前一阵子有一个学弟问kmeans算法的初始中心点怎么选,有没有什么算法。我让他看看kmeans++,结果学弟说有地方没看懂。然后,他不懂的地方,我给标注了一下。
下面是网上的资料,我对画线的地方做了标注。
k-means++算法选择初始seeds的基本思想就是:初始的聚类中心之间的相互距离要尽可能的远。wiki上对该算法的描述如下:
- 从输入的数据点集合中随机选择一个点作为第一个聚类中心
- 对于数据集中的每一个点x,计算它与最近聚类中心(指已选择的聚类中心)的距离D(x)
- 选择一个新的数据点作为新的聚类中心,选择的原则是:D(x)较大的点,被选取作为聚类中心的概率较大
- 重复2和3直到k个聚类中心被选出来
- 利用这k个初始的聚类中心来运行标准的k-means算法
从上面的算法描述上可以看到,算法的关键是第3步,如何将D(x)反映到点被选择的概率上,一种算法如下:
- 先从我们的数据库随机挑个随机点当“种子点”
- 对于每个点,我们都计算其和最近的一个“种子点”的距离D(x)并保存在一个数组里,然后把这些距离加起来得到Sum(D(x))。
- 然后,再取一个随机值,用权重的方式来取计算下一个“种子点”。这个算法的实现是,先取一个能落在Sum(D(x))中的随机值Random,然后用Random -= D(x),直到其<=0,此时的点就是下一个“种子点”。
- 这个Random 可以这么取: Random = Sum(D(x)) * 乘以0至1之间的一个小数
- 之所以取一个能落在Sum(D(x))中是值是因为,Random是随机的,那么他有更大的机率落在D(x)值较大的区域里。如下图,Random有更大的机率落在D(x3)中。
- Random -= D(x) 的意义在于找出 当前Random到底落在了哪个区间。
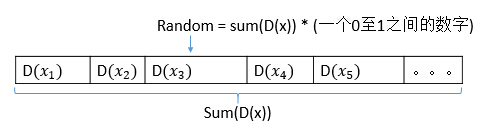
从上图可以看出,假设Random落在D(x3)这个区间内,“然后用Random -= D(x),直到其<=0"此时找到的点就是D(x3),就是这步的中心点。
- 重复2和3直到k个聚类中心被选出来
- 利用这k个初始的聚类中心来运行标准的k-means算法
其实这种算法还是对照着代码看比较清楚。下面粘个python的kmeans++
from math import pi, sin, cos
from collections import namedtuple
from random import random, choice
from copy import copy
try:
import psyco
psyco.full()
except ImportError:
pass
FLOAT_MAX = 1e100
class Point:
__slots__ = ["x", "y", "group"]
def __init__(self, x=0.0, y=0.0, group=0):
self.x, self.y, self.group = x, y, group
def generate_points(npoints, radius):
points = [Point() for _ in xrange(npoints)]
# note: this is not a uniform 2-d distribution
for p in points:
r = random() * radius
ang = random() * 2 * pi
p.x = r * cos(ang)
p.y = r * sin(ang)
return points
def nearest_cluster_center(point, cluster_centers):
"""Distance and index of the closest cluster center"""
def sqr_distance_2D(a, b):
return (a.x - b.x) ** 2 + (a.y - b.y) ** 2
min_index = point.group
min_dist = FLOAT_MAX
for i, cc in enumerate(cluster_centers):
d = sqr_distance_2D(cc, point)
if min_dist > d:
min_dist = d
min_index = i
return (min_index, min_dist)
def kpp(points, cluster_centers):
cluster_centers[0] = copy(choice(points))
d = [0.0 for _ in xrange(len(points))]
for i in xrange(1, len(cluster_centers)):
sum = 0
for j, p in enumerate(points):
d[j] = nearest_cluster_center(p, cluster_centers[:i])[1]
sum += d[j]
sum *= random()
for j, di in enumerate(d):
sum -= di
if sum > 0:
continue
cluster_centers[i] = copy(points[j])
break
for p in points:
p.group = nearest_cluster_center(p, cluster_centers)[0]
def lloyd(points, nclusters):
cluster_centers = [Point() for _ in xrange(nclusters)]
# call k++ init
kpp(points, cluster_centers)
lenpts10 = len(points) >> 10
changed = 0
while True:
# group element for centroids are used as counters
for cc in cluster_centers:
cc.x = 0
cc.y = 0
cc.group = 0
for p in points:
cluster_centers[p.group].group += 1
cluster_centers[p.group].x += p.x
cluster_centers[p.group].y += p.y
for cc in cluster_centers:
cc.x /= cc.group
cc.y /= cc.group
# find closest centroid of each PointPtr
changed = 0
for p in points:
min_i = nearest_cluster_center(p, cluster_centers)[0]
if min_i != p.group:
changed += 1
p.group = min_i
# stop when 99.9% of points are good
if changed <= lenpts10:
break
for i, cc in enumerate(cluster_centers):
cc.group = i
return cluster_centers
def print_eps(points, cluster_centers, W=400, H=400):
Color = namedtuple("Color", "r g b");
colors = []
for i in xrange(len(cluster_centers)):
colors.append(Color((3 * (i + 1) % 11) / 11.0,
(7 * i % 11) / 11.0,
(9 * i % 11) / 11.0))
max_x = max_y = -FLOAT_MAX
min_x = min_y = FLOAT_MAX
for p in points:
if max_x < p.x: max_x = p.x
if min_x > p.x: min_x = p.x
if max_y < p.y: max_y = p.y
if min_y > p.y: min_y = p.y
scale = min(W / (max_x - min_x),
H / (max_y - min_y))
cx = (max_x + min_x) / 2
cy = (max_y + min_y) / 2
print "%%!PS-Adobe-3.0
%%%%BoundingBox: -5 -5 %d %d" % (W + 10, H + 10)
print ("/l {rlineto} def /m {rmoveto} def
" +
"/c { .25 sub exch .25 sub exch .5 0 360 arc fill } def
" +
"/s { moveto -2 0 m 2 2 l 2 -2 l -2 -2 l closepath " +
" gsave 1 setgray fill grestore gsave 3 setlinewidth" +
" 1 setgray stroke grestore 0 setgray stroke }def")
for i, cc in enumerate(cluster_centers):
print ("%g %g %g setrgbcolor" %
(colors[i].r, colors[i].g, colors[i].b))
for p in points:
if p.group != i:
continue
print ("%.3f %.3f c" % ((p.x - cx) * scale + W / 2,
(p.y - cy) * scale + H / 2))
print ("
0 setgray %g %g s" % ((cc.x - cx) * scale + W / 2,
(cc.y - cy) * scale + H / 2))
print "
%%%%EOF"
def main():
npoints = 30000
k = 7 # # clusters
points = generate_points(npoints, 10)
cluster_centers = lloyd(points, k)
print_eps(points, cluster_centers)
main()