在实际的项目开发中,程序经常需要用到对字符串的操作,为此,C函数库提供了一些用来对字符串进行处理的函数,但由于字符串都有长度,如果随意对不同的字符串进行来凝结和复制操作,就可能出现意向不到的后果,本文重点将介绍下相关的字符串处理函数。
1、strcat函数
函数原型如下:
char *strcat(char *strDestination, const char *strSource);
strcat函数将strSource字符串拼接到strDestination后面,最后的返回值是拼装完成之后的字符串strDestination。
这里有一个问题,如果字符串石头人Source的长度大于strDestination数组的长度,就会吹西安数组越界的错误,程序就会崩溃,如下所示:
/********************************************************** * 内容:测试strcat函数 * 说明:无 * 日期:2017.11.1 * 版本:v1.0 ************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> typedef signed char INT8;//重定义数据类型 typedef signed int INT32; int main() { char szStrDestination[10] = "HELLO"; char szStrSource[100] = "HELLO123"; //打印源字符串和目的字符串 printf("The source string is :%s ", szStrDestination); printf("the destination string is :%s ", szStrSource); strcat(szStrDestination, szStrSource);//调用strcat函数 printf("the changed destination string is :%d ", szStrDestination); return 0; }
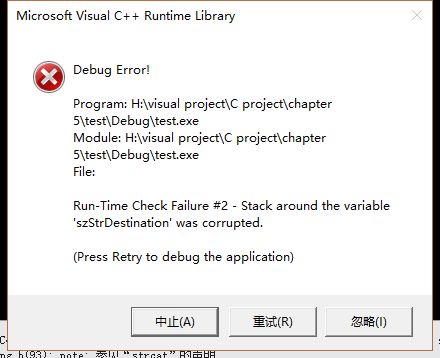
在该段代码中,szStrDestination数组的长度小于szStrSource中字符串的长度,当利用strcat函数进行字符串的连接操作时,异常就出现了。执行代码后弹出的异常框如图所示。
为了解决这个问题,在使用strcat函数之前,需要现对字符串和字符数组的长度进行比较,让字符串函数进行安全的连接操作,既保证最终字符串的长度不超过目的字符数组的长度,修改如下:
/********************************************************** * 内容:测试strcat函数 * 说明:无 * 日期:2017.11.1 * 版本:v1.0 ************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> typedef signed char INT8;//重定义数据类型 typedef signed int INT32; int main() { char szStrDestination[10] = "HELLO"; char szStrSource[10] = "HELLO123"; //打印源字符串和目的字符串 printf("The source string is :%s ", szStrDestination); printf("the destination string is :%s ", szStrSource); //对目的字符数组的长度进行异常保护begin if (sizeof(szStrDestination) - strlen(szStrDestination) < strlen(szStrSource)) { printf("The source string is too long ! "); return -1; } strcat(szStrDestination, szStrSource);//调用strcat函数 printf("the changed destination string is :%d ", szStrDestination); return 0; }
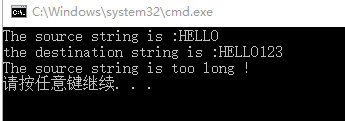
如上述代码所示,当源字符串太长时,程序便异常退出了,不会执行后面的字符串连接操作,虽然可以保证程序的正常运行,但毕竟没有完成我们需要的功能,这里就涉及到strncat了。
2、strncat函数
为了解决strcat函数可能出现的问题,C语言函数库提供了一个叫做strncat的函数,其函数原型如下:
char *strncat(char *strDest, const char *strSource, size_t count);
strncat函数只将strSource数组中的钱count个字符拼接到strDest数据的后main,因此,不管strSource数组中的字符串有多长,只要count控制得当,都不会吹响越界错误。
示例如下:
/********************************************************** * 内容:测试strncat函数 * 说明:无 * 日期:2017.11.1 * 版本:v1.0 ************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> typedef signed char INT8;//重定义数据类型 typedef signed int INT32; int main() { char szStrDestination[10] = "HELLO"; char szStrSource[10] = "HELLO123"; //打印源字符串和目的字符串 printf("The source string is :%s ", szStrDestination); printf("the destination string is :%s ", szStrSource); strncat(szStrDestination, szStrSource,sizeof(szStrDestination)-strlen(szStrDestination)-1);//调用strcat函数 printf("the changed destination string is :%s ", szStrDestination); return 0; }
编译结果如下:
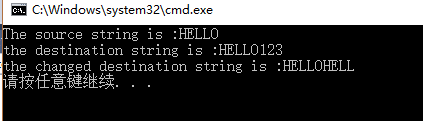
由此,通常用strncat代替strcat函数来实现字符串来实现字符串的连接。
3、strcpy函数和strncpy
strcpy函数的作用是将一个字符数组中的字符串复制到另外一个字符数组中。其定义是
char *strcpy(char *strDestination, const char *strSouorce);
strcpy函数将strSource字符串复制到strDestination数组中,最后的返回值就是复制完成后的字符串strDestination,同理,如果strSource的长度大于strDestination的长度还是会出错,这里就直接介绍strncpy,
strncpy的函数的定义如下:
char *strncpy(char *strDest,const char *strSource,size_t count);
同理strncpy函数只将strSource数组中的前count个字符复制到strDest数组中,因此,只要 count控制得当,都不会吹嘘那字符串的越界问题。
示例如下:
/********************************************************** * 内容:测试strncpy函数 * 说明:无 * 日期:2017.11.1 * 版本:v1.0 ************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> typedef signed char INT8;//重定义数据类型 typedef signed int INT32; int main() { INT8 szStrDestination[5] = { 0 }; INT8 szStrSource[10] = "HELLO1234"; //打印源字符串和目的字符串 printf("The source string is :%s ", szStrDestination); printf("the destination string is :%s ", szStrSource); //调用strncpy函数,并进行长度判断begin if (sizeof(szStrDestination) < strlen(szStrSource)) { strncpy(szStrDestination, szStrSource, sizeof(szStrDestination)- 1);//调用strcat函数 } else { strncpy(szStrDestination, szStrSource, strlen(szStrSource)); //调用strncpy函数,并进行长度判断end } printf("the changed destination string is :%s ", szStrDestination); return 0; }
结果如下:
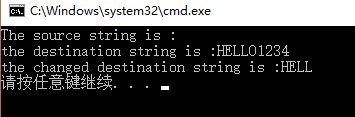
4、strcmp函数和strncmp
strcmp函数的作用是进行字符串的比较,其定义是:
int strcmp(const char *string1, const char *string2);
strcmp函数进行字符串的比较时,如果前者大于后者,则返回值大于0,如果前者等于后者,则返回值等于0,如果前者小于后者,则返回值小于0。
当然,C语言函数库还提供了一个strncmp的函数用于字符串的比较,其定义为:
int strncmp(const char *string1, const char *string2, size_t count);
strncmp函数纸币较两个字符串数组的前count个字符,如果返回值小于0,则前一个字符要小;如果返回值等于0,则两个字符串相等;如果大于0,则前一个字符串要大,可以看出strcmp是特殊的strncmp。
示例如下:
/********************************************************** * 内容:测试strcat函数 * 说明:无 * 日期:2017.11.1 * 版本:v1.0 ************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> typedef signed char INT8;//重定义数据类型 typedef signed int INT32; int main() { INT8 szStrCmp1[10] = "HELLO"; INT8 szStrCmp2[10] = "HELLO"; INT32 iRetVal = 0; //打印源字符串和目的字符串 printf("The source string is :%s ", szStrCmp1); printf("the destination string is :%s ", szStrCmp2); //调用strncmp函数,第三个参数也可以是strlen(szStrcmp2) iRetVal = strncmp(szStrCmp1, szStrCmp2, strlen(szStrCmp1)); if (iRetVal < 0) { printf("string1 is less than string2 "); } else if (iRetVal == 0) { printf("string1 is equal to string2 "); } else { printf("string1 is greater than string2 "); } return 0; }
