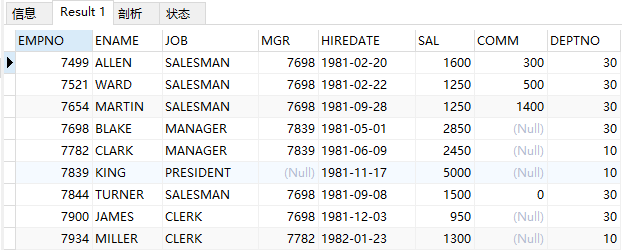
(1)查询emp表中员工在1或3部门的人员信息
select * from emp where deptno in(10, 30);
结果:
(2)查询显示不存在雇员的所有部门号
select d.deptno from dept d where d.deptno not in (select distinct deptno from emp);
distinct 关键字为去重。
结果:

3.带 between and 的范围查询
(1)查询emp表显示在1981年2月1日到1981年5月1日之间雇佣的雇员名、岗位及雇用日期,并以雇佣日期进行排序。
select ename,job,hiredate from emp where hiredate between '1981-02-01' and '1981-05-01' order by hiredate asc;
结果:

(2)查询81年入职的员工信息
select * from emp where hiredate between '1981-01-01' and '1981-12-31';
结果:

4.带 like 的字符匹配查询
like 关键字需要与通配符一起使用,通配符为 '%' 和 '_'。
'%' 匹配任意长度的字符,甚至包含零字符
'_' 一次只能匹配任意一个字符
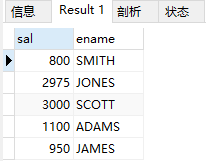
(1)查询姓名里面含有S员工信息 工资 姓名
select sal, ename from emp where ename like('%s%');
结果:
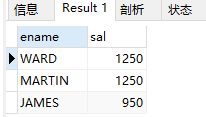
(2) 查询emp表显示第2个字符为“A”的所有雇员名及其工资
select ename,sal from emp where ename like('_A%');
结果:
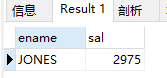
(3)求姓名以J开头第二个字符O的员工姓名与工资
select ename, sal from emp where ename like('jo%');
结果:
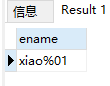
(4)求包含%的雇员姓名
因表里没有员工姓名里有百分号,为完成此题,需要给emp表中添加一条数据,如下:
insert into EMP (EMPNO, ENAME, JOB, MGR, HIREDATE, SAL, COMM, DEPTNO) values (7984, 'xiao%01', 'mansger', 7839, '1991-10-05', 1005, 1005, 30);
select ename from emp where ename like('%/%%') escape('/');
escape 关键字为转义。
结果:
学习完成可以删掉这条数据!
5.查询空值
(1)查询没有奖金的员工信息
select * from emp where comm is null;
结果:

表中的数据有一条 comm 为 0 的数据,注意 这里的奖金为 0 ,并不是没有奖金。
(2)查询工资大于1500且含有佣金的人员信息
select * from emp where sal >1500 and comm is not null;
结果:

6.带 and 的多条件查询
(1)查询部门为30且有奖金的员工信息
select * from emp where deptno = 30 and comm is not null;
结果:

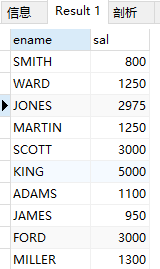
7.带 or 的多条件查询
(1)查询emp表显示工资不在1500~2850之间的所有雇员及工资
select ename, sal from emp where sal < 1500 or sal > 2850;
结果:
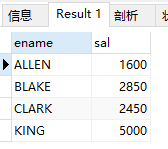
(2)查询emp表显示部门10和30中工资超过1500的雇员名及工资
select ename,sal from emp where (deptno = 10 or deptno = 30) and sal >1500;
and 的优先级大于or
结果:
8.对查询结果排序
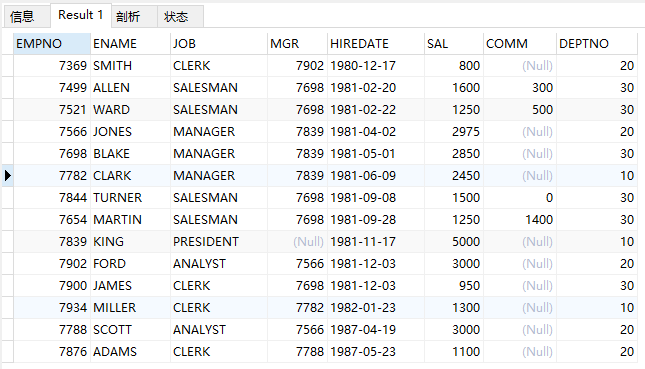
(1)按照员工编号降序查询全部信息
select * from emp order by empno desc;
desc 关键字为降序。
结果:

(2)按照员工入职时间升序查询全部信息
select * from emp order by hiredate asc;
asc 关键字为升序。
结果:
9.分组查询
分组查询是对数据按照某个或多个字段、表达式、列编号进行分组,MySQL中使用 group by 关键字对数据进行分组。
基本语法:
[ group by {字段名 |表达式 |列编号} [asc |desc],···[with rollup] ] [ having<分组条件表达式> ]
(1)创建分组
group by 从句根据所给的字段名返回分组的查询结果,可用于查询具有相同值的字段。
根据根据部门查询全部信息
select * from emp group by deptno;
结果:

group by 关键字通常和聚合函数一起使用,如 max() 、min()、count()、sum()、avg()。
1) 部门下员工的工资>2000的人数
select deptno, count(*) from emp where sal > 2000 group by deptno;
结果:
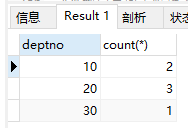
2)查询各部门人数
select deptno, count(*) from emp group by deptno;
结果:

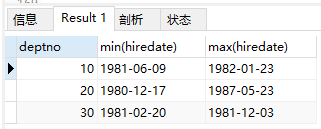
3)求部门里面工龄最大和工龄最小的
select deptno, min(hiredate), max(hiredate) from emp group by deptno;
结果:
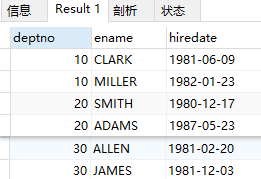
拓展:
在 3)的基础上,要知道人员姓名
select mm2.deptno, e1.ename, e1.hiredate from emp e1, (select min(hiredate) mind, max(hiredate) maxd, e.deptno from emp e group by e.deptno) mm2 where (e1.hiredate = mm2.mind or e1.hiredate = mm2.maxd) and e1.deptno = mm2.deptno;
结果:
4)求部门薪水最高
select deptno ,max(sal) from emp group by deptno;
结果:
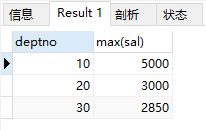
5)求部门薪水最低
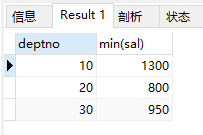
select deptno, min(sal) from emp group by deptno;
结果:
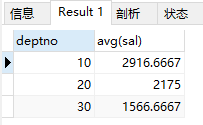
6)求部门平均薪水
select deptno ,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno;
结果:
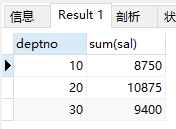
7)查询各个部门员工的工资之和
select deptno, sum(sal) from emp group by deptno;
结果:
(2)使用having过滤分组
使用 group by 对表中的数据分组后,可以通过 having 子句对分组后的数据进行条件筛选。
where 与 having 的区别:
1.where 不能与聚合函数连用。
2.where 在分组前过滤,having在分组后过滤。
3.where 排除的记录不再包含在分组中。
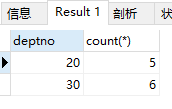
1)查询部门人数大于3的部门及部门人数
select deptno, count(*) from emp group by deptno having count(*) > 3;
结果:
(3)在 group by 子句中使用 with rollup
使用 with rollup 关键字之后,在所有查询出的分组纪录之后增加一条记录,该记录计算查询出的所有记录总和,及统计记录数量。
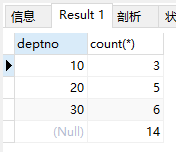
1)查询每个部门的人数
select deptno, count(*) from emp group by deptno with rollup;
结果:
(4)多字段分组
使用 group by 可以对多个字段进行分组,group by关键字后面跟需要分组的字段,MySQL根据多字段的值进行层次分组。分组层次从左到右。
1)根据部门编号和员工职位查询全部信息
select * from emp group by deptno, job;
结果:

(5)group by 和 order by 一起使用
某些情况下需要对分组进行 排序,order by 用来对查询记录排序,如果和 group by 一起使用,可以完成对分组之后的数据进行排序。
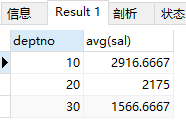
1)求部门的平均工资,由高到低。
select deptno, avg(sal) from emp group by deptno order by avg(sal) desc;
结果: