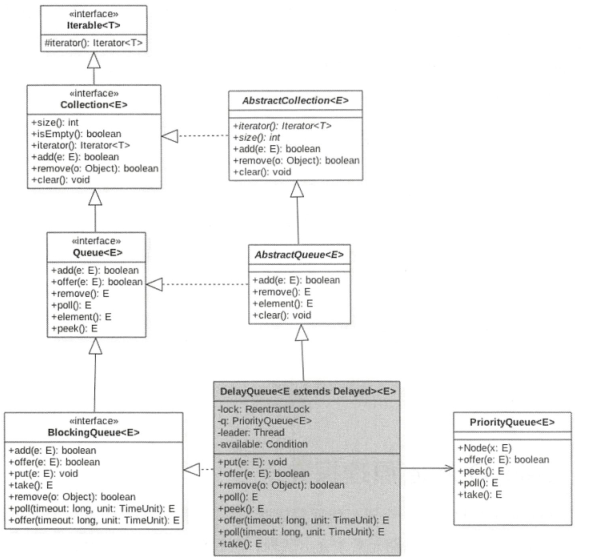
java并发包中的并发队列
7.1ConcurrentLinkedQueue
线程安全的无界非阻塞队列(非阻塞队列使用CAS非阻塞算法实现),其底层数组使用单向列表实现,对于出队和入队操作使用CAS非阻塞来实现线程安全的。
1、结构:
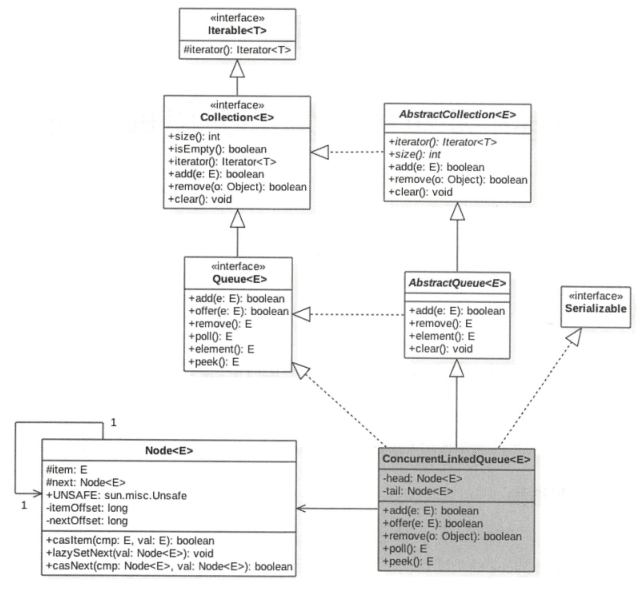
ConcurrentLinkedQueue内部的对列使用的是单向链表实现,并且有两个用volatile修改的节点头结点head和tail尾节点
private transient volatile Node<E> head; private transient volatile Node<E> tail; // 默认的无常构造使头节点和尾节点都指向一个值为null的哨兵节点 public ConcurrentLinkedQueue() { head = tail = new Node<E>(null); } // 同时还提供了一个有参构造,将指定集合中的数据插入到链表中 public ConcurrentLinkedQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) { Node<E> h = null, t = null; for (E e : c) { checkNotNull(e); Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e); if (h == null) h = t = newNode; else { t.lazySetNext(newNode); t = newNode; } } if (h == null) h = t = new Node<E>(null); head = h; tail = t; } // 内部类Node,使用Unsafe类来保证CAS操作的原子性 private static class Node<E> { // 元素值 volatile E item; // 下一个节点 volatile Node<E> next; Node(E item) { UNSAFE.putObject(this, itemOffset, item); } boolean casItem(E cmp, E val) { return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, itemOffset, cmp, val); } void lazySetNext(Node<E> val) { UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this, nextOffset, val); } boolean casNext(Node<E> cmp, Node<E> val) { return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val); } // Unsafe mechanics private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE; private static final long itemOffset; private static final long nextOffset; static { try { UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); Class<?> k = Node.class; itemOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (k.getDeclaredField("item")); nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (k.getDeclaredField("next")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new Error(e); } } }
2、offer方法
offer操作是在队列的尾部添加一个元素,如果提供的元素为null,则会抛出一个异常
public boolean offer(E e) {
// 校验提供的元素e,如果为null时则会抛出异常 checkNotNull(e);
// 使用原素e来构建一个新的节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e); for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) { Node<E> q = p.next; if (q == null) { // p is last node q为null则表明p是最后一个节点 ,下一步使用cas操作,将新建的节点赋给p if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) { // Successful CAS is the linearization point // for e to become an element of this queue, // and for newNode to become "live". if (p != t) // hop two nodes at a time 设置成功后,重置尾节点 casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK. return true; } // Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next } else if (p == q)
// 由于多线程操作,将head节点的next设置为自己,因此会出现p == q的情况 // We have fallen off list. If tail is unchanged, it // will also be off-list, in which case we need to // jump to head, from which all live nodes are always // reachable. Else the new tail is a better bet. // 如果之前的尾节点不是当前的尾节点(最新的尾节点),则将t重设为最新的尾节点(因为tail是内存可见的,其他线程操作后,当前线程是可以看得见的),
p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head; else // Check for tail updates after two hops. 循环找尾节点 p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q; } } // add方法内部也是走的offer方法 public boolean add(E e) { return offer(e); }
3、poll操作
获取在队列头部的节点,并移除,如果队列为空,则返回null
public E poll() { // goto标记 和循环充的continue restartFromHead关联,即重新走循环语句 restartFromHead: for (;;) { for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) { // 获取当前节点 E item = p.item; // CAS操作将当前head节点设置为null if (item != null && p.casItem(item, null)) { // Successful CAS is the linearization point // for item to be removed from this queue. // 设置成功后(判断是否成功,根据p和h,未修改之前时,p==h,修改成功后,p!=h),成功后,充值head节点 if (p != h) // hop two nodes at a time updateHead(h, ((q = p.next) != null) ? q : p); return item; } // p.next == null 表明链表为空 else if ((q = p.next) == null) { updateHead(h, p); return null; } else if (p == q) continue restartFromHead; else p = q; } } }
7.2LinkedBlockingQueue阻塞队列
1、类图:
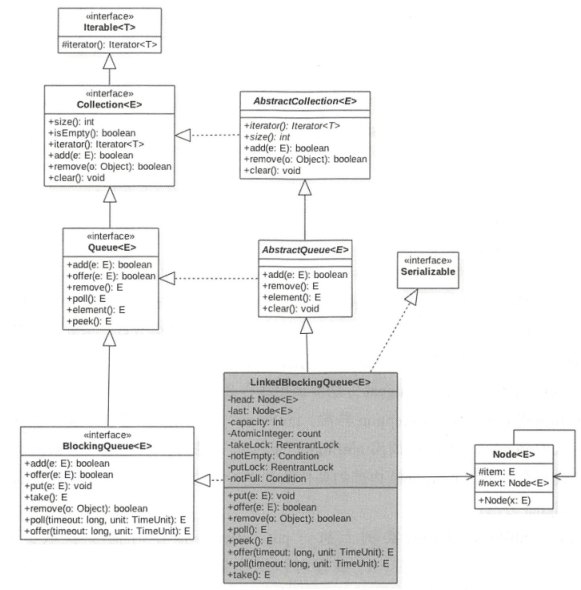
有上图可以看出LinkedBlockingQueue也是使用的单向链表实现的,也有两个Node,分别用来代表首节点和尾节点,一个AtomicInteger类型的count表示队列的元素个数,另外还有两个ReentrantLock类型的实例,分别控制入队和出队的原子性,以及两个Condition类型条件变量
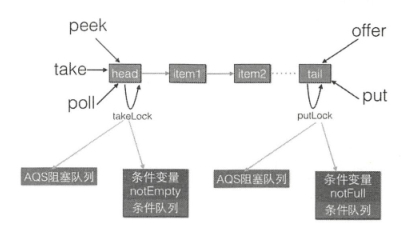
transient Node<E> head; private transient Node<E> last; /** 出队锁*/ private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock(); /** 非空条件变量 */ private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition(); /** 入队锁*/ private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock(); /** 非满条件变量*/ private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();
2、offer方法
向队尾插入一个元素,如果队列有空闲则插入成功,返回true,如果丢列已满,则返回false,注意,该方法是非阻塞的(put方法是阻塞的)
public boolean offer(E e) { // 如果参数e为null时,则会抛出异常 if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); // 获取容量count,AtomicInteger类型对象 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; // 判断当前容量是否已满,满的话返回false,不能入队 if (count.get() == capacity) return false; int c = -1; // 将参数e构建为节点对象 Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e); // 获取入队锁 final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; putLock.lock(); try { if (count.get() < capacity) { //入队 enqueue(node); // 节点数量++ c = count.getAndIncrement(); // 释放非满信号,可以继续入队 if (c + 1 < capacity) notFull.signal(); } } finally { putLock.unlock(); } if (c == 0) signalNotEmpty(); return c >= 0; } // 如对,链表的最后一个节点 private void enqueue(Node<E> node) { // assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread(); // assert last.next == null; last = last.next = node; }
3、put方法,基本和offer方法类似,只是在容量已满是,会阻塞当前线程,而不是直接返回false
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); // Note: convention in all put/take/etc is to preset local var // holding count negative to indicate failure unless set. int c = -1; Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e); final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; final AtomicInteger count = this.count; putLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { // 如果已满,则阻塞线程,等待相应唤醒,唤醒之后会继续判断是否已满(防止伪共享出现) while (count.get() == capacity) { notFull.await(); } enqueue(node); c = count.getAndIncrement(); if (c + 1 < capacity) // 发出唤醒其他线程可以入队的信号 notFull.signal(); } finally { putLock.unlock(); } if (c == 0) signalNotEmpty(); }
4、poll出队(非阻塞)、peek出队(非阻塞)、take出队(阻塞)
poll:出队会删除出队元素
peek:出队不会删除
take:出队删除,并且是阻塞的
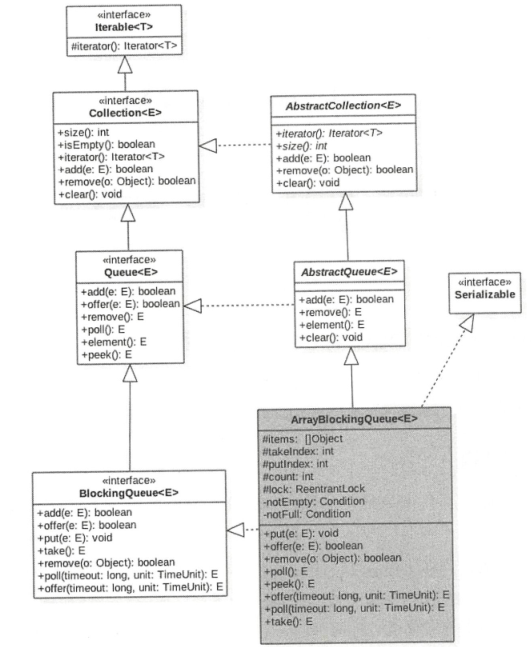
7.3ArrayBlockingQueue有界阻塞队列
1、类图
有类图可以看出ArrayBlockingQueue中有一个Object类型的数组,用来存放队列元素,putindex、takeIndex分别代表入队和出队索引,count代表队列元素个数,从定义可知,这些变量都没有使用volatile修改,因为相关的操作都是在锁内的,而锁又可以满足可见性和原子性,另外有两个条件变量notEmpty和notFull来控制入队和出队的同步。
/** 队列数组 */ final Object[] items; /** 出队索引 */ int takeIndex; /** 入队索引 */ int putIndex; /** 队列元素个数 */ int count; /* * Concurrency control uses the classic two-condition algorithm * found in any textbook. */ /** 一个独占锁 */ final ReentrantLock lock; /** 条件变量 */ private final Condition notEmpty; /** 条件变量 */ private final Condition notFull;
2、offer操作,向队尾插入一个元素,该方法是不阻塞的
offer操作和put操作类似,只不过put是阻塞的入队操作
public boolean offer(E e) { // 校验元素非空 checkNotNull(e); final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; // 加锁 lock.lock(); try { // 已满则返回false if (count == items.length) return false; else { enqueue(e); return true; } } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
private void enqueue(E x) { // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; // assert items[putIndex] == null; // 向入队索引处插入新元素 final Object[] items = this.items; items[putIndex] = x; // 插入之后,入队索引自增 if (++putIndex == items.length) putIndex = 0; count++; notEmpty.signal(); }
3、poll操作和take操作
同样的,一个非阻塞操作,一个阻塞操作
public E poll() { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public E take() throws InterruptedException { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lockInterruptibly(); try { while (count == 0) // 阻塞当前线程 notEmpty.await(); return dequeue(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
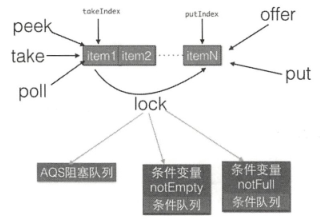
ArrayBlockingQueue通过使用全局独占锁实现了同时只有一个线程进行入队和出队操作,这个锁的粒度比较大,和在方法上添加synchronized关键字类似
7.4PriorityBlockingQueue带优先级的无界队列
该队列每次返回的都是优先级最高或者最低的元素,其内部是使用的二叉树堆实现的,所以每次遍历队列不保证有序。默认使用的是compareTo方法提供的比较规则。
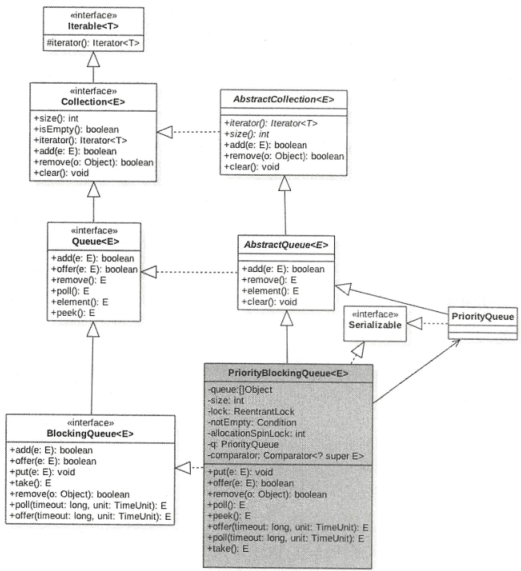
1、类图
有类图可以看出,PriorityBlockingQueue内部有一个Object类型的数组queue,用来存放队列元素的,size用来表示元素个数,allocationSpinLock是一个自旋锁,使用CAS操作来保证同时只有一个线程可以扩容队列,状态为0或1,0表示没有进行扩容,1表示正在进行扩容。comparator比较器,区分元素优先级的,lock独占锁用来控制同一时间只有一个线程可以进行入队和出队操作。notEmpte条件变量用来实现take方法的阻塞模式。(这里没有notFull条件变量,put方法是非阻塞的,因为PriorityBlockingQueue是一个无界队列)
2、offer操作和add操作
// add方法内部也是调用的offer方法 public boolean add(E e) { return offer(e); } public boolean offer(E e) { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); // 获取独占锁 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); int n, cap; Object[] array; // 判断您是否需要进行扩容 while ((n = size) >= (cap = (array = queue).length)) tryGrow(array, cap); try { // 获取当前的比较器,默认比较器为null(如果构建队列的时候没有提供比较器,则为null) Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator; if (cmp == null) siftUpComparable(n, e, array); else siftUpUsingComparator(n, e, array, cmp); size = n + 1; notEmpty.signal(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } return true; } // 扩容 private void tryGrow(Object[] array, int oldCap) { // 在扩容开始,先释放锁,是为了性能考虑,扩容是需要时间的,如果在扩容的同事占用锁,会降低并发性,所以为了提供并发性,使用CAS操作来保证只有一个线程可以进行扩容,让其他线程可以入队和出队 lock.unlock(); // must release and then re-acquire main lock // 扩容之后的数组 ,具体对象等计算出新的大小后会赋值 Object[] newArray = null; // allocationSpinLock为0,表示没有线程进行扩容,使用CAS操作设置该变量为1,则表示有线程正在进行扩容, 也就是锁CAS操作成功则进行扩容 if (allocationSpinLock == 0 && UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, allocationSpinLockOffset, 0, 1)) { try { // 当容量小的时候,扩容增速块,大64后,扩容为50% int newCap = oldCap + ((oldCap < 64) ? (oldCap + 2) : // grow faster if small (oldCap >> 1)); // 如果扩容后,大于Maxinteger-8,则设置默认最大容量 if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) { // possible overflow int minCap = oldCap + 1; if (minCap < 0 || minCap > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) throw new OutOfMemoryError(); newCap = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } // 新建指定大小的列表数组 if (newCap > oldCap && queue == array) newArray = new Object[newCap]; } finally { // 同时将allocationSpinLock重新设置为0,表名没有正在进行扩容的线程 allocationSpinLock = 0; } } // 这一个判断是当第一个线程CAS成功之后,第二个线程也进入扩容节点,则让第二线程让出cpu,让第一线程尽快执行完扩容 if (newArray == null) // back off if another thread is allocating Thread.yield(); lock.lock(); // 扩容成功之后,将旧数组中的数据复制到新数组中 if (newArray != null && queue == array) { queue = newArray; System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, oldCap); } } // 默认比较器的入队操作,也就是建堆算法 private static <T> void siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array) { // 新增的元素都是Compareable的子类 Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>) x; // k为之前队列个数,如果原来队列元素大于0,则需要判断当前新增元素的位置,否则,直接入队 while (k > 0) { int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; Object e = array[parent]; if (key.compareTo((T) e) >= 0) break; array[k] = e; k = parent; } array[k] = key; } private static <T> void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, T x, Object[] array, Comparator<? super T> cmp) { while (k > 0) { int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; Object e = array[parent]; if (cmp.compare(x, (T) e) >= 0) break; array[k] = e; k = parent; } array[k] = x; }
重点看建堆方法(即元素入队):
假设队列初始化大小2,默认比价器,以下为int类型的元素入队 分别是offer(2) / offer(4) / offer(6) / offer(1) 4次入队
1、当调用offer(2)时,在获取独占锁后,判断时候当前是否需要扩容,如果正在进行扩容,则自旋等待扩容完毕,没有则进入建堆方法(即下边的siftUpComparable(),该方法三个参数,第一:当前队列元素的数量,第二:入队的元素对象,第三:列表底层数组),
该方法内,会先进性判断k(当前列表内已有的元素数量),如果当前元素数量不大于0(即还没有元素),则直接将array[0] 设置为当前入队元素,否则进入while循环进行建堆,当本次调用offer(2)时,为第一次添加元素,则直接将array[0]设置为2。则当前元素数量n=1,当前队列大小size=1,容量cap=length=2,size+1
 ----->>>
----->>> 
2、当第二次调用offer方法是,即调用offer(4)时,同样先进性判断是否需要扩容,没有则进入siftUpComparable方法,此时参数k=1,进入while循环,循环内计算得到parent=0,e=2,key=4(key就是当前要入队的元素),因为key>e,退出循环,执行array[k] = key代码,即将当前入队的元素放置到下表为1的位置,size+1即如下图

3、第三次调用offer 方法,即调用offer(6)时,同样判断是否需要扩容,因为当前n=size=2 >= cap则需要进行扩容,进入扩容方法(这一块看上边代码,最终会将原数组内的元素复制到新的数组中),扩容后继续调用siftUpComparable方法,此时参数k=size=2,x=6,array为新的数组(长度为2+(2+2),即cap = cap+ (cap+2)这个实在容量较小的情况下,否则将容量扩大50%),key=6,此时k大于0,进入循环,计算的parent=0,e=2,因为key>e,则退出循环,将array[2]设置为6,size+1即下图

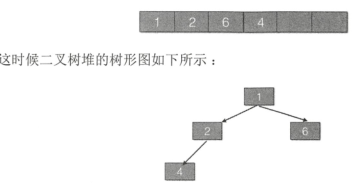
4、第四次调用offer方法,即调用offer(1),同样判断是否需要扩容,此时不需要扩容,则进入siftUpComparable方法,此时参数k=3,x=1,array=[2,4,6],key=1,此时k>0,进入循环,计算的parent=1,e=array[1]=4,此时key<e,则将元素4复制到k下标出,即
array[3]=4,此时数组为【2,4,6,4】,k重新设置为1,继续循环(因为k仍大于0),第二次循环,parent=0,e=array[0]=2,key=1,此时key<e,则将array[1]设置为2,k=0,此时数组为【2,2,6,4】,此时k=0,终止循环,最终将array[0]设置为1,此时数组为【1,2,6,4】
1 // 默认比较器的情况 2 private static <T> void siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array) { 3 Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>) x; 4 while (k > 0) { 5 int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; 6 Object e = array[parent]; 7 if (key.compareTo((T) e) >= 0) 8 break; 9 array[k] = e; 10 k = parent; 11 } 12 array[k] = key; 13 }
7.5DelayQueue无界阻塞延迟队列
该队列属于无界阻塞的延迟队列,队列中的每一个元素都有个过期时间,当从队列获取元素时,只有过期的元素才会出队,队列的头元素是最快要过期的元素。
1、类图:
用类图可以看出,延迟队列内部使用PriorityQueue存放数据,使用ReentrantLock实现线程同步。另外,队列里边的元素都要实现Delayed接口,由于每个元素都有一个过期时间,所以要实现获知当前元素还有多久时间过期的接口,由于内部是有优先级队列来实现,所以要实现元素之间相互比较的接口Delayed接口