二叉树的搜寻方法
一种是递归,一种是循环判断,本质区别并不大
#递归搜寻
def search_recursively(root,key): #1NN 搜索 ,递归法
if root is None or root.key == key:
return root
if key < root.key:
return search_recursively(root.left,key)
elif key > root.key:
return search_recursively(root.right,key)
#循环判断搜寻
def search_iterative(root, key): #1NN 搜索 ,循环判断
current_node = root
while current_node is not None:
if current_node.key == key:
return current_node
elif key < current_node.key:
current_node = current_node.left
elif key > current_node.key:
current_node = current_node.right
return current_node
二叉树的优势,减少搜寻的复杂度

实际运行结果
Search in 100 points, takes 7 comparison only #使用二叉树仅仅比较7次
Complexity is around O(log2(n)), n is number of
database points, if tree is balanced #假设二叉树是平衡的,复杂度为log2(n),n为二叉树的深度
Worst O(N) #最坏结果,比较100次
kNN Search: index - distance 24 - 0.00 85 - 1.00 42 - 1.00 12 - 2.00 86 - 2.00 In total 8 comparison operations. Radius NN Search: index - distance 24 - 0.00 85 - 1.00 42 - 1.00 12 - 2.00 86 - 2.00 In total 5 neighbors within 2.000000. There are 8 comparison operations.
二叉树的三种遍历方式
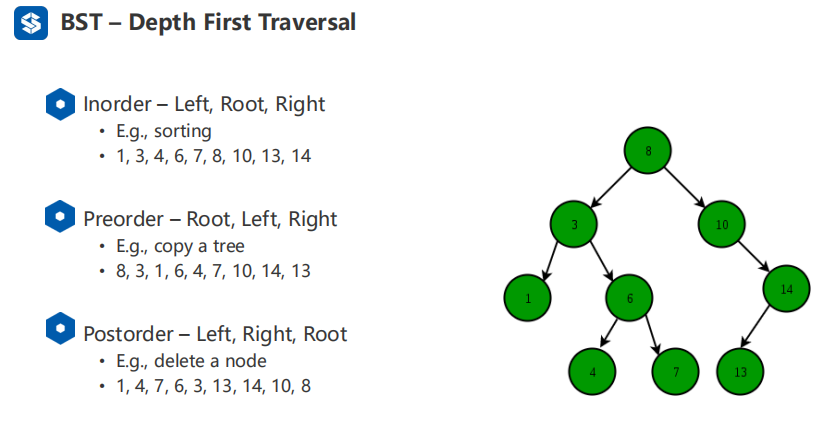
#二叉树的三种应用
def inorder(root):
# Inorder (Left, Root, Right)
if root is not None:
inorder(root.left)
print(root)
inorder(root.right)
def preorder(root):
# Preorder (Root, Left, Right)
if root is not None:
print(root)
preorder(root.left)
preorder(root.right)
def postorder(root):
# Postorder (Left, Right, Root)
if root is not None:
postorder(root.left)
postorder(root.right)
print(root)
1NN搜寻过程

KNN search
worst Distance for KNN

具体思路:
1.先创建一个能容纳需要的临近点结果的list
2.将暂时的KNN result 进行sorted
3.最大worst_dist 的点在KNN result list的最后(随时被替代)
4.根据worst_list的不断更新,动态修改KNN result里的结果
Radius NN search
方法思路和KNN算法差不多,区别在于
Worst distance is fixed.(Radius NN search预先设定检测radius,在radius里进行点的筛选)
KNN search VS Radius NN search

完整代码
bst.py
import random
import math
import numpy as np
from result_set import KNNResultSet,RadiusNNResultSet
class Node: #节点,每一个数都是一个分支节点
def __init__(self,key,value=-1):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.key =key
self.value = value #value可以用作储存其他数值,譬如点原来的序号
def __str__(self):
return "key: %s, value: %s" % (str(self.key), str(self.value))
def insert(root,key,value=-1): #构建二叉树
if root is None:
root = Node(key,value) #赋初值
else:
if key < root.key:
root.left = insert(root.left,key,value) #小数放左边
elif key > root.key:
root.right = insert(root.right,key,value) #大数放右边
else: # don't insert if key already exist in the tree
pass
return root
#二叉树的三种应用
def inorder(root):
# Inorder (Left, Root, Right)
if root is not None:
inorder(root.left)
print(root)
inorder(root.right)
def preorder(root):
# Preorder (Root, Left, Right)
if root is not None:
print(root)
preorder(root.left)
preorder(root.right)
def postorder(root):
# Postorder (Left, Right, Root)
if root is not None:
postorder(root.left)
postorder(root.right)
print(root)
def knn_search(root:Node,result_set:KNNResultSet,key):
if root is None:
return False
# compare the root itself
result_set.add_point(math.fabs(root.key - key),root.value) #计算worst_dist ,并把当前root.value(index二叉树)里的值加入到resut_set 中
if result_set.worstDist() == 0:
return True
if root.key >= key:
# iterate left branch first
if knn_search(root.left, result_set, key):
return True
elif math.fabs(root.key-key) < result_set.worstDist():
return knn_search(root.right, result_set, key)
return False
else:
# iterate right branch first
if knn_search(root.right, result_set, key):
return True
elif math.fabs(root.key-key) < result_set.worstDist():
return knn_search(root.left, result_set, key)
return False
def radius_search(root: Node, result_set: RadiusNNResultSet, key):
if root is None:
return False
# compare the root itself
result_set.add_point(math.fabs(root.key - key), root.value)
if root.key >= key:
# iterate left branch first
if radius_search(root.left, result_set, key):
return True
elif math.fabs(root.key-key) < result_set.worstDist():
return radius_search(root.right, result_set, key)
return False
else:
# iterate right branch first
if radius_search(root.right, result_set, key):
return True
elif math.fabs(root.key-key) < result_set.worstDist():
return radius_search(root.left, result_set, key)
return False
def search_recursively(root,key): #1NN 搜索 ,递归法
if root is None or root.key == key:
return root
if key < root.key:
return search_recursively(root.left,key)
elif key > root.key:
return search_recursively(root.right,key)
def search_iterative(root, key): #1NN 搜索 ,循环判断
current_node = root
while current_node is not None:
if current_node.key == key:
return current_node
elif key < current_node.key:
current_node = current_node.left
elif key > current_node.key:
current_node = current_node.right
return current_node
def main():
# Data generation
db_size = 100
k = 5 #搜寻5个点
radius = 2.0
data = np.random.permutation(db_size).tolist() #random.permutation 随机排列一个数组
root =None
for i,point in enumerate(data):
root = insert(root,point,i)
query_key = 6
result_set = KNNResultSet(capacity=k)
knn_search(root, result_set, query_key)
print('kNN Search:')
print('index - distance')
print(result_set)
result_set = RadiusNNResultSet(radius=radius)
radius_search(root, result_set, query_key)
print('Radius NN Search:')
print('index - distance')
print(result_set)
# print("inorder")
# inorder(root)
# print("preorder")
# preorder(root)
# print("postorder")
# postorder(root)
# node = search_recursive(root, 2)
# print(node)
#
# node = search_iterative(root, 2)
# print(node)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
result_set.py (KNN Radius NN search config fcn)
import copy
class DistIndex:
def __init__(self, distance, index):
self.distance = distance
self.index = index
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.distance < other.distance
class KNNResultSet:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.count = 0
self.worst_dist = 1e10
self.dist_index_list = []
for i in range(capacity):
self.dist_index_list.append(DistIndex(self.worst_dist, 0))
self.comparison_counter = 0
def size(self):
return self.count
def full(self):
return self.count == self.capacity
def worstDist(self):
return self.worst_dist
def add_point(self, dist, index):
self.comparison_counter += 1
if dist > self.worst_dist:
return
if self.count < self.capacity:
self.count += 1
i = self.count - 1
while i > 0:
if self.dist_index_list[i - 1].distance > dist:
self.dist_index_list[i] = copy.deepcopy(self.dist_index_list[i - 1])
i -= 1
else:
break
self.dist_index_list[i].distance = dist
self.dist_index_list[i].index = index
self.worst_dist = self.dist_index_list[self.capacity - 1].distance
def __str__(self):
output = ''
for i, dist_index in enumerate(self.dist_index_list):
output += '%d - %.2f\n' % (dist_index.index, dist_index.distance)
output += 'In total %d comparison operations.' % self.comparison_counter
return output
class RadiusNNResultSet:
def __init__(self, radius):
self.radius = radius
self.count = 0
self.worst_dist = radius
self.dist_index_list = []
self.comparison_counter = 0
def size(self):
return self.count
def worstDist(self):
return self.radius
def add_point(self, dist, index):
self.comparison_counter += 1
if dist > self.radius:
return
self.count += 1
self.dist_index_list.append(DistIndex(dist, index))
def __str__(self):
self.dist_index_list.sort()
output = ''
for i, dist_index in enumerate(self.dist_index_list):
output += '%d - %.2f\n' % (dist_index.index, dist_index.distance)
output += 'In total %d neighbors within %f.\nThere are %d comparison operations.' \
% (self.count, self.radius, self.comparison_counter)
return output