反转一个无符号整数的比特位.
Reverse the bits of an unsigned integer.
For example, x is 0x00001234, then reverse(x) is 0x2C480000.
static uint Reverse(uint x) {
uint y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; ++i) { y <<= 1; y |= (x & 1); x >>= 1; } return y; }
删除有序数组中的重复元素
void remove_duplicate(int *a, int len) { int i = 0; int j = 0; for (j = 0; j < len; j++) { if (a[i] == a[j]) continue; else a[++i] = a[j]; } printf("NEW LEN = %d\n", i + 1); }
插入排序
/* decreasing */ void insert_sort(int *a, int len) { int i; int j; int key; for (i = 1; i < len; i++) { j = i; key = a[j]; while (j > 0 && key > a[j-1]) { a[j] = a[j-1]; j--; } a[j] = key; } }
冒泡排序
for(int i =0; i < LEN; i++) { for(int j = LEN -1; j > i; j--) { if(a[j] > a[j-1]) { int temp = a[j]; a[j] = a[j-1]; a[j-1] = temp; } }
}
合并排序
void part_sort(int *a, int p, int q, int r) { int i, j; int *left = (int *)malloc((q-p+1)*sizeof(int)); int *right = (int *)malloc((r-q)*sizeof(int)); for(i = 0; i < q-p+1; i++) left[i] = a[p + i]; for(i = 0; i < r - q; i++) right[i] = a[q + i +1]; int m = 0; int n = 0; i = p; while (m < q-p+1 && n < r-q) a[i++] = left[m] > right[n] ? right[n++] : left[m++]; while (m < q-p+1) a[i++] = left[m++]; while (n < r-q) a[i++] = right[n++]; free(left); free(right); } void mergesort(int *a, int m, int n) { if(m < n) { int mid = (m + n)/2; mergesort(a, m, mid); mergesort(a, mid+1, n); part_sort(a, m, mid, n); } }
堆排序
static void max_heapify(int*&a, int i, int length) { int largest = i; while(largest <= length -1) { int left =2*largest +1; int right =2*largest +2; int temp = largest; if(left <= length -1&& a[left] > a[largest]) { largest = left; } if(right <= length -1&& a[right] > a[largest]) { largest = right; } if(largest != temp) { int exchange = a[largest]; a[largest] = a[temp]; a[temp] = exchange; } else { break; } } } void build_max_heap(int*&a, int length) { int root = length/2-1; for(int i = root; i >=0; i--) max_heapify(a, i, length); } void heap_sort(int*&a, int length) { build_max_heap(a, length); for(int i = length -1; i >=1; i--) { int temp = a[0]; a[0] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; max_heapify(a, 0, i); } } void heap_delete(int*&a, int i, int length) { if(i != length -1) { a[i] = a[length -1]; max_heapify(a, i, length); } } void heap_insert(int*&a, int x, int length) { int* temp = a; a = new int[length +1]; for(int i =0; i < length; i++) a[i] = temp[i]; delete temp; //用-10000000代替负无穷 a[length] =-10000000; increase_key(a, length, x); } void increase_key(int*&a, int i, int key) { if(a[i] > key) { cout<<"key should be larger than a[i]"<<endl; } else { int parent = (i -1)/2; a[i] = key; while(parent >= 0 && a[parent] < key) { int temp = a[parent]; a[parent] = key; a[i] = temp; i = parent; parent = (i -1)/2; } } }
快排
int partition(int *arr, int start, int end) { int pivot = arr[end]; int i = start - 1; int j; int tmp; for (j = start; j < end; ++j) { if (arr[j] <= pivot) { ++i; tmp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = tmp; } } arr[end] = arr[i+1]; arr[i+1] = pivot; return i+1; } int quicksort(int *arr, int start, int end) { int pivot_location; if (start < end) { pivot_location = partition(arr, start, end); quicksort(arr, start, pivot_location - 1); quicksort(arr, pivot_location + 1, end); } }
找第k小的数
#include <iostream> #include <time.h> using namespace std; //随机化分割 int randomized_partition(int* a, int p, int r); int randomized_select(int* a, int p, int r, int i); int main() { int arr[10] = {4, 34, 21, 8, 3, 10, 453, 32, 1, 400}; int n; while(true) { cout<<"输入第n小的数:"<<endl; cin>>n; cout<<randomized_select(arr, 0, 9, n - 1)<<endl; } return 0; } //下标为[p, r]之间的元素 int randomized_partition(int* a, int p, int r) { srand(time(NULL)); int q = rand()%(r - p + 1) + p; int temp = a[q]; a[q] = a[r]; a[r] = temp; int j = p; for(int i = p; i < r; i++) { if(a[i] < a[r]) { if(i != j) { int temp2 = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp2; } j++; } } temp = a[j]; a[j] = a[r]; a[r] = temp; return j; } int randomized_select(int* a, int p, int r, int i) { int q = randomized_partition(a, p, r); while(p != r) { if(i == q) return a[q]; else if(i < q) { r = q - 1; q = randomized_partition(a, p, r); } else { p = q + 1; q = randomized_partition(a, p, r); } } return a[p]; }
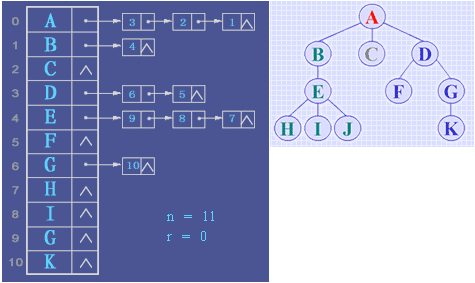
树的表示
typedef struct CTNode { // 孩子结点 int child; struct CTNode *next; } *ChildPtr; typedef struct { ElemType data; // 结点的数据元素 ChildPtr firstchild; // 孩子链表头指针 } CTBox; typedef struct { CTBox nodes[MAX_TREE_SIZE]; int n, r; // 结点数和根结点的位置 } CTree;
找二叉搜索树中的第K大的结点
/* Posted in Career Cup, I used showell30@yahoo.com's code to create the BST, thanks. */ #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <assert.h> struct Node { int val; struct Node *left; struct Node *right; }; typedef struct Node node_t; /* Core function * Inorder, from right first. */ void find_by_inorder(node_t *root, int *count, node_t **result, int k) { if (root != NULL) { find_by_inorder(root->right, count, result, k); (*count)++; if (*count == k) { *result = root;
return;
} find_by_inorder(root->left, count, result, k); } } node_t *make_node(int n) { node_t *node = malloc(sizeof(node_t)); node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; node->val = n; return node; } int main(int argc, char **argv) { node_t *node; node_t *t1 = make_node(1); node_t *t2 = make_node(2); node_t *t3 = make_node(3); node_t *t4 = make_node(4); node_t *t5 = make_node(5); node_t *t6 = make_node(6); t2->left = t1; t2->right = t3; t4->left = t2; t4->right = t5; t5->right = t6; node_t *result = NULL; int count = 0; int i; /* Test */ for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { find_by_inorder(t4, &count, &result, i); if (result != NULL) printf("%dth: %d\n", i, result->val); result = NULL; count = 0; } return 0; }
判断一棵二叉树是否为二叉搜索树
如果一上来直接判断一个结点的左孩子是否小于它,右孩子是否大于它,貌似正确,其实不然。下图就是反例。
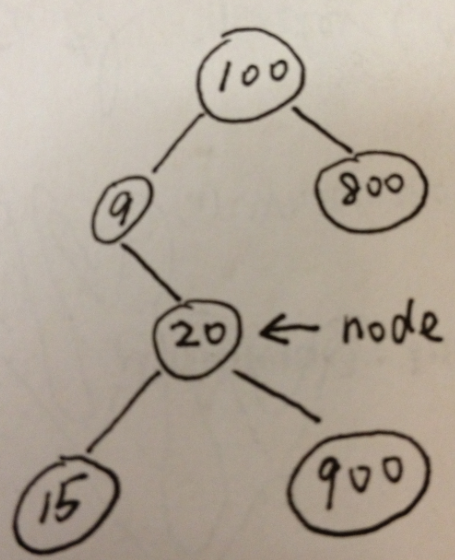
方法一:递归
// macros for comparison #define greater(a,b) (a > b ? true:false) #define between(a,b,c) ((a > b)&&(a < c) ? true:false) // recursive function to which we pass root node and // the limits of the root node, if only positive numbers // then we can pass 0 and INFINITY bool isBST(node* Node, int left_limit,int right_limit) { // the node's value must be greater than its // left child if(!greater(Node->value,Node->left->value)) return false; // the node's value must be smaller than its // right child if(!greater(Node->right->value,Node-> value)) return false; // the node's value must be lie between it's // left and right limit if(!between(Node->value,left_limit,right_limit)) return false; // to the left child pass the node's left limit as // as left limit and node's value as right limit bool left = isBST(Node-> left,left_limit,Node->value); // to the right child pass the node's value as left limit // and node's right limit as right limit bool right = isBST(Node-> right,Node->value,right_limit); return left && right; }
方法二:中序遍历,每个结点必须大于之前的结点。
stack< node* > S; bool(node* root) { prev,curr p = root do { prev = curr; while ( p != null) // traverse LST { S.push(p); p = p-> left; } if (!S.empty()) { p = S.top(); S.pop(); curr=p->info; // visit root if(curr < prev) return false; p = p-> right; } // traverse RST } while(!S.empty() || p != null) }
N皇后问题
递归解法(转载自http://blog.csdn.net/hackbuteer1/article/details/6657109)
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> /* * 把棋盘存储为一个N维数组a[N],数组中第i个元素的值代表第i行的皇后位置, * 这样便可以把问题的空间规模压缩维O(N),在判断是否冲突时也很简单,首先每行只有 * 一个皇后,且在数组中只占据一个元素的位置,行冲突就不存在了,其次是列冲突, * 判断一下是否有a[i]与当前要放置皇后的列j相等即可。至于斜线冲突,通过观察可以 * 发现所有在斜线上冲突的皇后的位置都有规律即它们所在的行列互减得绝对值相等, * 即| row – i | = | col – a[i] | 。这样某个位置是否可以放置皇后的问题已经解决。 */ #define N 20 //最多放皇后的个数 int q[N]; //各皇后所在的行号 int count = 0; //统计解得个数 //输出一个解 void print(int n) { int i,j; count++; printf("第%d个解:",count); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) printf("(%d,%d) ",i,q[i]); printf("\n"); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) //行 { for(j=1;j<=n;j++) //列 { if(q[i]!=j) printf("x "); else printf("Q "); } printf("\n"); } } //检验第i行的k列上是否可以摆放皇后 int find(int i,int k) { int j=1; while(j<i) //j=1~i-1是已经放置了皇后的行 { //第j行的皇后是否在k列或(j,q[j])与(i,k)是否在斜线上 if(q[j]==k || abs(j-i)==abs(q[j]-k)) return 0; j++; } return 1; } //放置皇后到棋盘上 void place(int k,int n) { int j; if(k>n) print(n); else { for(j=1;j<=n;j++) //试探第k行的每一个列 { if(find(k,j)) { q[k] = j; place(k+1,n); //递归总是在成功完成了上次的任务的时候才做下一个任务 } } } } int main(void) { int n; printf("请输入皇后的个数(n<=20),n=:"); scanf("%d",&n); if(n>20) printf("n值太大,不能求解!\n"); else { printf("%d皇后问题求解如下(每列的皇后所在的行数):\n",n); place(1,n); //问题从最初状态解起 printf("\n"); } return 0; }
非递归解法:(http://blog.csdn.net/pinkrobin/article/details/5378702)
/** * n皇后问题 * date : 2010-3-12 * author: lee */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> #define QUEEN 8 // the number of the queen #define INITIAL -10000 //defines the initial value of the board //container int a[QUEEN]; //check if the queen can be placed on the position int valid(int row, int col); //initialize the board void clear(); //print the result void print(); //run the n-queen program void queen(); int main(void) { clear(); queen(); return 0; } void clear() { int *p; for (p = a; p < a + QUEEN; ++p) { *p = INITIAL; } } void print() { int i, j; for (i = 0; i < QUEEN; ++i) { for (j = 0; j < QUEEN; ++j) { if (a[i] != j) printf("%c ", '.'); else printf("%c ", '#'); } printf("\n"); } printf("--------------------------------------------\n"); } int valid(int row, int col) { int i; for (i = 0; i < QUEEN; ++i) { if (a[i] == col || abs(i - row) == abs(a[i] - col)) return 0; } return 1; } void queen() { int n = 0; int i = 0, j = 0; while (i < QUEEN) { while (j < QUEEN) { if (valid(i, j)) { //test if the queen can be placed on the position a[i] = j; //place the queen on the next line j = 0; break; } else { // if not, check the next position ++j; } } if (a[i] == INITIAL) { //if the current queen can't find its place if (i == 0) // and this is the first line ,then program end break; else { //else backtrack --i; j = a[i] + 1; a[i] = INITIAL; continue; } } if (i == QUEEN - 1) { //already got a solution, print the result printf("answer %d : \n", ++n); print(); j = a[i] + 1; a[i] = INITIAL; continue; } ++i; // go on to place the queen on the next line if has any more } }
正方形判断问题
给出四个点,它们的坐标都是整数,判断这四个点是否构成一个正方形
1. 选取第一个点p1,计算p1p2, p1p3, p1p4之间的距离大小。 2. 若三个距离中,有两个相等,且其中一个大于它们,则继续,否则返回false 3. 若两个向量相与,即(p1 - p2) & (p1 - p3)为零,则p1p2与p1p3垂直,继续。 否则返回false 4. 若p2p3的中间点与p1p4的中间点相同,则是正方形,否则false
LCA(Lowest Common Ancestor) 最低公共祖先
情况一:二叉树
Node *LCA(Node *root, Node *p, Node *q) { if (!root) return NULL; if (root == p || root == q) return root; Node *L = LCA(root->left, p, q); Node *R = LCA(root->right, p, q); if (L && R) return root; // 如果p和q位于不同的子树 return L ? L : R; //p和q在相同的子树,或者p和q不在子树中 }
情况二:二叉搜索树
Node *LCA(Node *root, Node *p, Node *q) { if (!root || !p || !q) return NULL; if (max(p->data, q->data) < root->data) return LCA(root->left, p, q); else if (min(p->data, q->data) > root->data) return LCA(root->right, p, q); else return root; }
罐子问题
10个罐子,每个中有一百个珠子,其中一个罐子中的珠子是每个 1.1g,另外九个罐子中的珠子都是每个1g,现在有一个秤,几次能够找出那个每个珠子1.1g的那个罐子?
答:一次。
把十个罐子按顺序摆放,一次从第n个罐子中取出n个珠子,然后把这55个珠子拿到秤上称重,得到重量为W。
假设要找的罐子是第X个罐子,那么
1 + 2 + ... + 10 + (1.1 - 1)*X = W,即55 + 0.1X = W,求出X即可。
最小公倍数和最大公约数的算法
//return the greatest common divisor int gcd(int v1, int v2) { while (v2) { int tmp = v2; v2 = v1 % v2; v1 = tmp; } return v1; } //递归方法
int rgcd(int v1, int v2)
{
if (v2 != 0)
return rgcd(v2, v1%v2);
return v1;
}
//least common multiple lcm(v1, v2) = (v1 * v2) / gcd(v1, v2);