整个代码文件如下:

BertModel类实现了BERT模型,代码位于modeling.py模块中。
1.配置类(BertConfig)
这段代码定义了BERT模型的一些默认参数和4个文件处理函数。
参数:
- vocab_size:词表大小
- hidden_size:隐藏层神经元数
- num_hidden_layers:Transformer encoder中的隐藏层数
- num_attention_heads:multi-head attention 的head数
- intermediate_size:encoder的“中间”隐层神经元数(例如feed-forward layer)
- hidden_act:隐藏层激活函数
- hidden_dropout_prob:隐层dropout率
- attention_probs_dropout_prob:注意力部分的dropout
- max_position_embeddings:最大位置编码
- type_vocab_size:token_type_ids的词典大小
- initializer_range:truncated_normal_initializer初始化方法的stdev
函数:
- from_dict(cls,json_object):从字典中获取config参数;
- from_json(cls,json_file):从json文件中获取config参数;
- to_dict():将实例序列化为Python字典;
- to_json_string():将此实例序列化为JSON字符串。
class BertConfig(object):
"""Configuration for `BertModel`."""
def __init__(self,
vocab_size, # 词表大小
hidden_size=768, # 隐藏层神经元数
num_hidden_layers=12, # transformer encoder中的隐藏层数
num_attention_heads=12, # multi-head attention中head的数量
intermediate_size=3072, # encoder的"中间"隐层神经元数
hidden_act="gelu",# 隐藏层激活函数
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1, # 隐层dropout率
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1, # 注意力部分的dropout
max_position_embeddings=512, # 最大位置编码
type_vocab_size=16, # token_type_ids的词典大小
initializer_range=0.02): # 初始化方法的stdev
"""Constructs BertConfig.
Args:
vocab_size: Vocabulary size of `inputs_ids` in `BertModel`.
hidden_size: Size of the encoder layers and the pooler layer.
num_hidden_layers: Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder.
num_attention_heads: Number of attention heads for each attention layer in
the Transformer encoder.
intermediate_size: The size of the "intermediate" (i.e., feed-forward)
layer in the Transformer encoder.
hidden_act: The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the
encoder and pooler.
hidden_dropout_prob: The dropout probability for all fully connected
layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler.
attention_probs_dropout_prob: The dropout ratio for the attention
probabilities.
max_position_embeddings: The maximum sequence length that this model might
ever be used with. Typically set this to something large just in case
(e.g., 512 or 1024 or 2048).
type_vocab_size: The vocabulary size of the `token_type_ids` passed into
`BertModel`.
initializer_range: The stdev of the truncated_normal_initializer for
initializing all weight matrices.
"""
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.hidden_act = hidden_act
self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, json_object):
"""Constructs a `BertConfig` from a Python dictionary of parameters."""
config = BertConfig(vocab_size=None)
for (key, value) in six.iteritems(json_object):
config.__dict__[key] = value
return config
@classmethod
def from_json_file(cls, json_file):
"""Constructs a `BertConfig` from a json file of parameters."""
with tf.gfile.GFile(json_file, "r") as reader:
text = reader.read()
return cls.from_dict(json.loads(text))
def to_dict(self):
"""Serializes this instance to a Python dictionary."""
output = copy.deepcopy(self.__dict__)
return output
def to_json_string(self):
"""Serializes this instance to a JSON string."""
return json.dumps(self.to_dict(), indent=2, sort_keys=True) + "
"
2.获取词向量(embedding_lookup)
def embedding_lookup(input_ids,
vocab_size,
embedding_size=128,
initializer_range=0.02,
word_embedding_name="word_embeddings",
use_one_hot_embeddings=False)
功能:输入每句话每个单词的id,返回这句话的embedding表示(获得token embedding)
参数:
- input_ids:word id 【batch_size, seq_length】
- vocab_size:embedding词表
- embedding_size:embedding维度
- initializer_range:embedding初始化范围
- word_embedding_name:embeddding table命名
- use_one_hot_embeddings:是否使用one-hot embedding
返回:
- output:输出对应单词的词向量
[batch_size, seq_length, num_inputs*embedding_size] - embedding table:单词对应embedding的表【batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size】
如果使用one-hot,则先对输入word_ids进行one-hot处理,再乘以embedding_table,得到对应word的词向量;不使用one-hot,直接用从embedding_table中获取对应word_ids的词向量。
def embedding_lookup(input_ids,
vocab_size,
embedding_size=128,
initializer_range=0.02,
word_embedding_name="word_embeddings",
use_one_hot_embeddings=False):
"""Looks up words embeddings for id tensor.
获取词向量
Args:
input_ids: int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length] containing word
ids.
vocab_size: int. Size of the embedding vocabulary.
embedding_size: int. Width of the word embeddings.
initializer_range: float. Embedding initialization range.
word_embedding_name: string. Name of the embedding table.
use_one_hot_embeddings: bool. If True, use one-hot method for word
embeddings. If False, use `tf.gather()`.
Returns:
float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size].
"""
# This function assumes that the input is of shape [batch_size, seq_length,
# num_inputs].
#
# If the input is a 2D tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length], we
# reshape to [batch_size, seq_length, 1].
if input_ids.shape.ndims == 2:
input_ids = tf.expand_dims(input_ids, axis=[-1])
embedding_table = tf.get_variable(
name=word_embedding_name,
shape=[vocab_size, embedding_size],
initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
flat_input_ids = tf.reshape(input_ids, [-1]) #【batch_size*seq_length*input_num】
if use_one_hot_embeddings:
one_hot_input_ids = tf.one_hot(flat_input_ids, depth=vocab_size)
output = tf.matmul(one_hot_input_ids, embedding_table)
else:
output = tf.gather(embedding_table, flat_input_ids)
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_ids)
output = tf.reshape(output,
input_shape[0:-1] + [input_shape[-1] * embedding_size])
return (output, embedding_table)
3.词向量的后续处理(embedding_postprocessor)
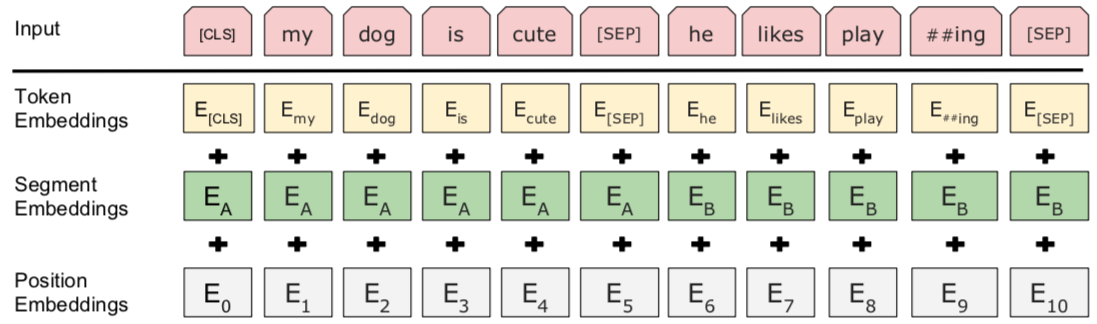
def embedding_postprocessor(input_tensor,
use_token_type=False,
token_type_ids=None,
token_type_vocab_size=16,# 一般是2
token_type_embedding_name="token_type_embeddings",
use_position_embeddings=True,
position_embedding_name="position_embeddings",
initializer_range=0.02,
max_position_embeddings=512,#最大位置编码,必须大于等于max_seq_len
dropout_prob=0.1):
功能:在token embedding的基础上,增加segment embedding和position embedding。
输入:
- input_tensor:float,[batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size].
- use_token_type: 布尔,是否添加‘token_type_ids’的embedding
- token_type_ids: (可选) int32,[batch_size, seq_length]. 只有use_token_type为True情况下使用
- token_type_vocab_size: int. “ token_type_ids”的词汇量
- token_type_embedding_name: string,token type ids的embedding table表名称
- use_position_embeddings: 布尔,是否添加position embeddings
- position_embedding_name: string,positional embedding的embedding table表名称
- initializer_range: float,权重初始化范围
- max_position_embeddings: int,此模型可能曾经使用的最大sequence长度。 该长度可以比input_tensor的序列长度长,但不能短。
- dropout_prob: float,应用于最终输出张量的dropout概率
def embedding_postprocessor(input_tensor,
use_token_type=False,
token_type_ids=None,
token_type_vocab_size=16,# 一般是2
token_type_embedding_name="token_type_embeddings",
use_position_embeddings=True,
position_embedding_name="position_embeddings",
initializer_range=0.02,
max_position_embeddings=512,#最大位置编码,必须大于等于max_seq_len
dropout_prob=0.1):
"""Performs various post-processing on a word embedding tensor.
Args:
input_tensor: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length,
embedding_size].
use_token_type: bool. Whether to add embeddings for `token_type_ids`.
token_type_ids: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length].
Must be specified if `use_token_type` is True.
token_type_vocab_size: int. The vocabulary size of `token_type_ids`.
token_type_embedding_name: string. The name of the embedding table variable
for token type ids.
use_position_embeddings: bool. Whether to add position embeddings for the
position of each token in the sequence.
position_embedding_name: string. The name of the embedding table variable
for positional embeddings.
initializer_range: float. Range of the weight initialization.
max_position_embeddings: int. Maximum sequence length that might ever be
used with this model. This can be longer than the sequence length of
input_tensor, but cannot be shorter.
dropout_prob: float. Dropout probability applied to the final output tensor.
Returns:
float tensor with same shape as `input_tensor`.
Raises:
ValueError: One of the tensor shapes or input values is invalid.
"""
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor, expected_rank=3)#【batch_size,seq_length,embedding_size】
batch_size = input_shape[0]
seq_length = input_shape[1]
width = input_shape[2]
output = input_tensor
# Segment position信息
if use_token_type:
if token_type_ids is None:
raise ValueError("`token_type_ids` must be specified if"
"`use_token_type` is True.")
token_type_table = tf.get_variable(
name=token_type_embedding_name,
shape=[token_type_vocab_size, width],
initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# This vocab will be small so we always do one-hot here, since it is always
# faster for a small vocabulary.
flat_token_type_ids = tf.reshape(token_type_ids, [-1])
one_hot_ids = tf.one_hot(flat_token_type_ids, depth=token_type_vocab_size)
token_type_embeddings = tf.matmul(one_hot_ids, token_type_table)
token_type_embeddings = tf.reshape(token_type_embeddings,
[batch_size, seq_length, width])
output += token_type_embeddings
# Position embedding信息
if use_position_embeddings:
# 确保seq_length小于等于max_position_embeddings
assert_op = tf.assert_less_equal(seq_length, max_position_embeddings)
with tf.control_dependencies([assert_op]):
full_position_embeddings = tf.get_variable(
name=position_embedding_name,
shape=[max_position_embeddings, width],
initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# Since the position embedding table is a learned variable, we create it
# using a (long) sequence length `max_position_embeddings`. The actual
# sequence length might be shorter than this, for faster training of
# tasks that do not have long sequences.
#
# So `full_position_embeddings` is effectively an embedding table
# for position [0, 1, 2, ..., max_positin_embeddings-1], and the current
# sequence has positions [0, 1, 2, ... seq_length-1], so we can just
# perform a slice.
position_embeddings = tf.slice(full_position_embeddings, [0, 0],
[seq_length, -1])
num_dims = len(output.shape.as_list())
# word embedding之后的tensor是[batch_size, seq_length, width]
# 因为位置编码是与输入内容无关,它的shape总是[seq_length, width]
# 我们无法把位置Embedding加到word embedding上
# 因此我们需要扩展位置编码为[1, seq_length, width]
# 然后就能通过broadcasting加上去了。
# Only the last two dimensions are relevant (`seq_length` and `width`), so
# we broadcast among the first dimensions, which is typically just
# the batch size.
position_broadcast_shape = []
for _ in range(num_dims - 2):
position_broadcast_shape.append(1)
position_broadcast_shape.extend([seq_length, width])
position_embeddings = tf.reshape(position_embeddings,
position_broadcast_shape)
output += position_embeddings
output = layer_norm_and_dropout(output, dropout_prob)
return output
4.构造attention_mask
def create_attention_mask_from_input_mask(from_tensor, to_mask):
"""Create 3D attention mask from a 2D tensor mask.
Args:
from_tensor: 2D or 3D Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, ...].
to_mask: int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, to_seq_length].
Returns:
float Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, to_seq_length].
"""
功能:从2维的mask生成3维的attention mask。
参数:
- from_tensor:padding后的input_ids,2D或者3D张量,[batch_size, from_seq_length,…]
- to_mask:mark标记向量[batch_size, to_seq_length]
返回:
- mask:[batch_size, from_seq_length, to_seq_length]
def create_attention_mask_from_input_mask(from_tensor, to_mask):
"""Create 3D attention mask from a 2D tensor mask.
Args:
from_tensor: 2D or 3D Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, ...].
to_mask: int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, to_seq_length].
Returns:
float Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, to_seq_length].
"""
from_shape = get_shape_list(from_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3])
batch_size = from_shape[0]
from_seq_length = from_shape[1]
to_shape = get_shape_list(to_mask, expected_rank=2)
to_seq_length = to_shape[1]
to_mask = tf.cast(
tf.reshape(to_mask, [batch_size, 1, to_seq_length]), tf.float32)
# We don't assume that `from_tensor` is a mask (although it could be). We
# don't actually care if we attend *from* padding tokens (only *to* padding)
# tokens so we create a tensor of all ones.
#
# `broadcast_ones` = [batch_size, from_seq_length, 1]
broadcast_ones = tf.ones(
shape=[batch_size, from_seq_length, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
# Here we broadcast along two dimensions to create the mask.
mask = broadcast_ones * to_mask
return mask
5.注意力层(attention layer)
def attention_layer(from_tensor,
to_tensor,
attention_mask=None,
num_attention_heads=1,
size_per_head=512,
query_act=None,
key_act=None,
value_act=None,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0,
initializer_range=0.02,
do_return_2d_tensor=False,
batch_size=None,
from_seq_length=None,
to_seq_length=None)
功能:实现multi-head attention,考虑key-query-value形式的attention,输入的from_tensor当做是query, to_tensor当做是key和value,当两者相同的时候即为self-attention。
参数:
- from_tensor:[batch_size, from_seq_length, from_width]
- to_tensor:[batch_size, to_seq_length, to_width]
- attention_mask=None:[batch_size,from_seq_length, to_seq_length]
- num_attention_heads=1:attention head numbers
- size_per_head=512:每个head的大小
- query_act=None:query变换的激活函数
- key_act=None:key变换的激活函数
- value_act=None:value变换的激活函数
- attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0:attention层的dropout
- initializer_range=0.02:初始化取值范围
- do_return_2d_tensor=False:是否返回2d张量,
- 如果True,输出形状[batch_size*from_seq_length,num_attention_heads*size_per_head]
- 如果False,输出形状[batch_size, from_seq_length, num_attention_heads*size_per_head]
- batch_size=None:如果输入是3D的, #那么batch就是第一维,但是可能3D的压缩成了2D的,所以需要告诉函数batch_size
- from_seq_length=None:同上
- to_seq_length=None:同上
具体过程参照:https://www.cnblogs.com/nxf-rabbit75/p/11945130.html
def attention_layer(from_tensor,
to_tensor,
attention_mask=None,
num_attention_heads=1,
size_per_head=512,
query_act=None,
key_act=None,
value_act=None,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0,
initializer_range=0.02,
do_return_2d_tensor=False,
batch_size=None,
from_seq_length=None,
to_seq_length=None):
"""Performs multi-headed attention from `from_tensor` to `to_tensor`.
This is an implementation of multi-headed attention based on "Attention
is all you Need". If `from_tensor` and `to_tensor` are the same, then
this is self-attention. Each timestep in `from_tensor` attends to the
corresponding sequence in `to_tensor`, and returns a fixed-with vector.
This function first projects `from_tensor` into a "query" tensor and
`to_tensor` into "key" and "value" tensors. These are (effectively) a list
of tensors of length `num_attention_heads`, where each tensor is of shape
[batch_size, seq_length, size_per_head].
Then, the query and key tensors are dot-producted and scaled. These are
softmaxed to obtain attention probabilities. The value tensors are then
interpolated by these probabilities, then concatenated back to a single
tensor and returned.
In practice, the multi-headed attention are done with transposes and
reshapes rather than actual separate tensors.
Args:
from_tensor: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length,
from_width].
to_tensor: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, to_seq_length, to_width].
attention_mask: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size,
from_seq_length, to_seq_length]. The values should be 1 or 0. The
attention scores will effectively be set to -infinity for any positions in
the mask that are 0, and will be unchanged for positions that are 1.
num_attention_heads: int. Number of attention heads.
size_per_head: int. Size of each attention head.
query_act: (optional) Activation function for the query transform.
key_act: (optional) Activation function for the key transform.
value_act: (optional) Activation function for the value transform.
attention_probs_dropout_prob: (optional) float. Dropout probability of the
attention probabilities.
initializer_range: float. Range of the weight initializer.
do_return_2d_tensor: bool. If True, the output will be of shape [batch_size
* from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head]. If False, the
output will be of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, num_attention_heads
* size_per_head].
batch_size: (Optional) int. If the input is 2D, this might be the batch size
of the 3D version of the `from_tensor` and `to_tensor`.
from_seq_length: (Optional) If the input is 2D, this might be the seq length
of the 3D version of the `from_tensor`.
to_seq_length: (Optional) If the input is 2D, this might be the seq length
of the 3D version of the `to_tensor`.
Returns:
float Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head]. (If `do_return_2d_tensor` is
true, this will be of shape [batch_size * from_seq_length,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head]).
Raises:
ValueError: Any of the arguments or tensor shapes are invalid.
"""
def transpose_for_scores(input_tensor, batch_size, num_attention_heads,
seq_length, width):
output_tensor = tf.reshape(
input_tensor, [batch_size, seq_length, num_attention_heads, width])
output_tensor = tf.transpose(output_tensor, [0, 2, 1, 3])
return output_tensor
from_shape = get_shape_list(from_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3])
to_shape = get_shape_list(to_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3])
if len(from_shape) != len(to_shape):
raise ValueError(
"The rank of `from_tensor` must match the rank of `to_tensor`.")
if len(from_shape) == 3:
batch_size = from_shape[0]
from_seq_length = from_shape[1]
to_seq_length = to_shape[1]
elif len(from_shape) == 2:
if (batch_size is None or from_seq_length is None or to_seq_length is None):
raise ValueError(
"When passing in rank 2 tensors to attention_layer, the values "
"for `batch_size`, `from_seq_length`, and `to_seq_length` "
"must all be specified.")
# Scalar dimensions referenced here:
# B = batch size (number of sequences)
# F = `from_tensor` sequence length
# T = `to_tensor` sequence length
# N = `num_attention_heads`
# H = `size_per_head`
from_tensor_2d = reshape_to_matrix(from_tensor)
to_tensor_2d = reshape_to_matrix(to_tensor)
# `query_layer` = [B*F, N*H]
query_layer = tf.layers.dense(
from_tensor_2d,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head,
activation=query_act,
name="query",
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# `key_layer` = [B*T, N*H]
key_layer = tf.layers.dense(
to_tensor_2d,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head,
activation=key_act,
name="key",
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# `value_layer` = [B*T, N*H]
value_layer = tf.layers.dense(
to_tensor_2d,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head,
activation=value_act,
name="value",
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# query_layer` = [B, N, F, H]
query_layer = transpose_for_scores(query_layer, batch_size,
num_attention_heads, from_seq_length,
size_per_head)
# `key_layer` = [B, N, T, H]
key_layer = transpose_for_scores(key_layer, batch_size, num_attention_heads,
to_seq_length, size_per_head)
# Take the dot product between "query" and "key" to get the raw
# attention scores.
# `attention_scores` = [B, N, F, T]
attention_scores = tf.matmul(query_layer, key_layer, transpose_b=True)
attention_scores = tf.multiply(attention_scores,
1.0 / math.sqrt(float(size_per_head)))
if attention_mask is not None:
# `attention_mask` = [B, 1, F, T]
attention_mask = tf.expand_dims(attention_mask, axis=[1])
# Since attention_mask is 1.0 for positions we want to attend and 0.0 for
# masked positions, this operation will create a tensor which is 0.0 for
# positions we want to attend and -10000.0 for masked positions.
adder = (1.0 - tf.cast(attention_mask, tf.float32)) * -10000.0
# Since we are adding it to the raw scores before the softmax, this is
# effectively the same as removing these entirely.
attention_scores += adder
# Normalize the attention scores to probabilities.
# `attention_probs` = [B, N, F, T]
attention_probs = tf.nn.softmax(attention_scores)
# This is actually dropping out entire tokens to attend to, which might
# seem a bit unusual, but is taken from the original Transformer paper.
attention_probs = dropout(attention_probs, attention_probs_dropout_prob)
# `value_layer` = [B, T, N, H]
value_layer = tf.reshape(
value_layer,
[batch_size, to_seq_length, num_attention_heads, size_per_head])
# `value_layer` = [B, N, T, H]
value_layer = tf.transpose(value_layer, [0, 2, 1, 3])
# `context_layer` = [B, N, F, H]
context_layer = tf.matmul(attention_probs, value_layer)
# `context_layer` = [B, F, N, H]
context_layer = tf.transpose(context_layer, [0, 2, 1, 3])
if do_return_2d_tensor:
# `context_layer` = [B*F, N*H]
context_layer = tf.reshape(
context_layer,
[batch_size * from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head])
else:
# `context_layer` = [B, F, N*H]
context_layer = tf.reshape(
context_layer,
[batch_size, from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head])
return context_layer
6.Transformer
def transformer_model(input_tensor, # 【batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size】
attention_mask=None, # 【batch_size, seq_length, seq_length】
hidden_size=768,
num_hidden_layers=12,
num_attention_heads=12,
intermediate_size=3072,
intermediate_act_fn=gelu, # feed-forward层的激活函数
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
initializer_range=0.02,
do_return_all_layers=False)
功能:实现Transformer模型
参数:
- input_tensor:[batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size]
- attention_mask=None:[batch_size, seq_length, seq_length]
- hidden_size=768:Transformer隐藏层大小
- num_hidden_layers=12:Transformer的层(block)数
- num_attention_heads=12:attention头的数目
- intermediate_size=3072:transformer的“中间”隐层神经元数
- intermediate_act_fn=gelu:feed-forward层的激活函数
- hidden_dropout_prob=0.1
- attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1
- initializer_range=0.02
- do_return_all_layers=False
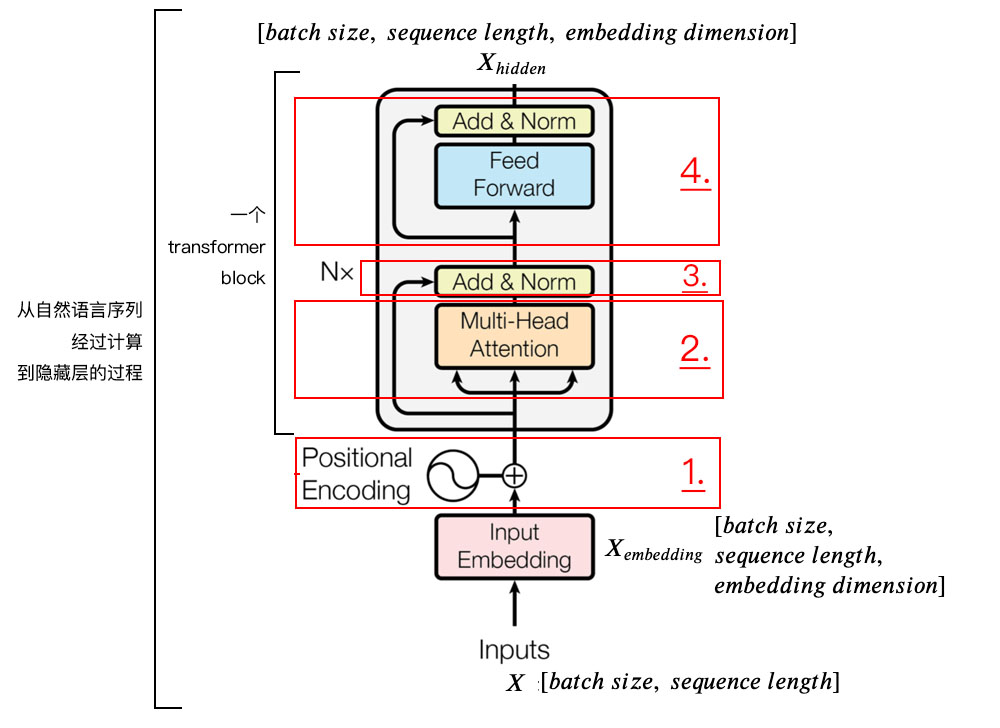
def transformer_model(input_tensor,
attention_mask=None,
hidden_size=768,
num_hidden_layers=12,
num_attention_heads=12,
intermediate_size=3072,
intermediate_act_fn=gelu,
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
initializer_range=0.02,
do_return_all_layers=False):
"""Multi-headed, multi-layer Transformer from "Attention is All You Need".
This is almost an exact implementation of the original Transformer encoder.
See the original paper:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762
Also see:
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensor2tensor/blob/master/tensor2tensor/models/transformer.py
Args:
input_tensor: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size].
attention_mask: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length,
seq_length], with 1 for positions that can be attended to and 0 in
positions that should not be.
hidden_size: int. Hidden size of the Transformer.
num_hidden_layers: int. Number of layers (blocks) in the Transformer.
num_attention_heads: int. Number of attention heads in the Transformer.
intermediate_size: int. The size of the "intermediate" (a.k.a., feed
forward) layer.
intermediate_act_fn: function. The non-linear activation function to apply
to the output of the intermediate/feed-forward layer.
hidden_dropout_prob: float. Dropout probability for the hidden layers.
attention_probs_dropout_prob: float. Dropout probability of the attention
probabilities.
initializer_range: float. Range of the initializer (stddev of truncated
normal).
do_return_all_layers: Whether to also return all layers or just the final
layer.
Returns:
float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size], the final
hidden layer of the Transformer.
Raises:
ValueError: A Tensor shape or parameter is invalid.
"""
if hidden_size % num_attention_heads != 0:
raise ValueError(
"The hidden size (%d) is not a multiple of the number of attention "
"heads (%d)" % (hidden_size, num_attention_heads))
attention_head_size = int(hidden_size / num_attention_heads)
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor, expected_rank=3)
batch_size = input_shape[0]
seq_length = input_shape[1]
input_width = input_shape[2]
# The Transformer performs sum residuals on all layers so the input needs
# to be the same as the hidden size.
if input_width != hidden_size:
raise ValueError("The width of the input tensor (%d) != hidden size (%d)" %
(input_width, hidden_size))
# We keep the representation as a 2D tensor to avoid re-shaping it back and
# forth from a 3D tensor to a 2D tensor. Re-shapes are normally free on
# the GPU/CPU but may not be free on the TPU, so we want to minimize them to
# help the optimizer.
prev_output = reshape_to_matrix(input_tensor)
all_layer_outputs = []
for layer_idx in range(num_hidden_layers):
with tf.variable_scope("layer_%d" % layer_idx):
layer_input = prev_output
with tf.variable_scope("attention"):
attention_heads = []
with tf.variable_scope("self"):
attention_head = attention_layer(
from_tensor=layer_input,
to_tensor=layer_input,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads,
size_per_head=attention_head_size,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=attention_probs_dropout_prob,
initializer_range=initializer_range,
do_return_2d_tensor=True,
batch_size=batch_size,
from_seq_length=seq_length,
to_seq_length=seq_length)
attention_heads.append(attention_head)
attention_output = None
if len(attention_heads) == 1:
attention_output = attention_heads[0]
else:
# In the case where we have other sequences, we just concatenate
# them to the self-attention head before the projection.
attention_output = tf.concat(attention_heads, axis=-1)
# Run a linear projection of `hidden_size` then add a residual
# with `layer_input`.
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
attention_output = tf.layers.dense(
attention_output,
hidden_size,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
attention_output = dropout(attention_output, hidden_dropout_prob)
attention_output = layer_norm(attention_output + layer_input)
# The activation is only applied to the "intermediate" hidden layer.
with tf.variable_scope("intermediate"):
intermediate_output = tf.layers.dense(
attention_output,
intermediate_size,
activation=intermediate_act_fn,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# Down-project back to `hidden_size` then add the residual.
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
layer_output = tf.layers.dense(
intermediate_output,
hidden_size,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
layer_output = dropout(layer_output, hidden_dropout_prob)
layer_output = layer_norm(layer_output + attention_output)
prev_output = layer_output
all_layer_outputs.append(layer_output)
if do_return_all_layers:
final_outputs = []
for layer_output in all_layer_outputs:
final_output = reshape_from_matrix(layer_output, input_shape)
final_outputs.append(final_output)
return final_outputs
else:
final_output = reshape_from_matrix(prev_output, input_shape)
return final_output
7.函数入口(init)
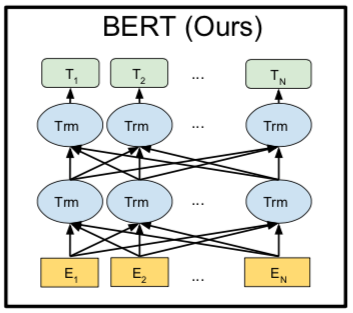
def __init__(self,
config, # BertConfig对象
is_training,
input_ids, # 【batch_size, seq_length】
input_mask=None, # 【batch_size, seq_length】
token_type_ids=None, # 【batch_size, seq_length】
use_one_hot_embeddings=False, # 是否使用one-hot;否则tf.gather()
scope=None):
config = copy.deepcopy(config)
if not is_training:
config.hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0
config.attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_ids, expected_rank=2)
batch_size = input_shape[0]
seq_length = input_shape[1]
# 不做mask,即所有元素为1
if input_mask is None:
input_mask = tf.ones(shape=[batch_size, seq_length], dtype=tf.int32)
if token_type_ids is None:
token_type_ids = tf.zeros(shape=[batch_size, seq_length], dtype=tf.int32)
with tf.variable_scope(scope, default_name="bert"):
with tf.variable_scope("embeddings"):
# word embedding
(self.embedding_output, self.embedding_table) = embedding_lookup(
input_ids=input_ids,
vocab_size=config.vocab_size,
embedding_size=config.hidden_size,
initializer_range=config.initializer_range,
word_embedding_name="word_embeddings",
use_one_hot_embeddings=use_one_hot_embeddings)
# 添加position embedding和segment embedding
# layer norm + dropout
self.embedding_output = embedding_postprocessor(
input_tensor=self.embedding_output,
use_token_type=True,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
token_type_vocab_size=config.type_vocab_size,
token_type_embedding_name="token_type_embeddings",
use_position_embeddings=True,
position_embedding_name="position_embeddings",
initializer_range=config.initializer_range,
max_position_embeddings=config.max_position_embeddings,
dropout_prob=config.hidden_dropout_prob)
with tf.variable_scope("encoder"):
# input_ids是经过padding的word_ids: [25, 120, 34, 0, 0]
# input_mask是有效词标记: [1, 1, 1, 0, 0]
attention_mask = create_attention_mask_from_input_mask(
input_ids, input_mask)
# transformer模块叠加
# `sequence_output` shape = [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size].
self.all_encoder_layers = transformer_model(
input_tensor=self.embedding_output,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
hidden_size=config.hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=config.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=config.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=config.intermediate_size,
intermediate_act_fn=get_activation(config.hidden_act),
hidden_dropout_prob=config.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=config.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
initializer_range=config.initializer_range,
do_return_all_layers=True)
# `self.sequence_output`是最后一层的输出,shape为【batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size】
self.sequence_output = self.all_encoder_layers[-1]
# ‘pooler’部分将encoder输出【batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size】
# 转成【batch_size, hidden_size】
with tf.variable_scope("pooler"):
# 取最后一层的第一个时刻[CLS]对应的tensor, 对于分类任务很重要
# sequence_output[:, 0:1, :]得到的是[batch_size, 1, hidden_size]
# 我们需要用squeeze把第二维去掉
first_token_tensor = tf.squeeze(self.sequence_output[:, 0:1, :], axis=1)
# 然后再加一个全连接层,输出仍然是[batch_size, hidden_size]
self.pooled_output = tf.layers.dense(
first_token_tensor,
config.hidden_size,
activation=tf.tanh,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(config.initializer_range))
举例:
# Already been converted into WordPiece token ids
input_ids = tf.constant([[31, 51, 99], [15, 5, 0]])
input_mask = tf.constant([[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0]])
token_type_ids = tf.constant([[0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0]])
config = modeling.BertConfig(vocab_size=32000, hidden_size=512,
num_hidden_layers=8, num_attention_heads=6, intermediate_size=1024)
model = modeling.BertModel(config=config, is_training=True,
input_ids=input_ids, input_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
label_embeddings = tf.get_variable(...)
pooled_output = model.get_pooled_output()
logits = tf.matmul(pooled_output, label_embeddings)
参考文献:
【3】tf.one_hot()函数简介 - nini_coded的博客